MPV 2WD V6-3.0L SOHC (1992)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
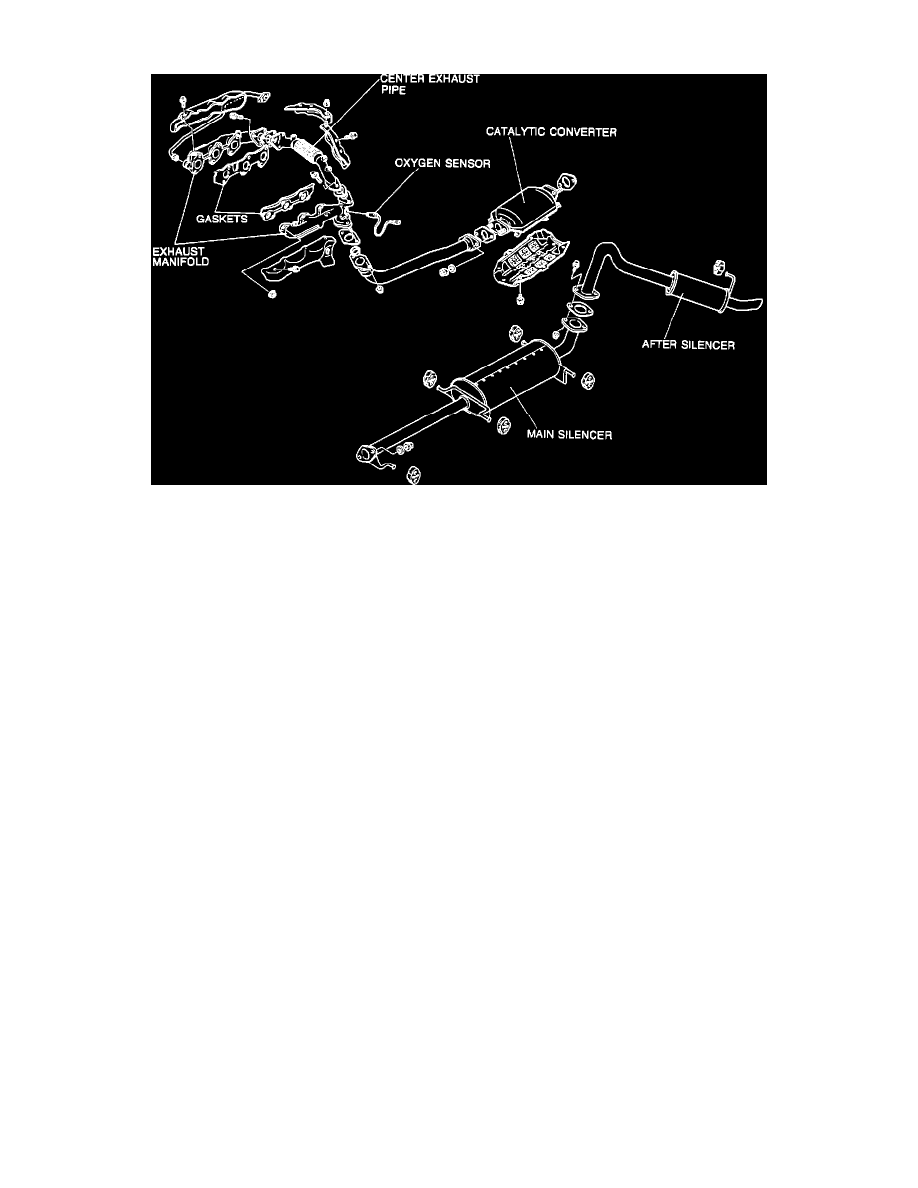
Exhaust System
A three-way catalytic converter (TWC), downstream from the exhaust manifold, reduces oxides of nitrogen (NOx) while oxidizing hydrocarbons
(HC) and carbon monoxide (CO). The converter contains catalyst elements platinum, rhodium, and palladium, which promote oxidation and
reduction reactions. Emissions are converted into carbon dioxide, water vapor and nitrogen.
The Three-Way Catalytic Converter is designed to react with all three major exhaust pollutants. It works best to reduce NOx when exhaust CO
level is between 0.8 and 1.5 percent. Exhaust gas first passes through the catalyst, where oxides of nitrogen are reduced; then through the catalyst
where HC and CO are changed to H2O and CO2.
OXIDATION REACTION
To break down HC and CO, catalytic elements (platinum and palladium) start an oxidation, or burning, reaction in the catalytic converter.
Oxidation adds oxygen to an element or compound. During the oxidation process, oxygen mixes with excess HC and CO to form H2O and CO2.
During oxidation, considerable heat (900°F to 1,600°F) is generated. Use caution while working on or around catalytic converters and other
exhaust system components.
REDUCTION REACTION
Reduction is the opposite of oxidation, or the chemical removal of oxygen from a material. Reduction changes NOx to nitrogen and free oxygen,
which is then consumed in the oxidation reaction with other pollutants. Catalytic elements required for the reduction process are platinum and
rhodium.
