G 2500 3/4 Ton Van V8-350 5.7L VIN K TBI (1995)
The second type of Circuit Breaker is identified in Electrical Diagnosis as a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Circuit Breaker. This type increases
its resistance greatly when excessive current passes through it. The excessive current heats the PTC device. As the device heats, its resistance increases,
thus the name, "Positive Temperature Coefficient." Eventually the resistance gets so HI that the circuit is effectively open. Unlike the ordinary Circuit
Breaker, the PTC unit will not reset until the circuit is opened, removing voltage from its terminals. Once voltage is removed, the Circuit Breaker will
re-close within a second or two.
Fuses
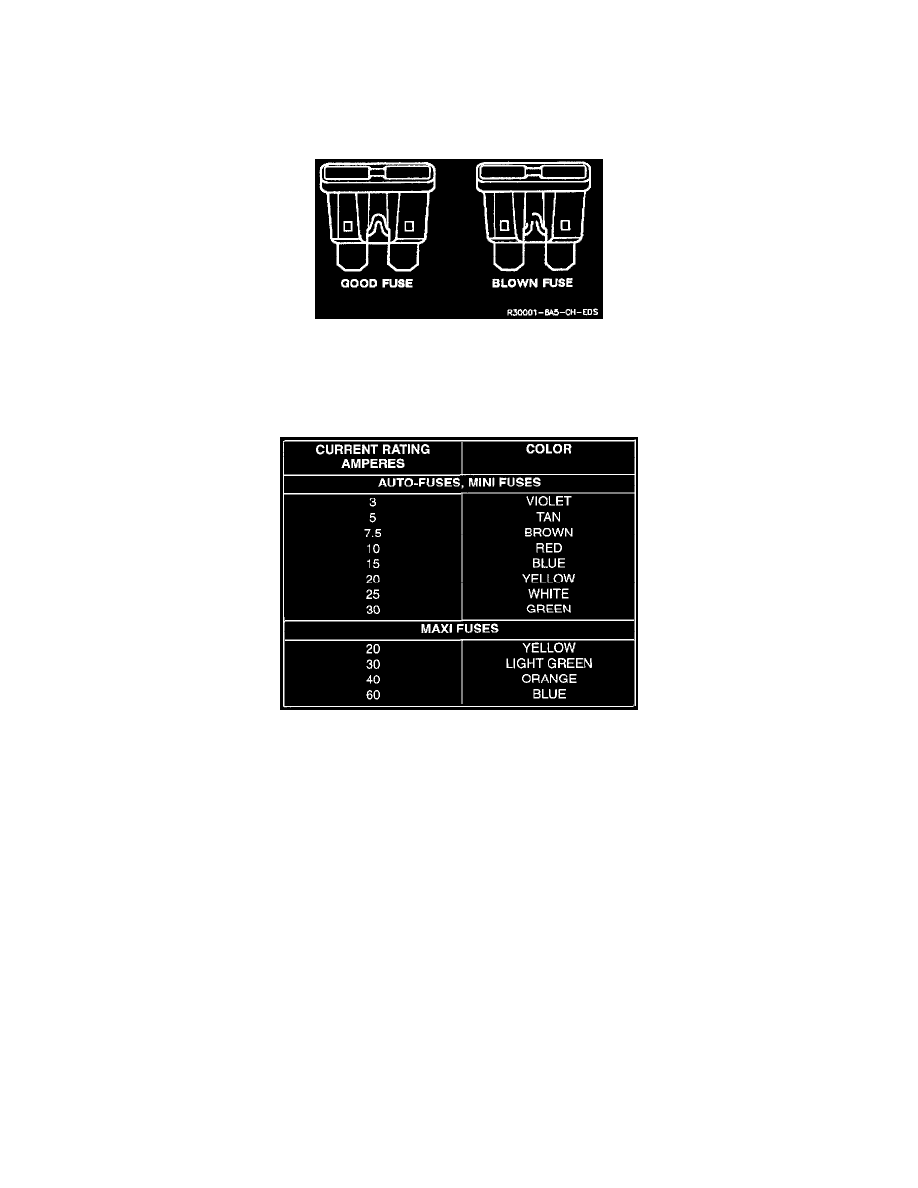
Sample Fuses
The most common method of automotive wiring circuit protection is the fuse. Whenever there is an excessive amount of current flowing through a circuit
the fusible element will melt and create an open or incomplete circuit. Fuses are a "one time" protection device and must be replaced each time the
circuit is overloaded.
Fuse Rating And Color
Auto Fuses, Mini Fuses and Maxi Fuses are color coded. The standardized color identification and ratings are shown.
For service replacement, non-color coded fuses of the same respective current rating can be used. The current rating of each fuse is molded into its head.
To determine whether or not a fuse is blown, remove the suspect fuse and examine the element in the fuse for a break. If the element is broken, replace
the fuse with one of equal current rating.
There are, however, additional specific circuits with in-line fuses. In-line fuses are located within the individual wiring harness.
General Information
All electrical circuits are protected against excessive loads which might occur because of shorts or overloads in the wiring system. Such protection is
provided by a fuse or circuit breaker. A short may cause a fuse to blow or a circuit breaker to open.
IMPORTANT: After any electrical repair is made, always test the circuit by operating the devices in the circuit. This confirms not only that the repair
is correct, but also that the cause of the complaint was correctly identified.
General Information
OPEN CIRCUIT
An open circuit is an incomplete circuit. Power cannot reach the load or the ground. If a circuit is open, active components do not energize.
SHORT CIRCUIT
A short circuit is an unwanted connection between one part of the circuit and either ground or another part of the circuit. A short circuit causes a
fuse to blow or a circuit breaker to open.
