B4000 2WD V6-4.0L OHV (1994)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
PURPOSE
The Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is mounted under the vehicle body within the exhaust system, and is designed to convert harmful
exhaust gas pollutants, Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrocarbons (HC), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) to harmless by-products of Nitrogen (N),
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O) through a catalytic chemical reaction.
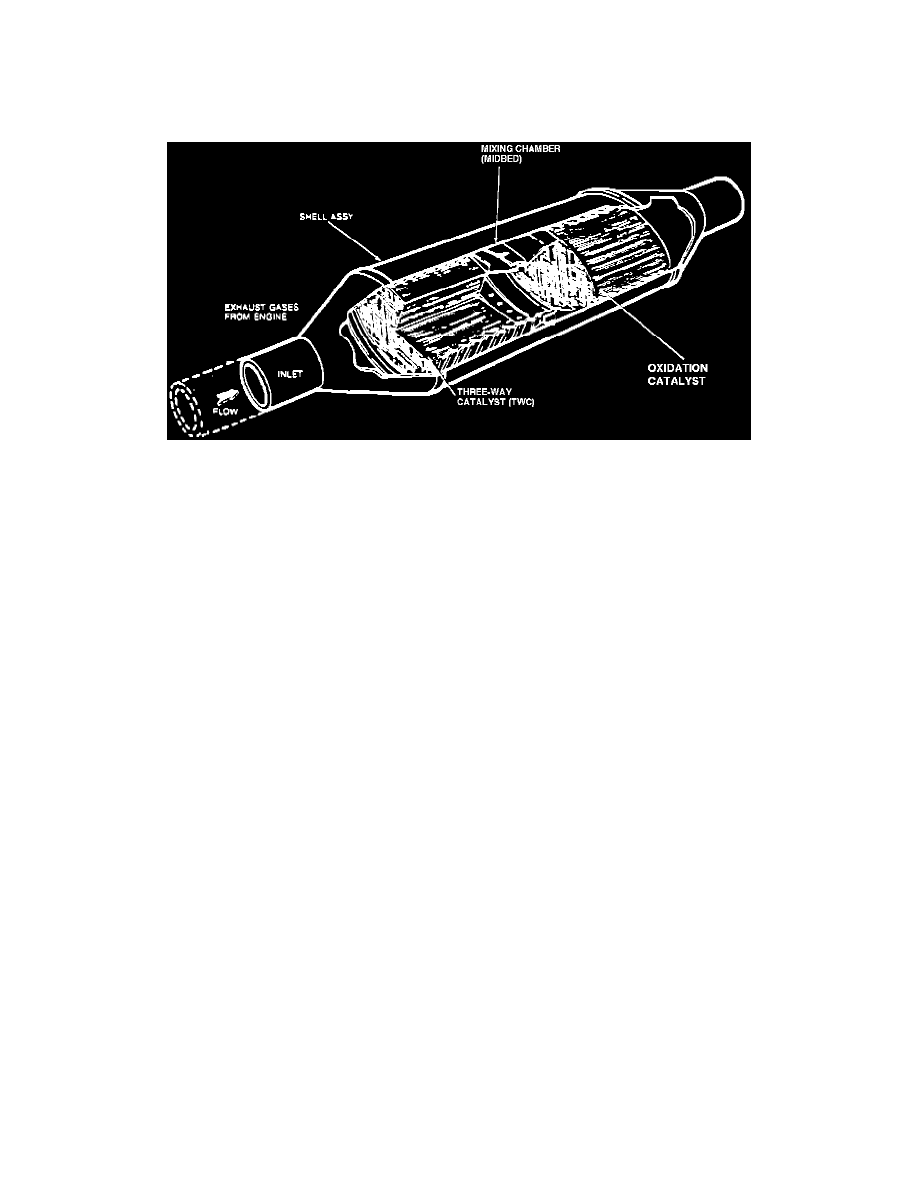
View: Typical Three-Way Catalytic Converter
CONSTRUCTION
The TWC contains one or two ceramic monolithic honeycomb substrates. The substrate bricks or beds are impregnated with the catalyzing
element(s), then covered by a wire mesh sleeve for insulation and protection from shock and severe jolts. A diffuser inside the shell allows the
exhaust gases to flow uniformly over the entire area of the substrate.
THE OXIDATION REACTION
In order to change (HC) and (CO) into harmless materials, the catalytic elements (platinum and palladium) start an oxidation, or burning, reaction
in the catalytic converter. Oxidation is the addition of oxygen to an element or compound. During the oxidation process, Oxygen (O2) mixes with
the excess (HC) and (CO) to form (H2O) and (CO2).
Caution should be taken while working on or around catalytic converters and other exhaust system components, due to the considerable heat 480°
C to 870°C (900°F to 1,600°F) that is generated during the oxidation process.
THE REDUCTION REACTION
Reduction is the opposite of oxidation, or the chemical removal of oxygen from a material. The reduction reaction changes (NOx) to harmless
nitrogen (N) and carbon dioxide (CO2) by chemically moving the oxygen from the (NOx) compound to the (CO) compound. The catalytic element
required for the reduction process is rhodium.
The Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is designed to reduce all three exhaust pollutants, but works best to reduce (NOx) when the (CO)
level of the exhaust is between 0.8 and 1.5 percent. As the (CO) level increases or decreases from that percentage, the TWC converters efficiency
decreases. Exhaust gas first passes through the catalyst, where (NOx) is reduced to (N2) and (CO2); then through the catalyst where (HC) and
(CO) are changed to (H2O) and (CO2).
