Hombre S Regular Cab 2WD L4-2.2L CPC (1998)
correlation between oxygen storage and conversion efficiency may be altered enough to set a false DTC.
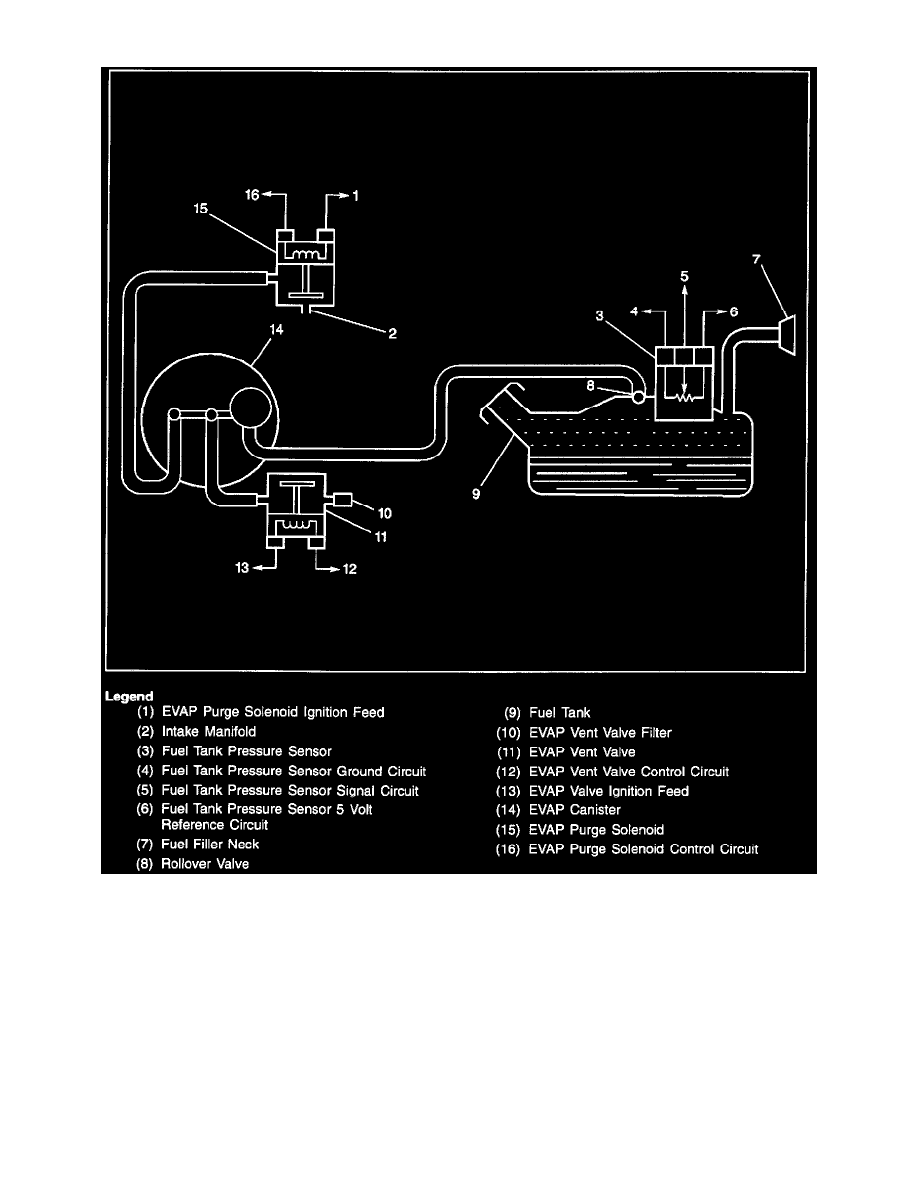
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Purge System Vacuum Switch
The EVAP system uses a switch located in the closed, applying a 12 volt signal to the control purge line between the canister and the purge valve
module as a NO PURGE signal. When the canister in order to detect when the purge is occurring. This purging occurs, the switch opens,
interrupting OFF switch senses the flow from the engine through the the 12 volt signal to the control module. A scan tool purge valve. When no
purge is present, the switch is display will indicate that the purge is occurring.
Clogging of the canister fresh air vent could allow the purge hose between the switch and the canister to trap the vacuum with the purge valve
closed. This would result in a diagnostic indication of a purge valve stuck open or a vacuum switch failure. Similarly, leaks or blockages in the
purge hoses may result in misdiagnosis of the purge valve or the vacuum switch.
When servicing a purge valve diagnostic trouble code, check the canister fresh air vent, the vacuum switch and the integrity of all of the purge
hoses prior to servicing the valve.
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on the crankshaft rotational velocity (reference period) variations. The control module determines the
crankshaft rotational velocity using the crankshaft position sensor and the camshaft position sensor. When a cylinder misfires the crankshaft slows
down momentarily. By monitoring the crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals, the control module can calculate when a misfire occurs.
