Sierra 2500 4WD V8-6.0L (2008)
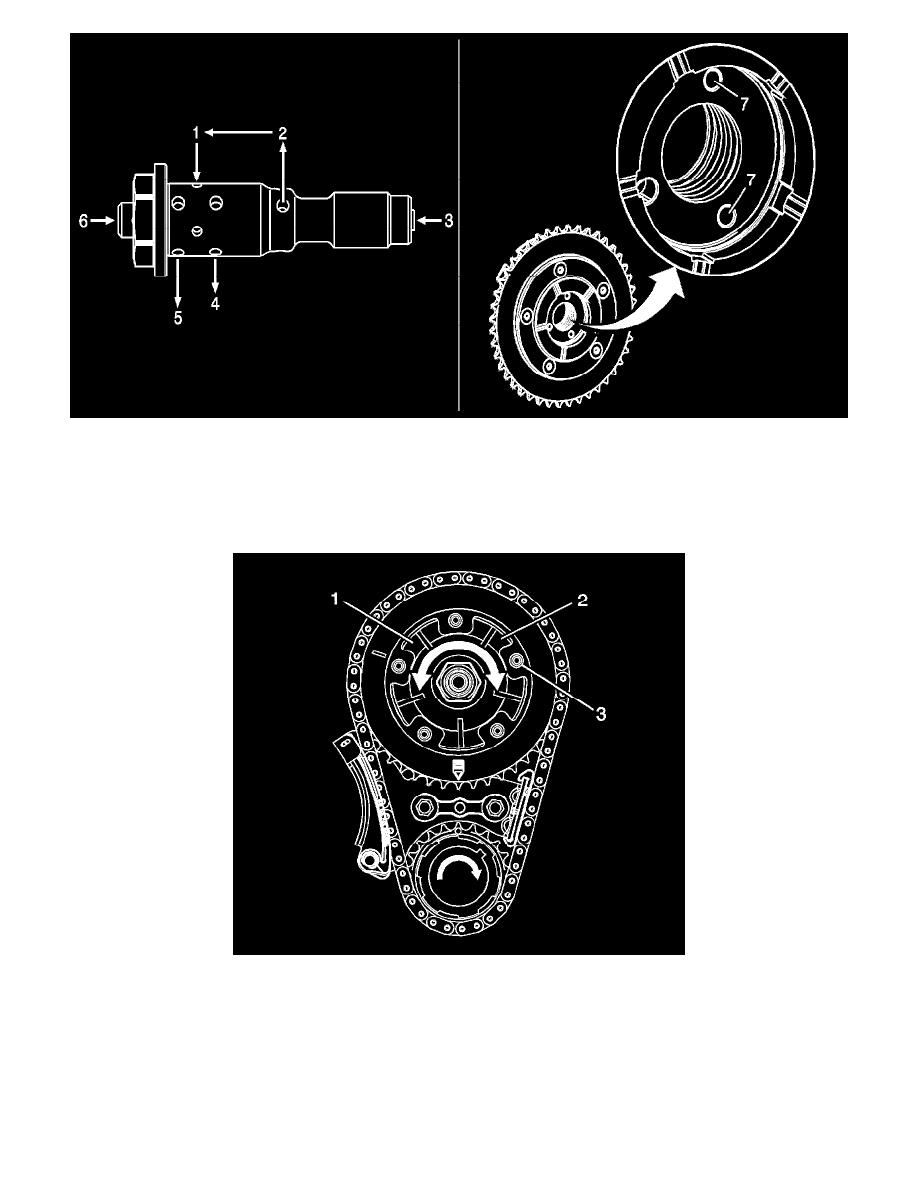
1. Oil flows from the camshaft into the valve inlet (3) through the internal check ball and filter.
2. Oil exits the valve (2) and travels within the internal passages of the camshaft into the entry ports (7) of the actuator.
3. The center oil groove of the actuator is pressurized and oil reenters the valve (1).
4. Valve spool position directs oil out of the valve advance (5) or retard (4) ports to the actuator.
The valve may also, under certain conditions, be positioned in a neutral position with no flow to either the advance or retard passages of the actuator.
1. Pressurized oil enters the retard cavities (2) of the actuator and moves the park pin (3) from the locked position.
2. As pressure increases within the retard cavities (2), the rotor and camshaft rotate counter clockwise retarding valve timing.
3. As the duty cycle decreases, the spool is repositioned and oil is sent to the advance cavities (1), rotating the rotor and camshaft clockwise,
advancing valve timing.
*
With a 0 percent duty cycle signal to the magnet, the spool is positioned in the fully extended position and there is full flow to the advance
cavities of the actuator. As duty cycle increases to near 50 percent, flow to the advance cavities is decreased.
*
With a 50 percent duty cycle, the spool is positioned neutral, with no flow to either the advance and retard cavities.
*
With a 51-100 percent duty cycle, the spool is positioned to provide oil flow to retard cavities. As the duty cycle increases, the flow to retard
cavities increases.
