Wrangler 2WD V6-3.8L (2008)
Leak Detection Pump: Description and Operation
OPERATION
The ESIM (Evaporative System Integrity Monitor) is very similar to the NVLD. However, the design of the ESIM has been simplified and unlike the
NVLD the ESIM does not require a solenoid. The ESIM mounts directly to the canister, eliminating the need for a mounting bracket. It is critical that the
ESIM is mounted vertically. On vehicles where the canister is mounted on an angle, the ESIM requires an adaptor to maintain a vertical position. When
the ESIM is installed vertically, the electrical connector is in the 3 o'clock position.
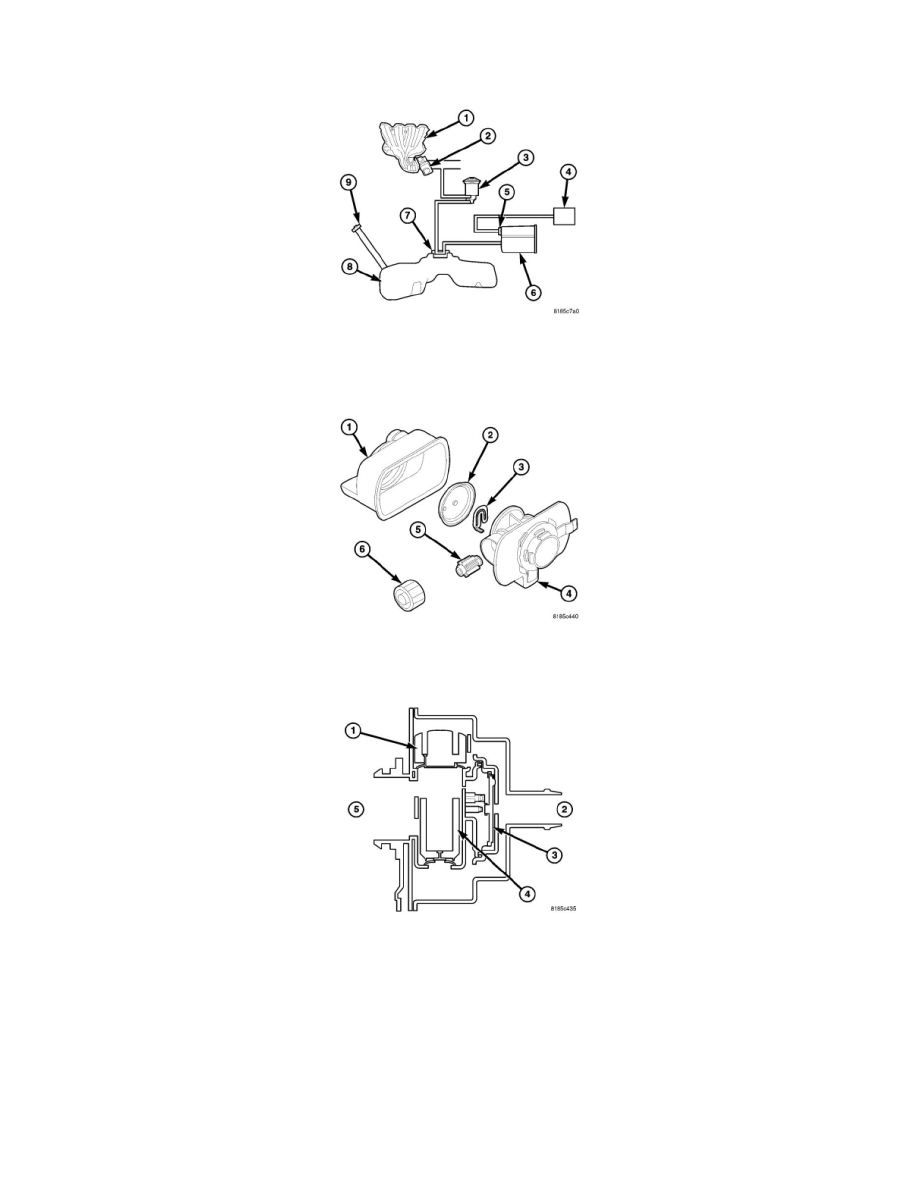
The ESIM assembly consists of a housing, a small weight and a large weight that serve as check valves, a diaphragm, a switch and a cover. There is one
large weight and one small weight check valve in the ESIM assembly. A seal is attached at the end of each weighted check valve. The large weight check
valve seals for pressure. The small weight check valve seals for vacuum. The weighted check valves are contained within the ESIM housing.
The ESIM (Evaporative System Integrity Monitor), while physically different than the NVLD system, performs the same basic function as the NVLD
does - controlling evaporative emissions. The ESIM has been simplified because the solenoid used on the NVLD is not used on the ESIM.
The ESIM consists of housing, two check valves (sometimes referred to as weights), a diaphragm, a switch and a cover. The larger check valve seals for
pressure and the smaller one seals for vacuum.
During refueling, pressure is built up in the evaporative system. When pressure reaches approximately.5 inches of water, the large check valve unseats
and pressure vents to the fresh air filter.
Conversely, when the system cools, and the resulting vacuum lifts the small check valve from its seat and allows fresh air to enter the system and relieves
the vacuum condition. When a calibrated amount of vacuum is achieved in the evaporative system, the diaphragm is pulled inward, pushing on the spring
and closing the contacts.
