Metro L4-079 1.3L VIN 9 TBI (1995)
Oxygen Sensor: Description and Operation
Description
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output
DESCRIPTION
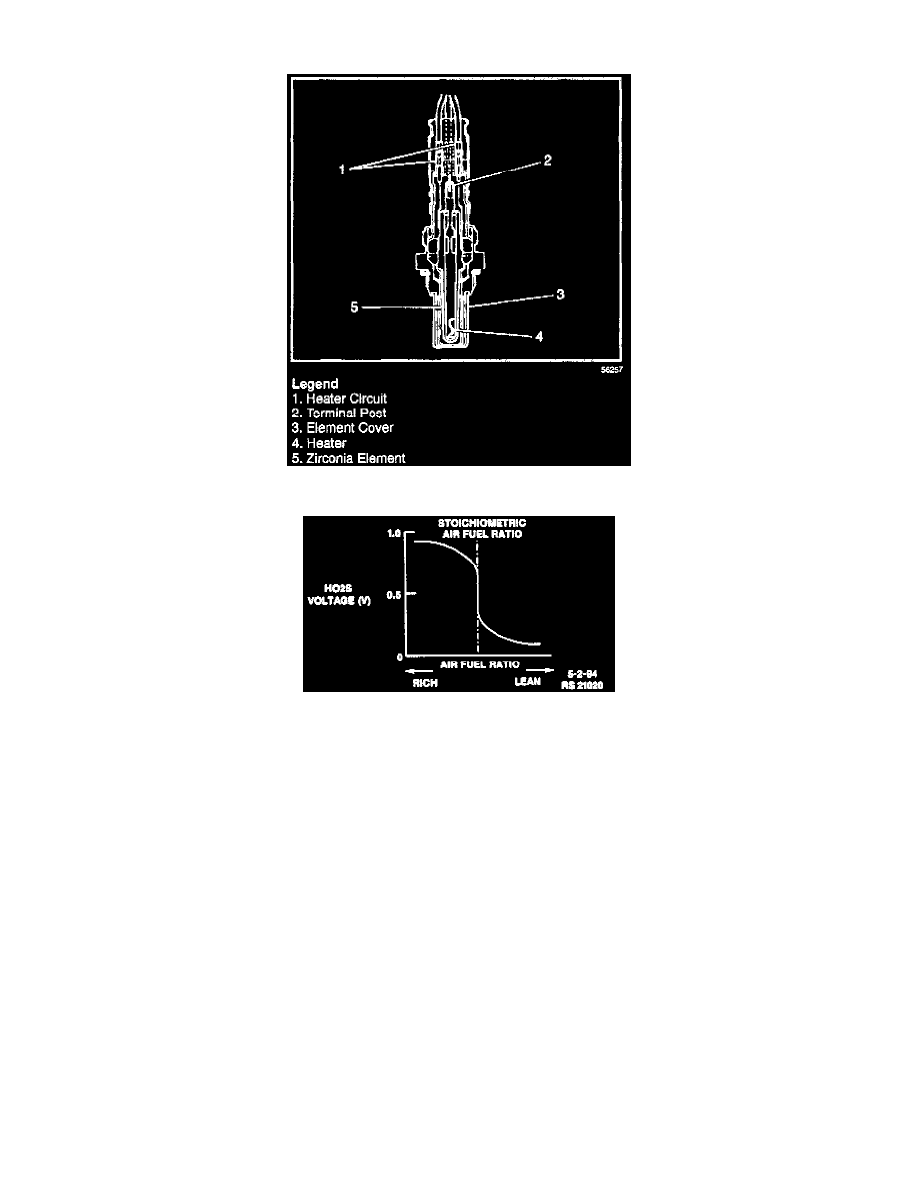
The Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) detects the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust gases. It consists of the zirconia element (with thin
platinum surface coating) which generates voltage, a lead wire which carries the voltage, a heater which promotes activation of the zirconia
element, lead wires for the heater power and ground circuit and cover and housing which protect the zirconia element from damage.
OPERATION
The zirconia element, by its property, generates a voltage when a difference in oxygen concentration exists between its faces. As its temperature
rises, the change of voltage is amplified by catalytic reaction of the platinum. The HO2S makes use of this property. Atmosphere is introduced into
the HO2S, the inside of the zirconia element is exposed to the atmosphere and outside to exhaust gases. Thus, the difference in concentration
between the inside and the outside of the zirconia element varies with the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gases.
VOLTAGE GENERATOR
A large oxygen concentration difference results in about 1 volt and a small difference results in about 0.01 volt. If the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gases is less (air-fuel mixture is richer than the stoichiometric mixture), about 1 volt is generated and if more (air-fuel mixture is leaner
than stoichiometric mixture), almost no voltage is generated (refer to chart in accompanying image). In this way, the HO2S detects whether the
oxygen concentration is high or low (the mixture is leaner or richer than the stoichiometric mixture).
