Town Car V8-281 4.6L SOHC (1991)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
The Catalytic Converter is mounted under the vehicles body within the exhaust system, and is designed to convert harmful exhaust gas pollutants,
Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrocarbons (HC), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) to harmless by-products of Nitrogen (N), Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and water
vapor (H2O) through a catalytic chemical reaction.
Two types of converters in use today are the Conventional Oxidation Converter (COC) and Oxidation-Reduction Converter. Both consists of two
stamped aluminum or stainless steel pieces welded together to form a round or oval housing.
Some oval-type converters contain tiny pellets that are impregnated with the catalyzing element(s). Although this type of converter is known to create a
fair amount of exhaust restriction, it is less expensive to manufacture and in some vehicle models contaminated pellets may be replaced.
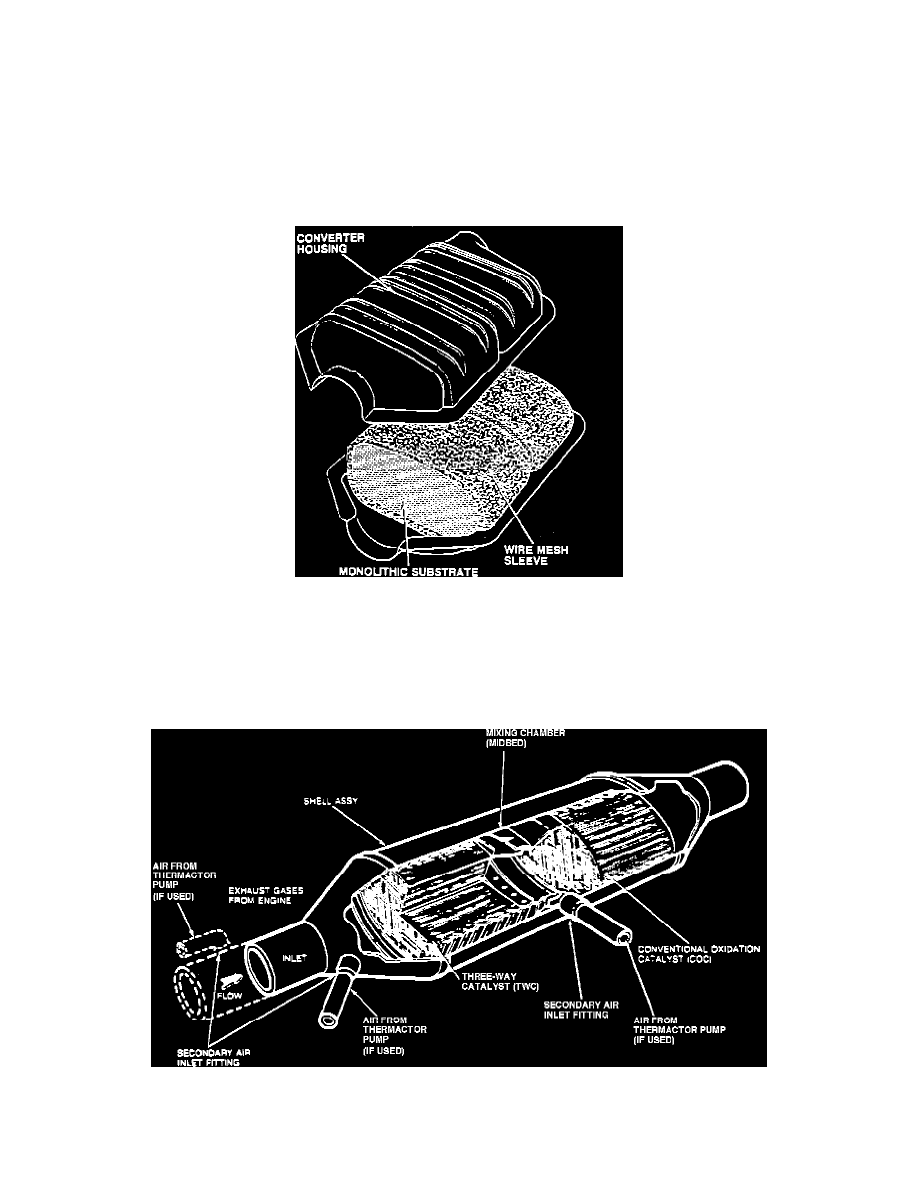
Single Brick Catalytic Converter
The round-type converters may contain one or two ceramic monolithic honeycomb substrates. The substrate bricks or beds are impregnated with the
catalyzing element(s), then covered by a wire mesh sleeve for insulation and protection from shock and severe jolts. A diffuser inside the shell allows the
exhaust gases to flow uniformly over the entire area of the substrate.
Dual Brick Catalytic Converter
