Wrangler L4-150 2.5L VIN H TBI (1986)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
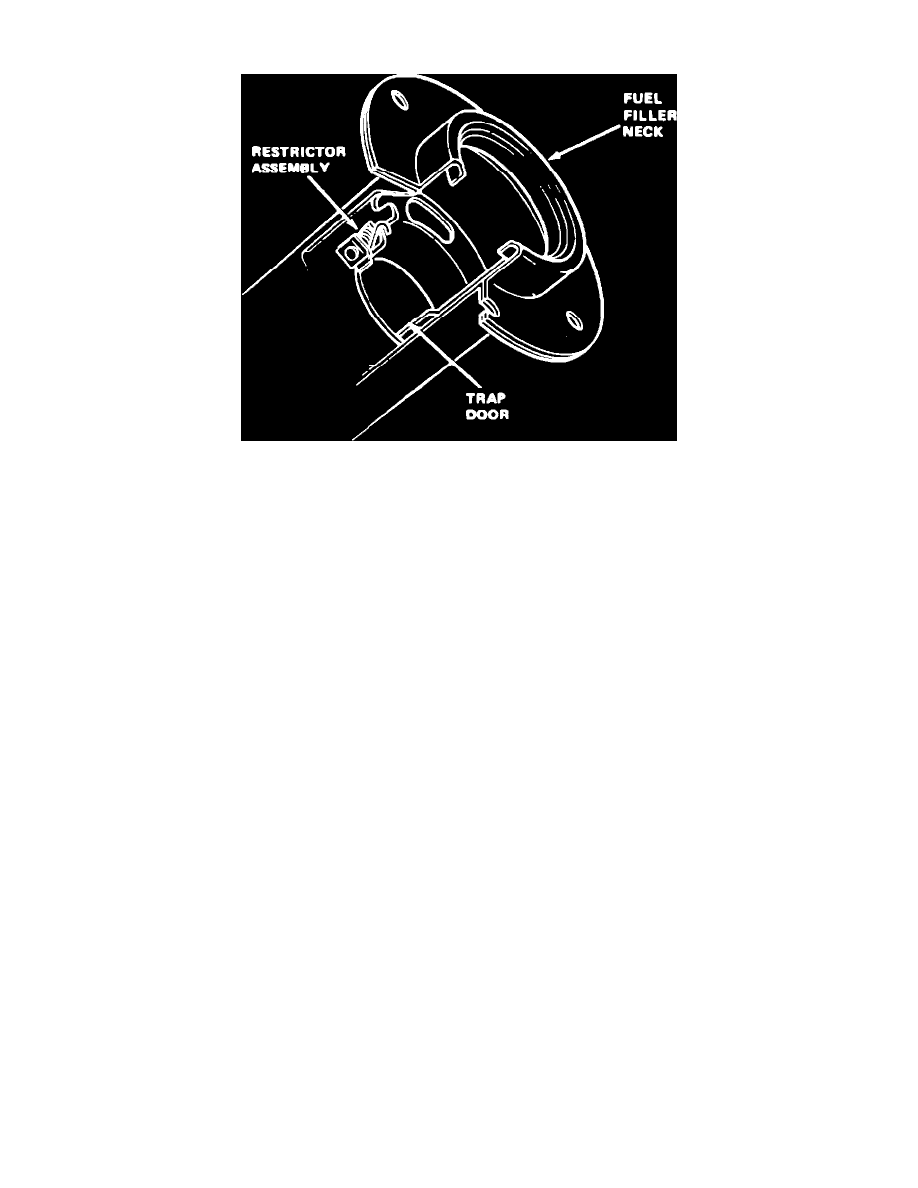
Fig. 3 Fuel tank filler nozzle
Catalytic converters are used to convert carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) into water vapor (H2O), carbon
dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen (N2). The catalysts used to create these conversions are platinum, palladium and rhodium (depending on type of converter).
During engine operation, all of the exhaust gases flow through the converter where a chemical change takes place. This change causes the temperature
inside the converter to be higher than the temperature of the exhaust gases when they leave the engine. Due to this increase in heat, the converter is
insulated so that its outside temperature is about the same temperature as the muffler. However, due to its solid mass, the converter remains hot much
longer than the muffler.
The body of the catalytic converter is made of stainless steel designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat can bulge or distort the converter.
Since excessive heat build up is not the fault of the converter, the carburetor or ignition system should be checked whenever a converter is damaged by
overheating.
Although all vehicles with catalytic converter must use unleaded fuel, small amounts of leaded fuel can be used in case of an emergency. To prevent
adding leaded fuel, the fuel tank filler nozzle has a built-in restrictor, Fig. 3.
