B4000 2WD V6-4.0L OHV (1994)
The New Generation Star (NGS) tester is recommended for checking TPS output voltage. A voltmeter can be used however the NGS tester monitors
voltage output without disturbing the connector. This is important, for example, because the following concerns may temporarily correct themselves if
the connector is disturbed for testing.
^
Loose / Poor Connection
^
Dirt Under Connector
^
Oxidation on Connector
These concerns also may mis-lead the technician into replacing a good TPS, leaving the real source of the concern to return later.
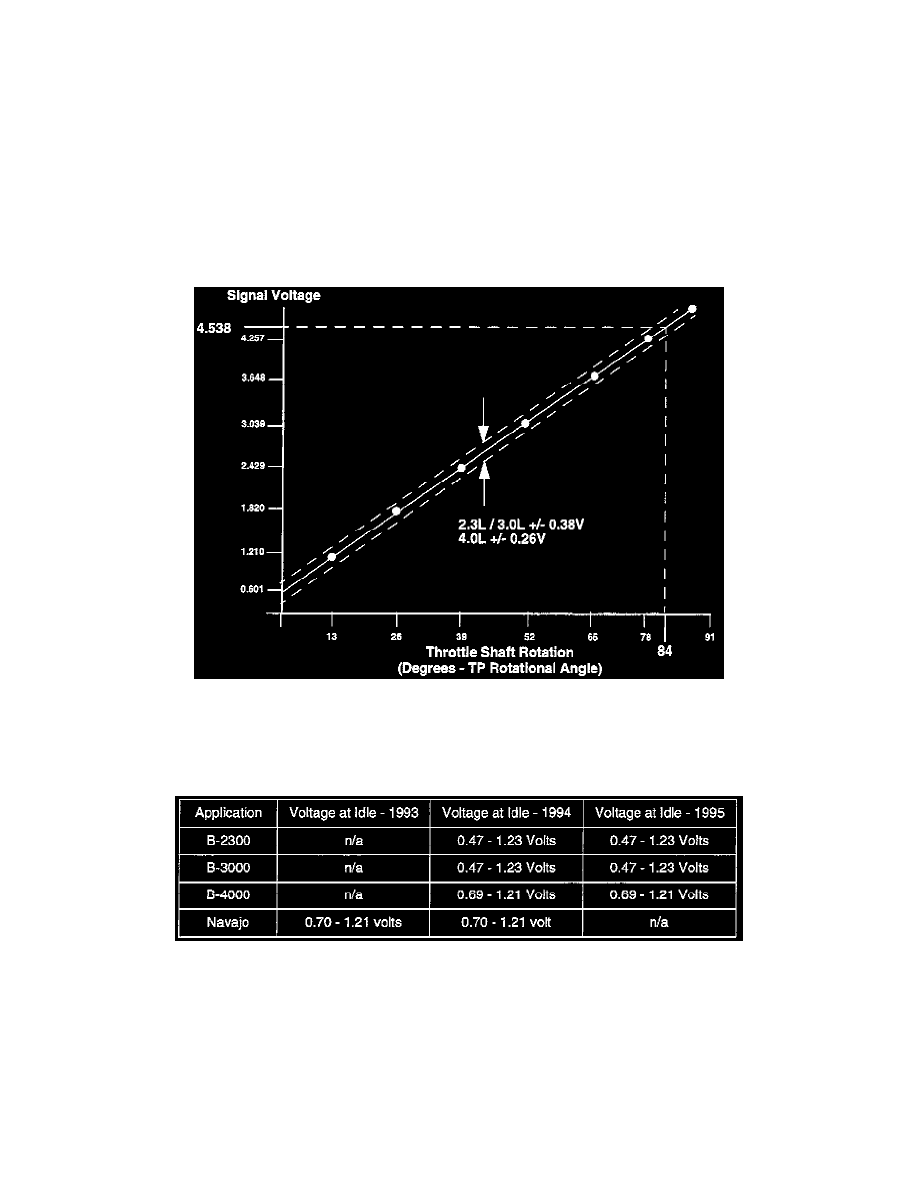
MEASURING TPS VOLTAGE
When diagnosing a TPS problem, it is important to measure the voltage at idle. This is important because most of the TPS operational life is spent within
10 degrees of the idle position. The figure illustrates how the TPS voltage changes between idle and WOT conditions.
NOTE:
The normal range for throttle angle measurement is from 0 to 85 degrees.
The chart contains TPS idle voltage ranges for B-Series trucks and Navajos. These values replace those listed in the 1994 - 95 workshop manuals.
TP voltage increases when the throttle is depressed. Idle is typically 0.4 to 1.2 volts (refer to the idle voltage range chart). As the TPS senses plate
rotation toward WOT, the voltage increases. WOT is generally 4.0 volts.
CAUTION:
Many voltmeters will automatically change ranges when measuring TPS output from idle to WOT. To avoid mistaken TPS replacement, set the range
lock feature on the meter prior to recording voltage.
If your voltmeter does not change ranges automatically, and the meter is set to the millivolts scale when reading full range voltage, the meter display may
not indicate an valid value.
