Yukon/Denali 4WD V8-4.8L VIN V (2005)
Spark Plug: Testing and Inspection
SPARK PLUG INSPECTION
-
Verify that the correct spark plug is installed. An incorrect spark plug causes driveability conditions. Refer to Ignition System Specifications for
the correct spark plug.
-
Ensure that the spark plug has the correct heat range. An incorrect heat range causes the following conditions:
-
Spark plug fouling - Colder plug
-
Pre-ignition causing spark plug and/or engine damage - Hotter plug
-
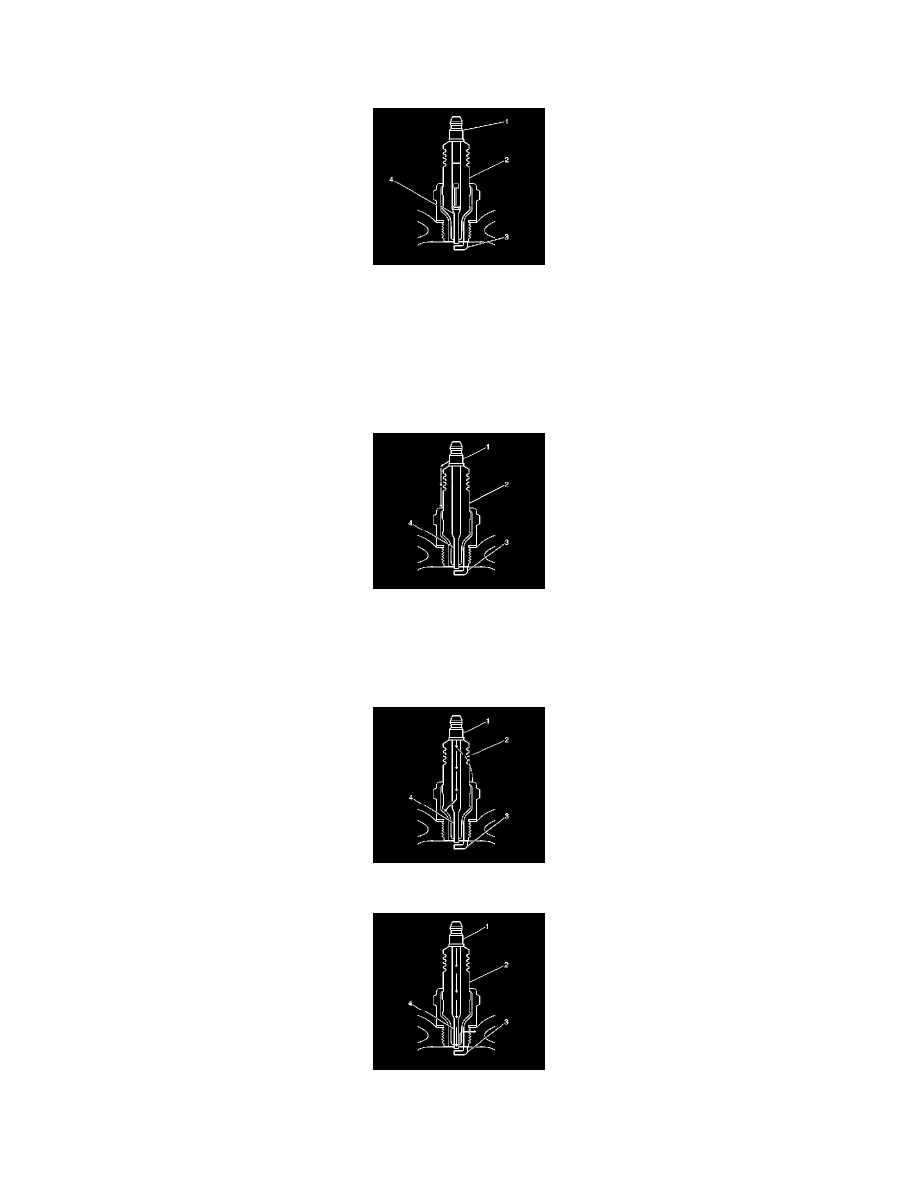
Inspect the terminal post (1) for damage.
-
Inspect for a bent or broken terminal post (1).
-
Test for a loose terminal post (1) by twisting and pulling the post. The terminal post (1) should not move.
-
Inspect the insulator (2) for flashover or carbon tracking, or soot. This is caused by the electrical charge traveling across the insulator (2) between
the terminal post (1) and ground. Inspect for the following conditions:
-
Inspect the spark plug boot for damage.
-
Inspect the spark plug recess area of the cylinder head for moisture, such as oil, coolant, or water. A spark plug boot that is saturated will cause
arcing to ground.
-
Inspect the insulator (2) for cracks. All or part of the electrical charge may arc through the crack instead of the electrodes (3, 4).
-
Inspect for evidence of improper arcing.
-
Measure the gap between the center electrode (4) and the side electrode (3). Refer to Ignition System Specifications. An excessively wide
electrode gap can prevent correct spark plug operation.
