MPV 2WD V6-3.0L SOHC (1992)
Spark Plug: Description and Operation
PURPOSE
The spark plugs protrude into the combustion chambers. When the ignition coil discharges, a high voltage spark jumps across the air gap between
the center and ground electrodes. It's this spark that ignites the compressed air/fuel mixture.
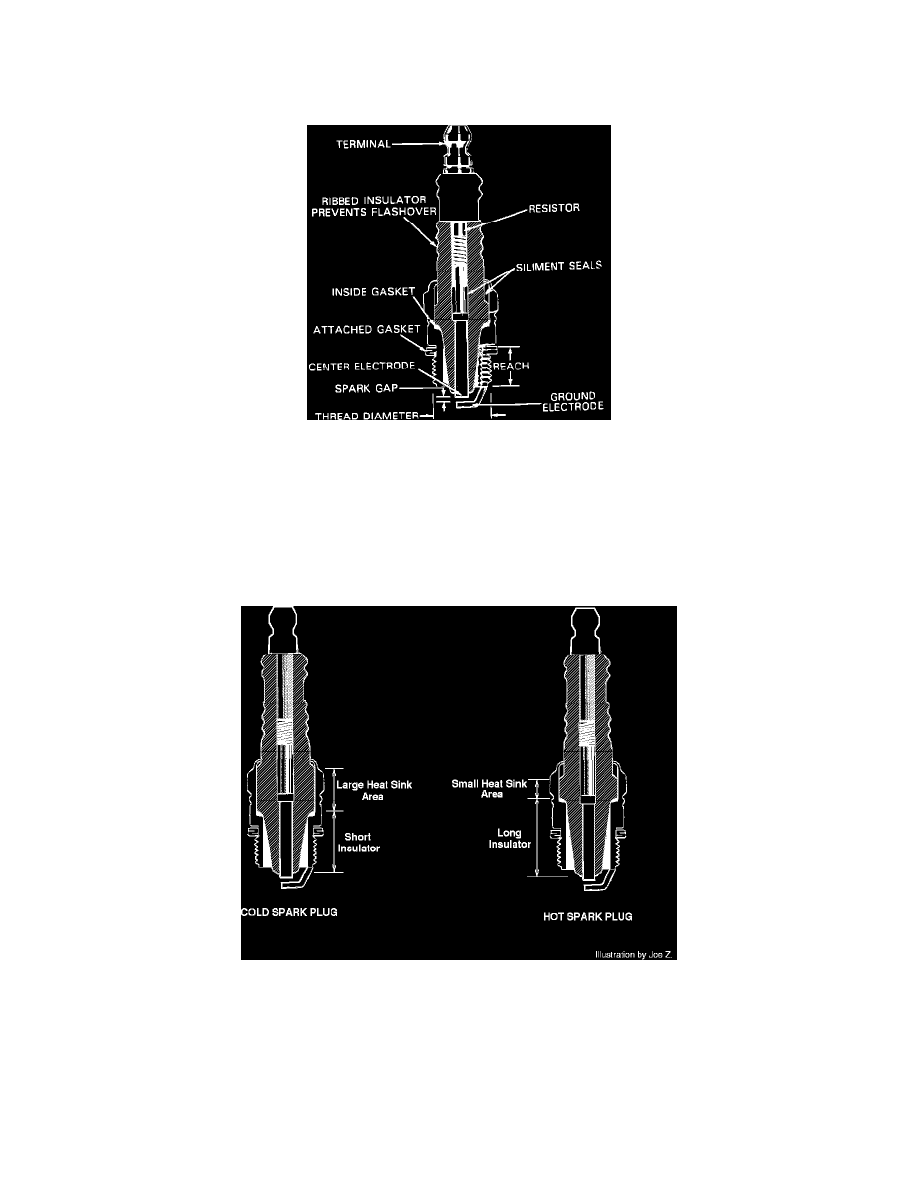
Typical Spark Plug Construction
CONSTRUCTION
There are many different types of spark plugs for the many different applications. Each type has specific advantages for its applications. Different
features include but are not limited to:
1.
THREAD SIZE - The diameter and pitch of the threaded portion of the spark plug varies with different applications.
2.
REACH - The length of the threaded portion and how far the electrode protrudes into the combustion chamber varies with different applications.
Spark Plug Heat Range Illustrated
3.
HEAT RANGE - The ability of the spark plug to cool its center electrode.
^ Hot plugs have longer insulators around the center electrode and less cross-sectional area for heat to transfer from the electrode to the cylinder
head. Heat is conducted away from the center electrode more slowly and the electrode tip stays at a higher operating temperature.
^ Cold plugs have shorter insulators around the center electrode and a larger cross-sectional area for heat to transfer to the cylinder head. Heat is
conducted away from the center electrode quickly and the electrode remains at a cooler operating temperature.
