Odyssey EX V6-3.5L (1999)
The pressure reduction control has three modes: pressure reducing, pressure retaining, and pressure intensifying.
Electronic Brake Distribution (EBD) Control
The electronic brake distribution (EBD) function helps control vehicle braking by adjusting the rear brake force before the ABS operates. Based on
wheel sensor signals, the ABS control unit uses the modulator to control the rear brakes individually. When the rear wheel speed is less than the front
wheel speed, the ABS control unit retains the current rear brake fluid pressure by closing the inlet valve in the modulator. As the rear wheel speed
increases and approaches the front wheel speed, the control unit increases the rear brake fluid pressure by momentarily opening the inlet valve. This
whole process is repeated very rapidly.
Self-diagnosis
1. The ABS control unit is equipped with a main CPU and a sub-CPU. Each CPU checks the other for problems.
2. The CPUs check the circuit of the system.
3. Self-diagnosis can be classified into 2 categories:
-
Initial diagnosis: Performed right after the engine starts and until the ABS indicator goes off.
-
Regular diagnosis: Performed right after the initial diagnosis until the ignition switch is turned OFF.
4. When a problem is detected by self-diagnosis, the system shifts to fail-safe mode.
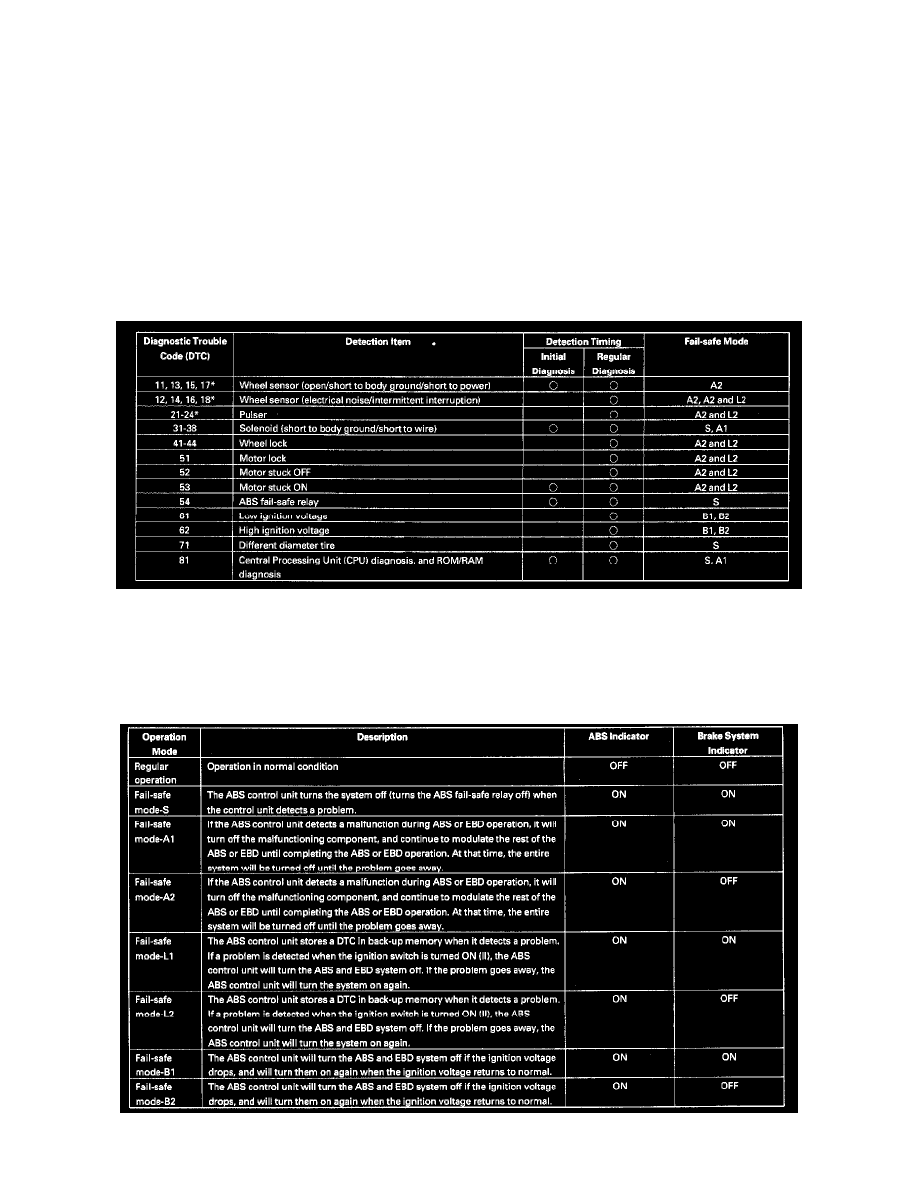
Self-diagnosis Table
NOTE:
-
At the DTCs with "*" mark, there are cases that the ABS control unit shifts to fail-safe mode A1, L1 when the ABS control unit detects more than
one DTC and for different wheel.
-
If the ABS control unit detects the DTCs which have different fail-safe mode individually, the control unit take priority the large number mode.
Operation Mode Table
