Civic L4-1.3L Hybrid (2008)
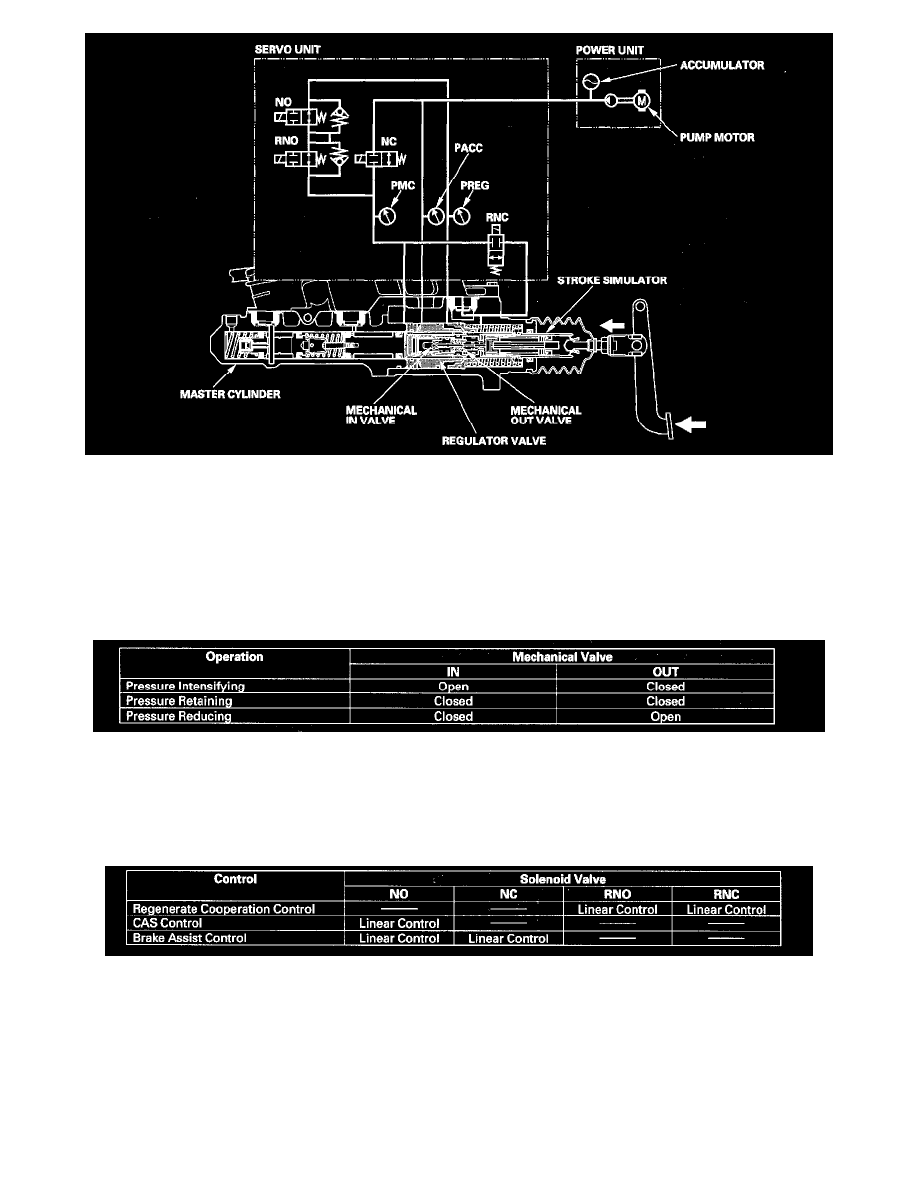
ECU (electric control unit)
The ECU monitors the pressure in the servo unit and feedback from other system controls.
Mechanical Valves for Conventional Brake Operations
When the brake pedal is pressed, force is applied to the regulator valve through the compressed spring, the bushing, and the stroke simulator.
The regulator valve applies accumulator pressure to the master cylinder in proportion to the brake pedal stroke.
The mechanical IN valve and the mechanical OUT valve in the regulator valve are operated by the conventional brake.
The hydraulic control has three operations: Pressure intensifying, pressure retaining, and pressure reducing.
NOTE: If the power unit has a problem, and the accumulator pressure (PACC) is low or depleted, the normal brake system is affected. The primary
and the secondary pistons in the master cylinder are pushed by the brake pedal without assist from the booster.
Solenoid Valves for Master Cylinder Electrical Controls
The pressure to the master cylinder is controlled by four solenoid valves.
The solenoid valves control these operations: Regenerate cooperation control, CAS control, brake assist control.
Pressure Sensors
The servo unit monitors the master cylinder pressure (PMC), the accumulator pressure (PACC), and the regulator pressure (PREG) with independent
pressure sensors that send feedback to the CPU.
NOTE: The regulator pressure sensor recognizes brake pedal operation. The brake pedal stroke sensor checks for regulator pressure sensor or servo
unit CPU malfunctions.
Servo Unit Electronic Control
The servo unit has a ECU (electronic control unit) that does these functions:
