Sierra 1500 2WD V8-6.0L Hybrid (2010)
Repairs/Connector Repairs)
*
Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections (See: Testing and Inspection/Component Tests and General Diagnostics/General
Electrical Diagnostic Procedures/Circuit Testing/Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections)
*
Wiring Repairs (See: Testing and Inspection/Component Tests and General Diagnostics/General Electrical Diagnostic Procedures/Wiring
Repairs/Wiring Repairs)
Scan Tool Reference
Control Module References (See: Testing and Inspection/Programming and Relearning) for scan tool information.
Circuit/System Testing
1. Test for less than 2.0 ohms between the ground circuits terminal 4 of the DLC and ground, and terminal 5 of the DLC and ground.
‹› If greater than the specified range, test the ground circuit for an open/high resistance.
2. Ignition ON, verify a test lamp illuminates between the B+ circuit terminal 16 at the DLC and ground.
‹› If the test lamp does not illuminate, test the voltage supply circuit for a short to ground or an open/high resistance.
3. If all circuits test normal, refer to the scan tool/CANdi module user guide.
Repair Instructions
Perform the Diagnostic Repair Verification (See: Testing and Inspection/Diagnostic Trouble Code Tests and Associated Procedures/Verification Tests
and Procedures) after completing the repair.
Scan Tool Does Not Communicate with Powertrain High Speed GMLAN Device
Scan Tool Does Not Communicate with Powertrain High Speed GMLAN Device
Diagnostic Instructions
*
Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle (See: Testing and Inspection/Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview/Diagnostic System
Check - Vehicle) prior to using this diagnostic procedure.
*
Review Strategy Based Diagnosis (See: Testing and Inspection/Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview/Strategy Based Diagnosis) for an
overview of the diagnostic approach.
*
Diagnostic Procedure Instructions (See: Testing and Inspection/Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview/Diagnostic Procedure Instructions
)provides an overview of each diagnostic category.
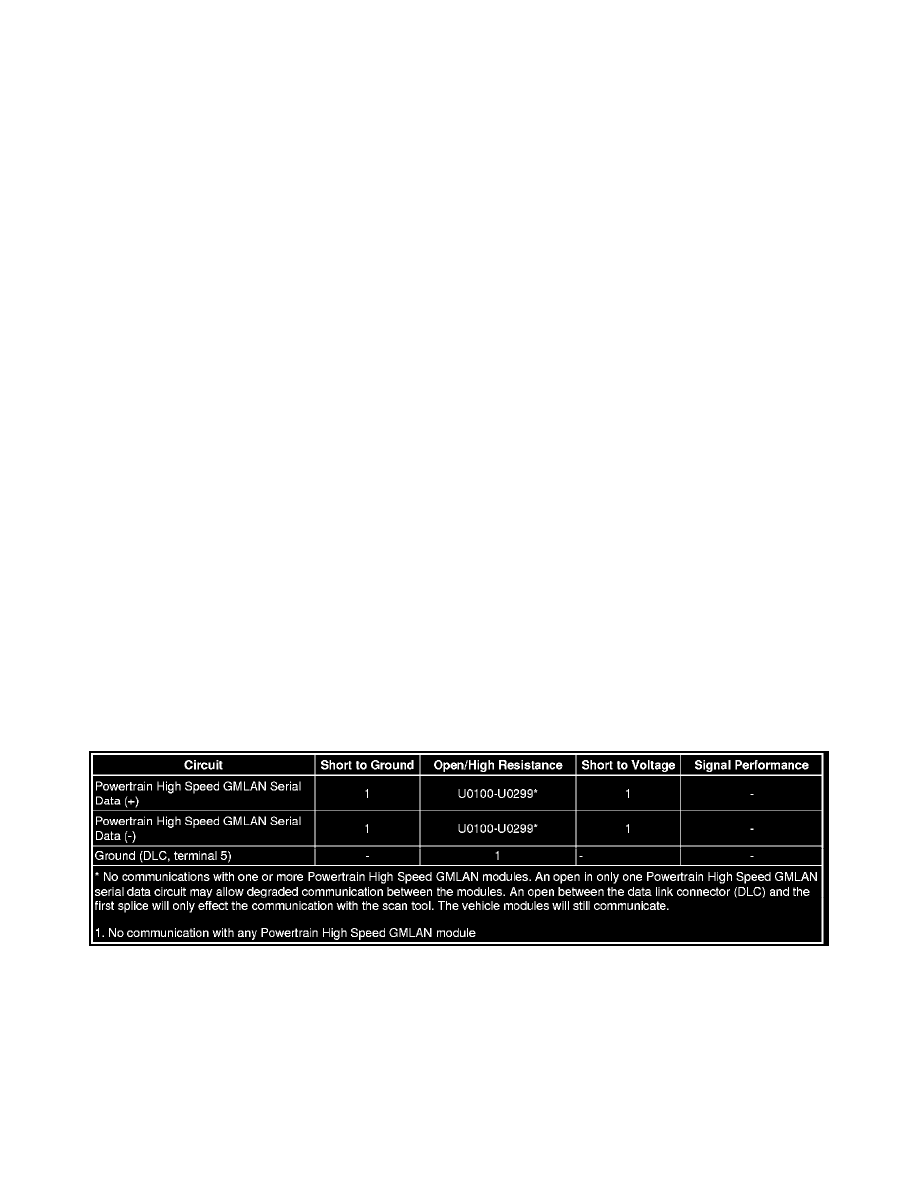
Diagnostic Fault Information
Circuit/System Description
The serial data is transmitted on two twisted wires that allow speeds up to 500 Kb/s. The twisted pair is terminated with two 120 ohms resistors, one is
internal to the engine control module (ECM) and the other can be a separate resistor in a connector assembly or in another control module. The resistors
are used as the load for the Powertrain High Speed GMLAN buss during normal vehicle operation. The Powertrain High Speed GMLAN is a differential
bus. The Powertrain High Speed GMLAN serial data bus (+) and Powertrain High Speed GMLAN serial data (-) are driven to opposite extremes from a
rest or idle level of approximately 2.5 V. Driving the lines to their extremes, adds one volt to the Powertrain High Speed GMLAN serial data bus (+)
circuit and subtracts one volt from the Powertrain High Speed GMLAN serial data bus (-) circuit. If serial data is lost, control modules will set a no
communication code against the non-communicating control module. Note that a loss of serial data DTC does not represent a failure of the module that
set it.
