Accent L4-1.6L (2003)
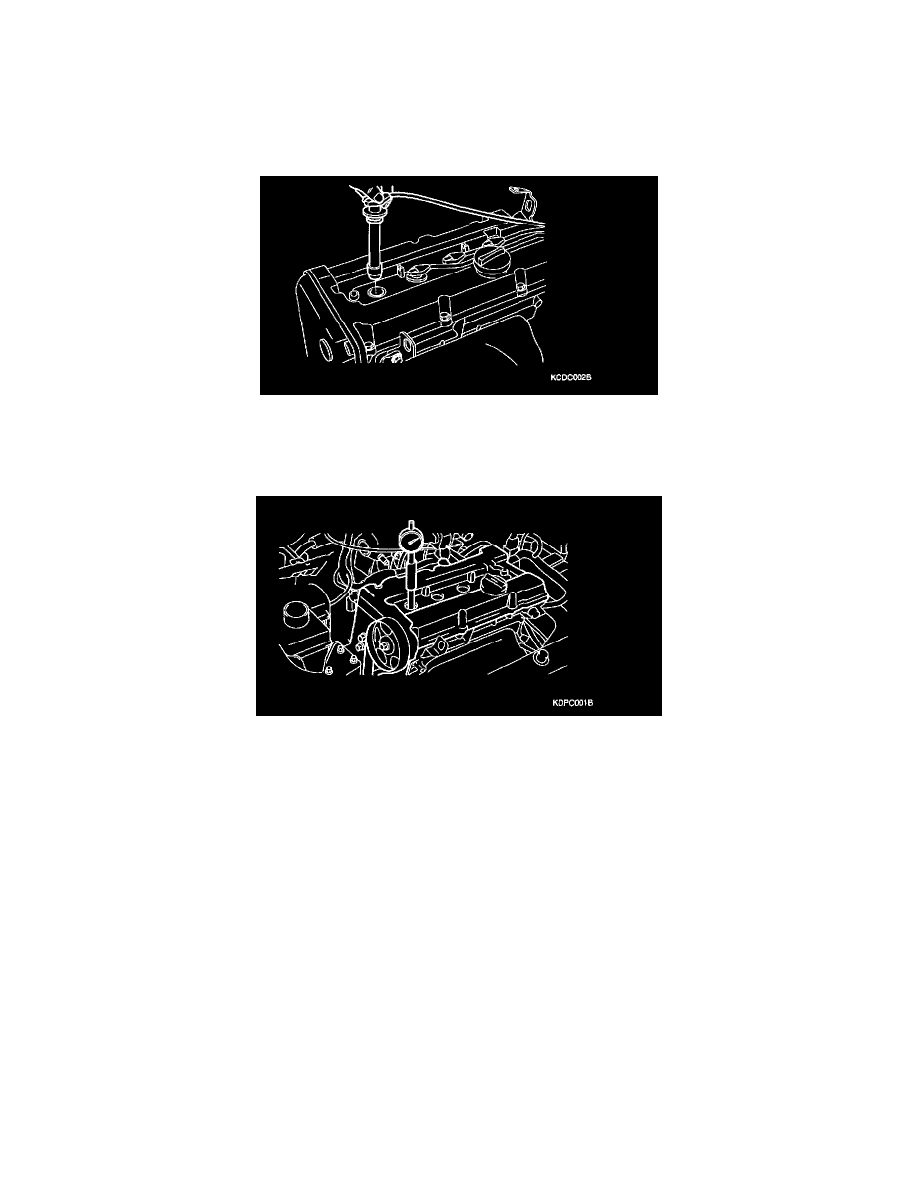
Compression Check: Testing and Inspection
CHECKING COMPRESSION PRESSURE
1. Before checking engine compression, check the engine oil level. Also check that the starter motor and battery are all in normal operating
condition.
2. Check the DTC and note it. Use the scan tool to clear the ECM'S memory.
3. Start the engine and wait until engine coolant temperature reaches 80 - 95°C (176 - 205°F).
4. Disconnect the fuel pump connector.
5. Turn off engine and disconnect the spark clue cables.
6. Remove the spark plugs.
7. Disconnect the I.G. connector.
8. Crank the engine to remove any foreign material in the cylinders.
9. Insert the compression gauge into the spark plug hole.
10. Depress the accelerator pedal to open the throttle fully.
11. Crank the engine and read the gauge.
Standard value: .......1500 kPa (15 Kg/cm2, 218 psi)
Limit: ..........1400 kPa (14 Kg/cm2, 203 psi)
12. Repeat steps 9 to 11 over all cylinders, ensuring that the pressure differential for each of the cylinders is within the specified limit.
Limit: .......Max 100 kPa (1.0 kg/cm2,14 psi) between cylinders
13. If a cylinder's compression or pressure differential is outside the specification, add a small amount of oil through the spark plug hole, and repeat
steps 9 to 12.
1) If the addition of oil makes the compression to rise, it is likely that there may be wear between the piston ring and cylinder wall.
2) If compression remains the same, valve seizure, poor valve seating or a compression leak from the cylinder head gasket are all possible causes.
Tightening torque
Spark plug: ......20 - 30 Nm (200 - 300 kg-cm, 14 - 22 ft. lbs.)
