Prizm L4-108 1.8L DOHC VIN 8 MFI (1995)
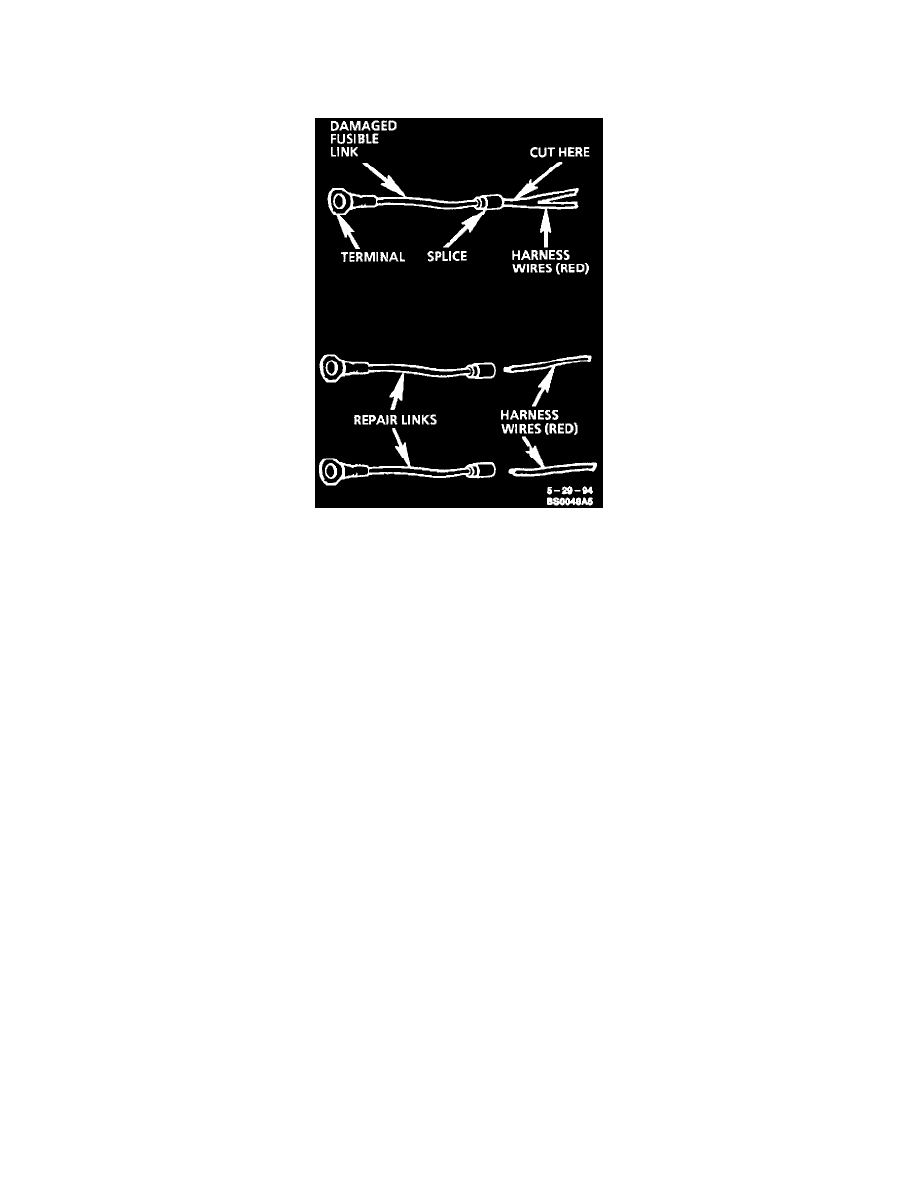
To replace a damaged fusible link, cut it off beyond the splice. Replace with a repair link. When connecting the repair link, strip wire and use
staking-type pliers to crimp the splice securely in two places. For more details on splicing procedures, refer to "Typical Electrical Repair Procedures."
Use crimp and seal splices whenever possible. See: Wire Repair Procedures/Typical Electrical Repair Procedures
Double Wire Feed Fusible Links
To replace a damaged fusible link which feeds two harness wires, cut them both off beyond the splice. Use two repair links, one spliced to each harness
wire.
General Information
The purpose of circuit protection is to protect the wiring assembly during normal and overload conditions. An overload is defined as a current
requirement that is higher than normal. This overload could be caused by a short circuit or system malfunction. The short circuit could be the result of a
pinched or cut wire or an internal device short circuit, such as an electronic module failure.
The circuit protection device is only applied to protect the wiring assembly, and not the electrical load at the end of the assembly. For example, if an
electronic component short circuits, the circuit protection device will assure a minimal amount of damage to the wiring assembly. However, it will not
necessarily prevent damage to the component.
There are three basic types of circuit protection devices: Circuit Breaker, Fuse and Fusible Link.
