Taurus V6-3.0L VIN 2 Flex Fuel (1997)
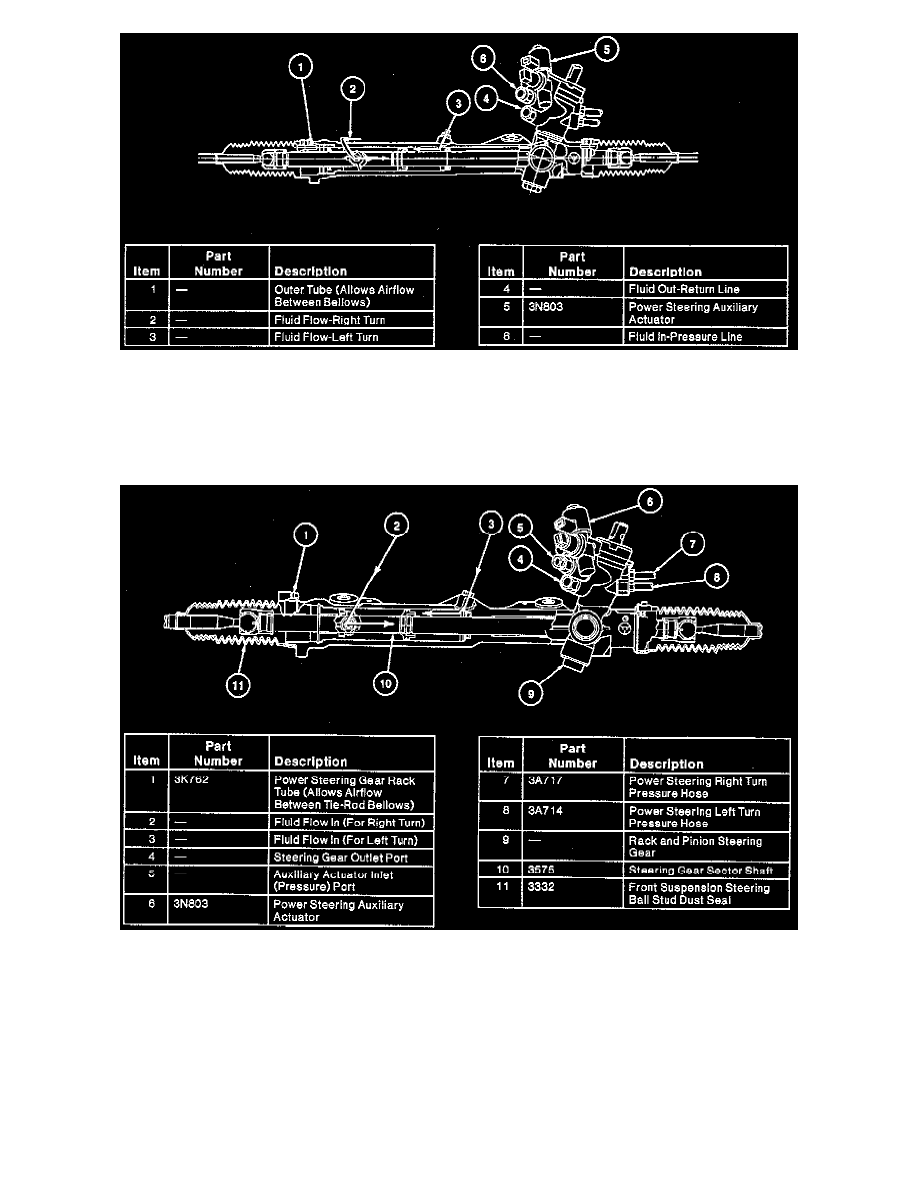
Internal valving directs pump flow and controls pressure, as required, to reduce steering effort during operation. The power rack and pinion
steering gear contains a rotary hydraulic fluid control valve integrated to the power steering gear input shaft and control and a boost cylinder
integrated with the steering gear rack.
Mechanical Operation
The power rack and pinion steering gear uses an integral piston and rack design to provide power-assisted vehicle steering control.
Hydraulic Operation
The power rack and pinion steering gear uses integral valving that directs pump flow and controls pressure as required to reduce steering effort
during operation. The power rack and pinion steering gear contains:
^
a rotary hydraulic fluid control valve integrated to the power steering gear input shaft and control.
^
a boost cylinder integrated with the steering gear rack.
Rotary Valve
The rotary design control valve uses relative rotational motion of the power steering gear input shaft and control and valve sleeve to direct
fluid flow.
^
When the steering wheel is turned, resistance of the wheels and the weight of the vehicle cause a torsion bar to deflect.
^
This deflection changes the position of the input shaft and sleeve ports, directing fluid under pressure to the appropriate end of the power
cylinder.
^
The difference in pressure forces on the piston help move the steering gear rack to assist turning effort.
^
The piston is retained directly to the steering gear rack, and the steering gear housing functions as the power cylinder.
