Prizm L4-1800cc 1.8L DOHC (1993)
Spark Plug: Testing and Inspection
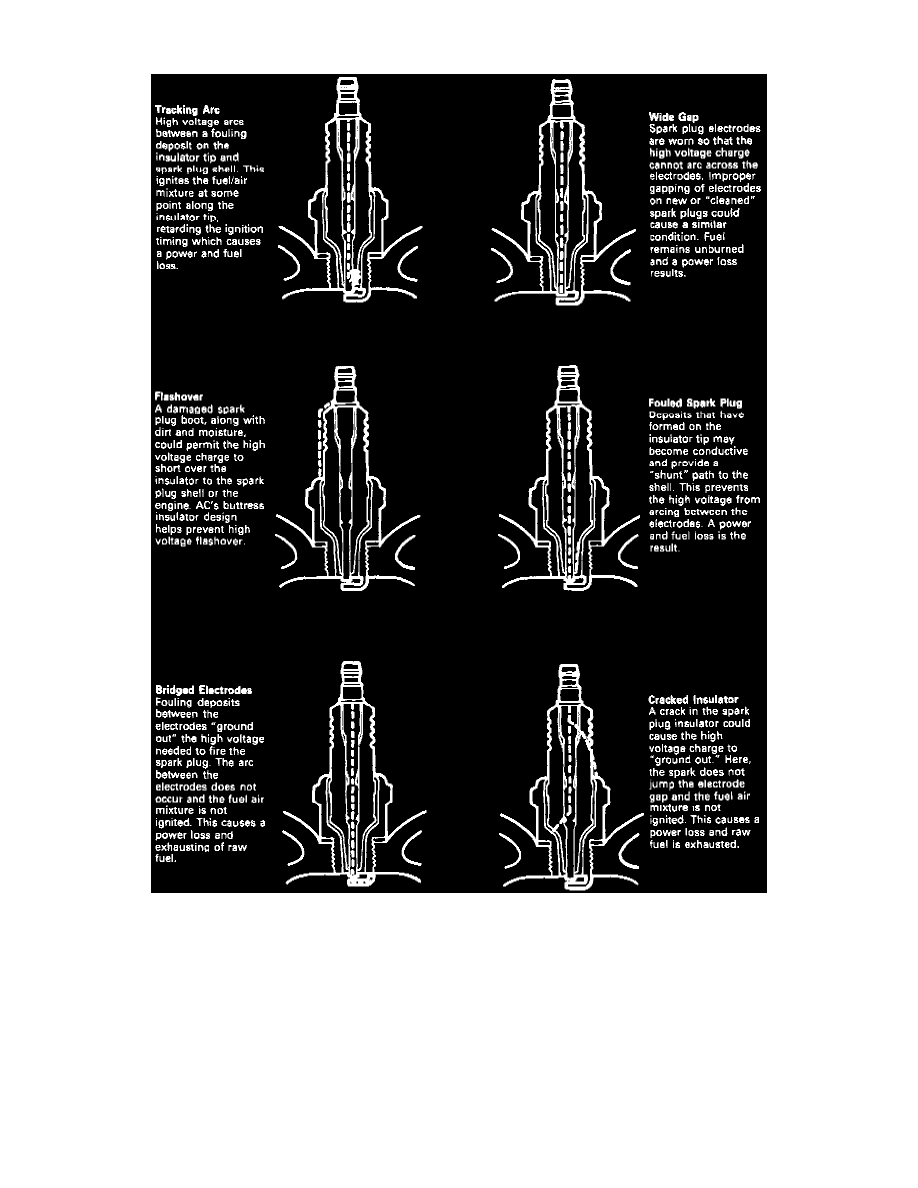
Spark Plug Diagnosis
At idle speed worn or dirty spark plugs may provide satisfactory performance, but under more demanding operating conditions, they will frequently
misfire. A number of symptoms can help detect misfiring spark plugs. These symptoms include poor fuel economy, power loss, loss of speed, hard
starting and generally poor engine performance. Misfiring spark plugs may be caused by carbon fouling, an excessive air gap, a broken insulator, bridged
electrodes, or a damaged spark plug wire and/or boot.
Fouled spark plugs are indicated by black carbon deposits on electrodes. These black deposits are usually the result of slow-speed driving and short runs
in which sufficient operating temperature is seldom achieved. Other causes of carbon deposits are worn pistons, rings, faulty ignition, over-rich air/fuel
mixture and the incorrect spark plug heat range.
Carbon deposits on the spark plug insulator tip may become conductive and cause the high-voltage arc to track along the tip, to some point where it arcs
to join the spark plug shell. This arc then ignites the air/fuel mixture later than normal which, in effect, retards ignition timing. Heavy carbon deposits
may be conductive to the extent that the arc path now becomes a shunt path to the spark plug shell. This condition prevents the high voltage from arcing
