Yukon 4WD V8-6.5L DSL Turbo VIN S (1997)
shavings.
Noise Diagnosis
Noise from the relief valve is normal when the brakes are applied. Firmly applying the brake pedal when the vehicle is parked also causes noise. These
noises are caused by the air that temporarily gets in the fluid during these conditions. Power steering pump noise can be confused with transmission, rear
axle or generator noise.
The following noises are associated with the hydraulic booster and may or may not be cause for a customer complaint. Some noises are normal and
temporary in nature. Other noises can be a sign of wear or air in the hydraulic booster or steering system.
1. A moan or low frequency hum usually accompanied by a vibration in the brake pedal or steering column may be noticed during parking or other
low speed maneuvers. This may be caused by a low power steering fluid level or air in the fluid. Holding the power steering pump at relief
pressure (steering wheel held all the way in one direction) for more than 5 seconds causes air to enter the system. Check the fluid level and fill as
needed. The system must then sit for one hour with the engine off to remove the air. If the condition persists, refer to Steering and Suspension.
2. A high-speed fluid noise may be heard when the brake pedal is applied fully. This condition is normal.
3. A slight hiss may be noticed when the accumulator pressure is used. It is the sound of the hydraulic fluid escaping through the accumulator valve.
This condition is normal.
4. If the accumulator is empty and the engine is started, another hissing sound may be heard during the first brake application or steering maneuver.
This is caused by fluid rushing through the accumulator charging orifice. It is normal and should only be heard once after the accumulator is
emptied. If this sound continues, even though no apparent accumulator pressure assist was made, it could be an indication that the accumulator is
not holding pressure and should be checked. Refer to Accumulator Leakdown Test. See: Component Tests and General Diagnostics/System
Tests/Accumulator Leakdown Test
Seal Leak Diagnosis
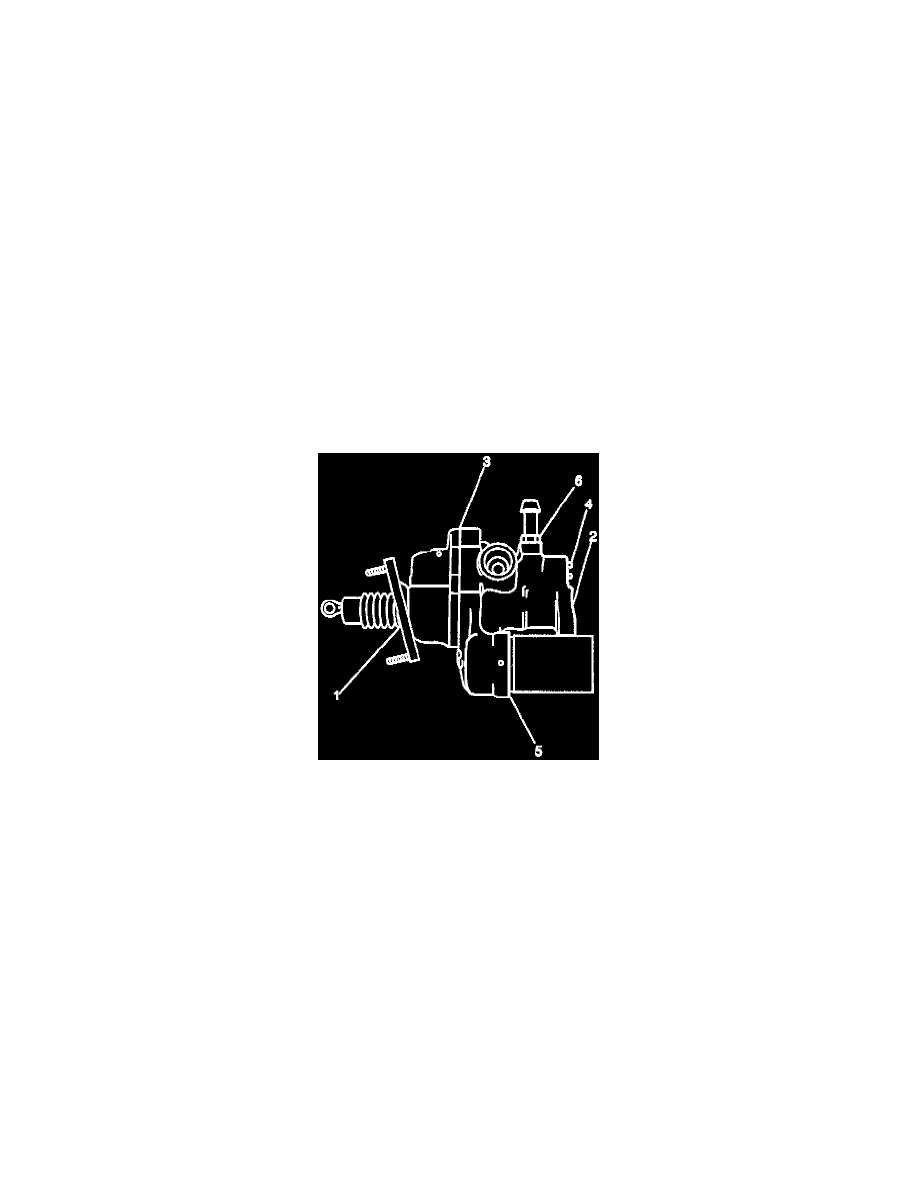
Seal Leak Diagnosis
LEGEND
(1) Input Rod Seal
(2) Power Piston Seal
(3) Housing Seal
(4) Spoon Valve Plug Seal
(5) Accumulator Seal
(6) Return Port Seal
INPUT ROD SEAL:
A damaged input rod seal will show as a fluid leak from the mounting bracket vent hole. The booster must be removed and disassembled. Check the
input rod bore for any scratches that may cause the leak. If scratches are present, the housing cover must be replaced. If no excessive scratches are
present, replace all seals using a booster seal kit.
POWER PISTON SEAL:
Power piston seal damage is noticed by fluid leaking at the common master cylinder brake booster vent and a possible reduction in power assist. The
booster must be removed and disassembled. Check the piston for any scratches that may be the cause of the leak. If no scratches are present, replace
all seals using a booster seal kit.
HOUSING SEAL:
If the housing seal is damaged, fluid will leak between the two housings. The booster must be removed and disassembled. A booster seal kit should be
