S15/T15 Sonoma P/U 2WD L4-2.2L VIN 4 (1995)
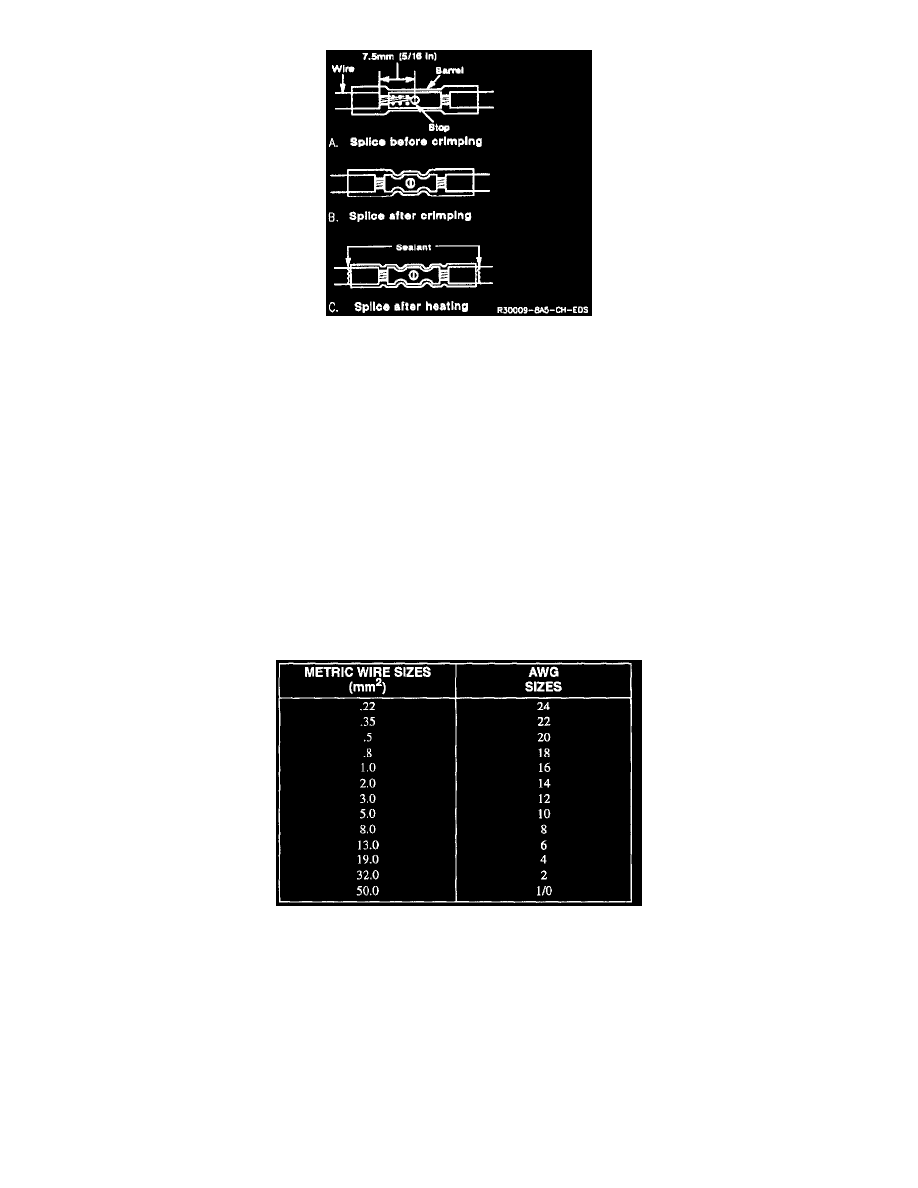
Seal Splice Sequence
Step Six: Shrink the Insulation around the Splice
Using a heat torch, apply heat where the barrel is crimped.
Gradually move the heat barrel to the open end of the tubing, shrinking the tubing completely as the heat is moved along the insulation. A small
amount of sealant will come out of the end of the tubing when sufficient shrinkage is achieved.
Splicing Copper Wire Using Splice Clips
Splice clips are included in the J 38125 Terminal Repair Kit. The Splice Clip is a general purpose wire repair device. It may not be acceptable for
applications having special requirements such as moisture sealing.
Step One: Open the Harness
If the harness is taped, remove the tape. To avoid wire insulation damage, use a sewing "seam ripper" to cut open the harness (available from
sewing supply stores). If the harness has a black plastic conduit, simply pull out the desired wire.
Step Two: Cut the Wire
Begin by cutting as little wire off the harness as possible. You may need the extra length of wire later if you decide to cut more wire off to change
the location of a splice. You may have to adjust splice locations to make certain that each splice is at least 40 mm (1-1/2 in) away from other
splices, harness branches, or connectors. This will help prevent moisture from bridging adjacent splices and causing damage.
Wire Size Conversion Table
Step Three: Strip the Insulation
The table shows the commercial (AWG) wire sizes than can be used to replace each of the metric wire sizes. Each AWG size shown is equal to or
larger than the equivalent metric wire size.
When replacing wire, use wire of equal or greater size than the original. The wire's insulation must have the same or higher temperature rating.
To find the correct wire size, either find the wire on the schematic and convert or use an AWG gage.
The type of wire insulation must also be carefully selected. For areas not subject to high temperatures, such as the passenger compartment,
instrument panel or cargo compartment, a general purpose insulation may be used. The most common general purpose insulation is Polyvinyl
Chloride (PVC). PVC may be used where temperatures do not exceed 80°C (176°F).
