Accord L4-2.2L SOHC VTEC (1994)
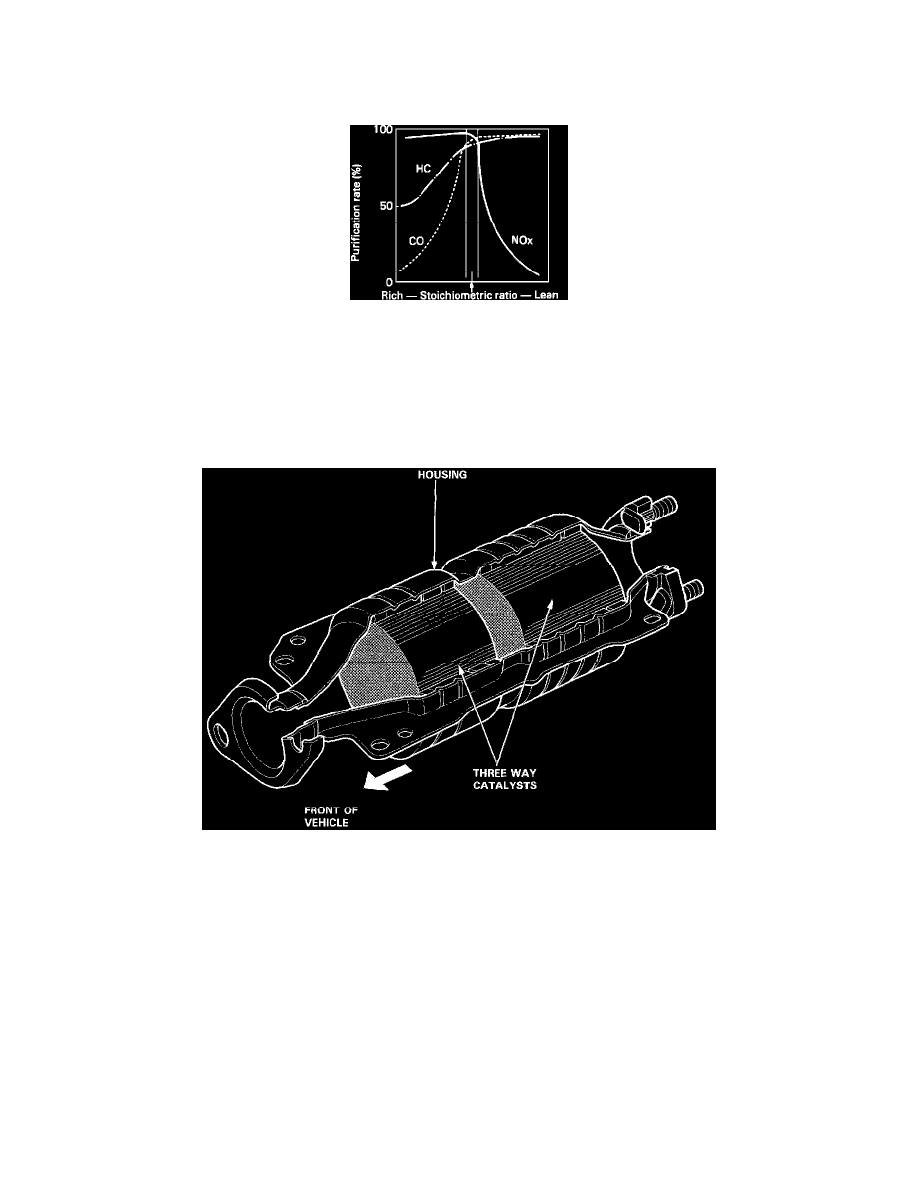
Three Way Catalytic (TWC) Converter: Description and Operation
PURPOSE
The Three Way Catalytic (TWC) converter is used to convert hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the
exhaust gas, to carbon dioxide (CO2), dinitrogen (N2) and water vapor.
Converter Efficiency VS. Stoichiometric Fuel/Air Ratio
OPERATION
The TWC removes CO, HC, and NOx from the exhaust stream most effectively at the stoichiometric (14.7 to 1 ±1.0 %) fuel-air mixture ratio and
at temperatures between 400 to 800° C (750 to 1500° F). Engine malfunctions, such as misfiring, can result in exhaust temperatures exceeding
1400° C (2500° F). These extremely high temperatures can cause the substrate to melt, resulting in destruction of the converter. The use of leaded
fuels should also be avoided. Lead in the exhaust residue coats the catalyst, preventing catalytic action. Excessive oil residues in the exhaust can
also poison the catalyst.
CONSTRUCTION
The TWC is a monolythic three-way device that uses catalytic compounds applied to an integrally constructed honeycomb carrier surface in the
center of the exhaust pipe.
