929 V6-3.0L DOHC (1993)
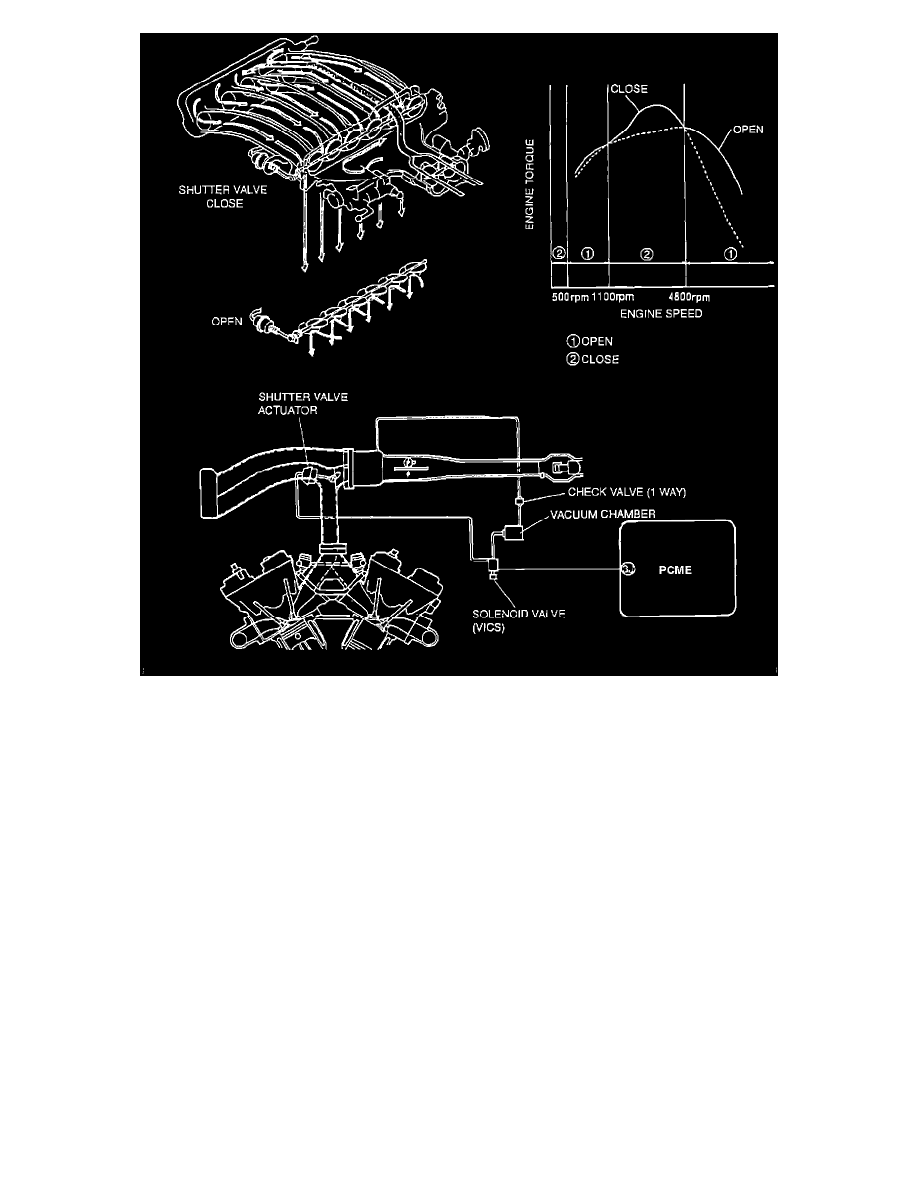
Variable Inertia Charging System (VICS)
The intake manifold has two paths that air can take on the way to the cylinders, a long and a short path. The two paths are separated by a shutter
valve, like a throttle valve in each intake runner. When the shutter valves are closed, air must take the long path. When the valves are open, air can
take a more direct short path to the engine. The PCME opens and closes the shutter valves at different engine speeds to take advantage of
harmonic oscillations in the intake manifold runners. This helps "pack" more fuel and air into the cylinders during each cylinder cycle (improved
volumetric efficiency), increasing torque and horsepower over a broader rpm range.
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
Ignition timing is also controlled by the computer. The PCME monitors signals from sensors in the distributor. From these signals, the PCME can
calculate crankshaft position and engine speed. The PCME uses this information, compared with information from other engine sensors, to
determine the correct spark advance for the engine speed and load at any given time. The ignition coil "fires" when the PCME interrupts the low
voltage signal to a power switching transistor (igniter). The igniter turns the primary coil circuit "OFF" causing the ignition coil to discharge. For
more information on the ignition coil, igniter, and other secondary ignition components, refer to Ignition System
SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
The EGI system has self-diagnostic capability. When a fault is detected in a monitored component and/or circuit, the PCME will store a numbered
code in its memory (malfunction code) and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will light and stay on while the engine is running, alerting the
driver to seek service. The technician can then access PCME fault memory and display trouble codes identifying the faulty component(s) or
circuit(s), to aid in troubleshooting and repair.
FAIL-SAFE MODE
To provide a margin of safety and maintain driveability in the event of certain system failures, the PCME has a fail-safe mode. In this mode, it will
substitute a fixed "in range" signal for that of the failed sensor. This allows the vehicle to be operated until repaired, although driveability will
probably be affected. The PCME automatically switches to fail-safe mode if a fault is detected in any of these inputs:
^ Airflow meter
