Hombre XS Space Cab 2WD V6-4.3L (1998)
Eliminate all add-on equipment in order to diagnose a malfunction.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
NOTICE: In order to prevent possible Electrostatic Discharge damage to the PCM, Do Not touch the connector pins or the soldered components on the
circuit board.
Visual and Physical Underhood Inspection
Carefully perform a visual and physical underhood inspection when performing any diagnostic procedure. This inspection will often lead to
repairing a malfunction without further action.
System Status and Drive Cycle For Inspection/Maintenance (I/M)
Some areas require that certain vehicles run and pass on-board diagnostic test of particular emissions systems.
Using a scan tool, the technician has the ability to monitor the System Status of the following systems:
-
The Catalyst Monitoring system
-
The Evaporative (EVAP) system
-
The Oxygen Sensor (H025)
-
The Heated Oxygen Sensor (H025) heater
-
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system
-
The Air Injection Reaction (AIR) system (if so equipped).
Important: The System Status display indicates whether or not a diagnostic test is completed. Diagnose and repair the system if any of the
on-board diagnostic tests has failed the last test. Verify that all of the required diagnostic tests pass prior to returning the vehicle to the
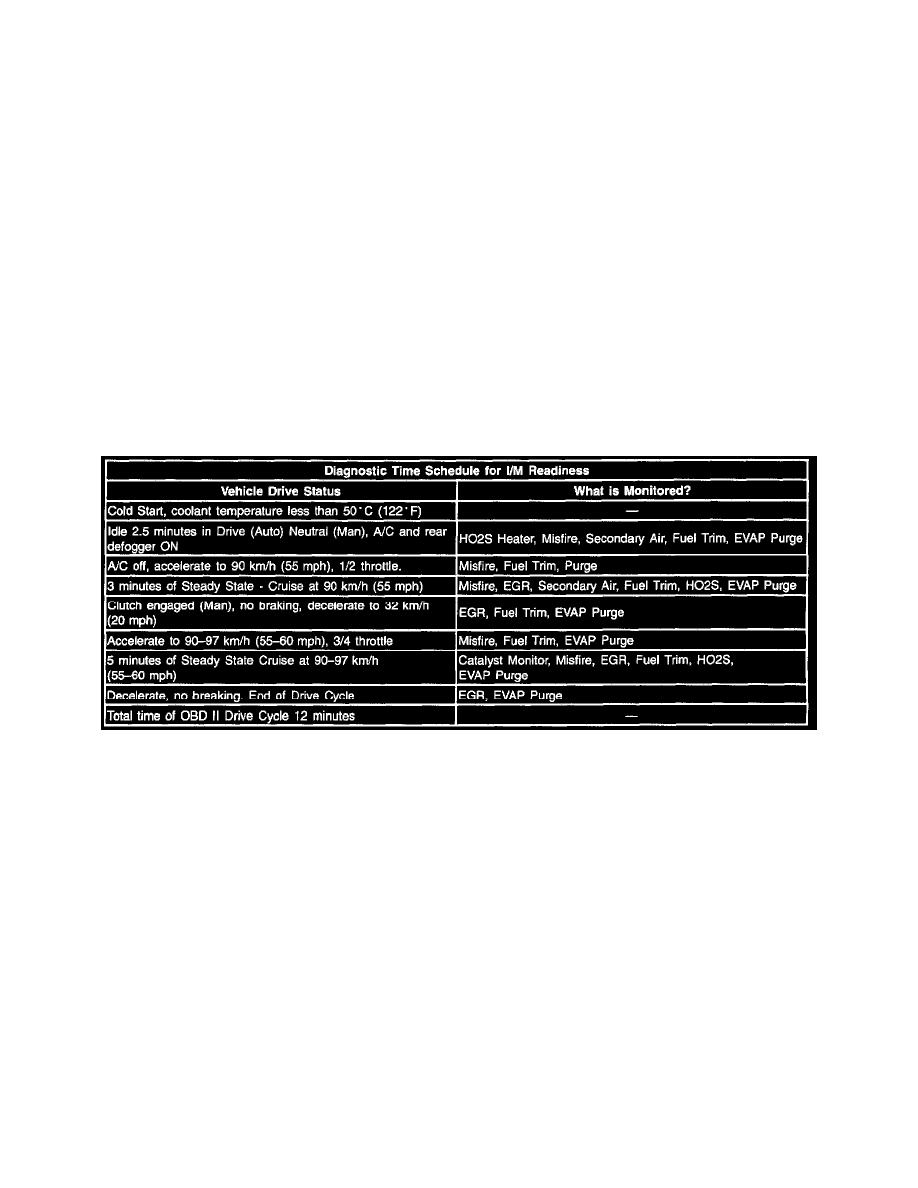
customer. Use the Typical Drive Cycle table as a guide to complete the System Status test associated with I/M.
Typical OBD II Drive Cycle
System Diagnostics
The system diagnostics are tests that monitor and evaluate a particular emissions system and the effect that system has on vehicle emissions. The
system diagnostics consist of the following:
-
The Catalyst Monitor diagnostic tests.
-
The Misfire Monitor diagnostic tests.
-
The Fuel Trim System diagnostic tests.
-
The Evaporative (EVAP) System diagnostic tests.
Catalyst Monitor Diagnostic Tests
The emissions control system used on this vehicle has a Three-Way Catalytic (TWC) converter in order to reduce exhaust emissions of
Hydrocarbons (HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx). The catalyst material that is inside of the converter promotes a
chemical reaction in order to combine oxygen with the HC and CO, converting them to water vapor (H2O) and harmless Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
The NOx is converted to Nitrogen (N) by the converter.
The control module has the ability to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter through the use of a Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) mounted
in the engine exhaust gas stream after the catalytic converter (post-catalyst).
