Prelude L4-1958cc SOHC (1988)
Deceleration Valve: Description and Operation
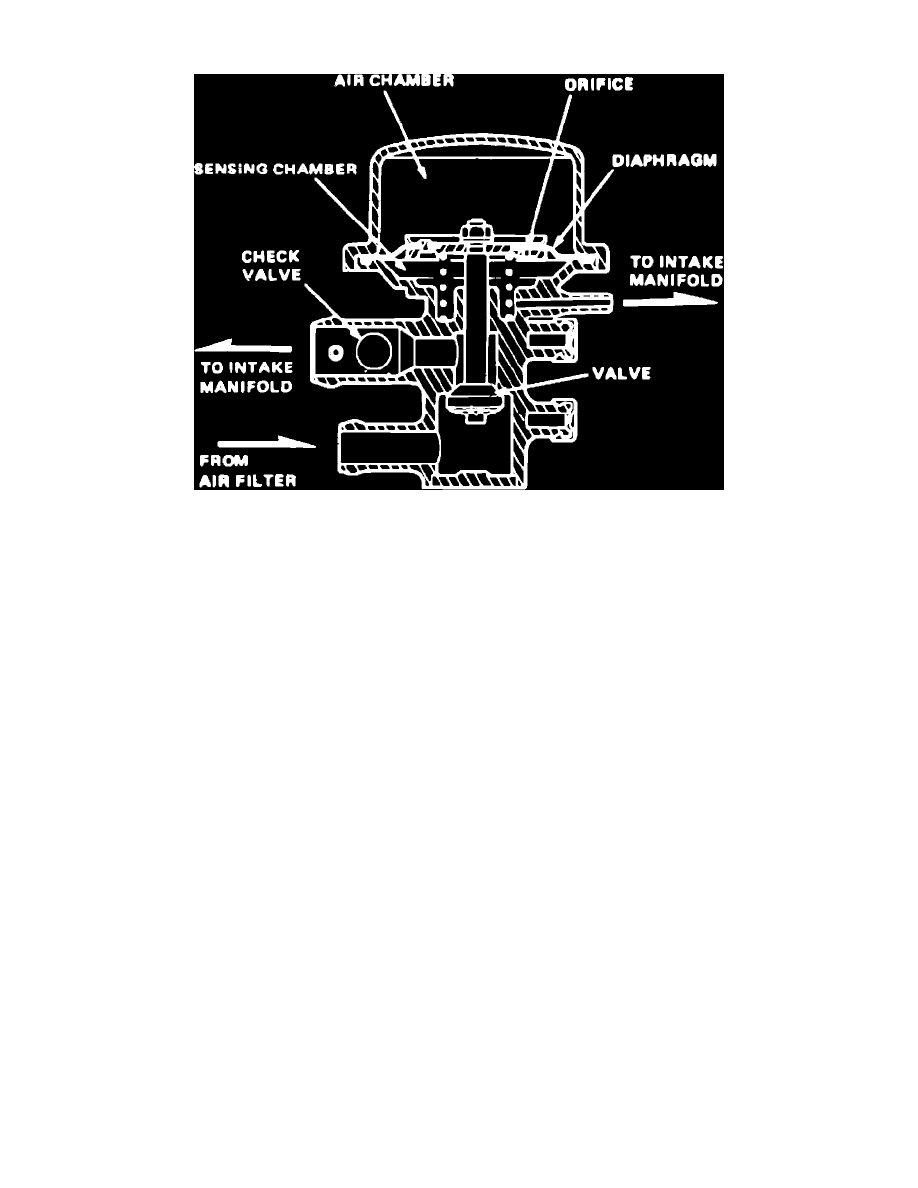
Fig. 70 Typical anti-afterburn valve.
The mixture control system is used on carbureted engines to provide additional air in the intake stream during periods of high vacuum operation such
as deceleration, and on some models, during hot starting. The system includes an anti-afterburn valve and a group of valves and solenoids that are used
to control anti-afterburn valve operation.
The anti-afterburn valve, Fig. 70, lets fresh air into the intake manifold when manifold vacuum suddenly increases. The valve is sensitive only to
sudden increases in vacuum. The length of time it stays open is controlled by a diaphragm that senses change in manifold vacuum.
When manifold vacuum suddenly increases, the diaphragm/valve unit is pulled downward. Air flow from the air chamber to the sensing chamber is
restricted by an orifice, creating a pressure differential on the diaphragm, which holds the valve open. This unbalanced condition lasts for a few seconds
until the pressure in both chambers is equalized by air entering through the orifice, then the spring pushes the diaphragm up, closing the valve.
The anti-afterburn solenoid valve, used on Civic and Prelude is designed to cut off manifold vacuum flow to the top portion of the anti-afterburn valve
diaphragm. The anti-afterburn control solenoid valve, used on 1985---86 Accord, is designed to control the operation of the anti-afterburn valve by
introducing manifold vacuum to the top of the anti-afterburn valve diaphragm. When the anti-afterburn control solenoid valve opens, the anti-afterburn
valve does not open because there is no vacuum difference on both sides of the diaphragm. Depending upon application, the control solenoid is activated
to prevent anti-afterburn valve operation when the engine is cold, when the engine is idling in neutral or par, when vehicle speed or engine RPM is below
a certain value, and during starting. Operation of the control solenoid is controlled by the emission system electronic control unit.
An air valve is used on Civic and CRX models . Manifold vacuum applied to the air valve opens the air passage when manifold vacuum is above set
vacuum of the control switch.
The air control solenoid valve, used on 1985-87 Civic 1300 and CRX HF, is designed to bleed manifold vacuum to the atmosphere. When solenoid
valve is open, it takes a higher level of vacuum to open the control switch.
The vacuum control valve is used on 1985-87 high altitude Civic 1300 and CRX HF and Civic 1500 exc. Calif. with manual transmission. When
engine coolant temperature exceeds the set temperature of thermovalve D and manifold vacuum suddenly increases, the diaphragm valve is opened,
which allows manifold vacuum into the air valve.
