MPV 4WD V6-3.0L SOHC (1990)
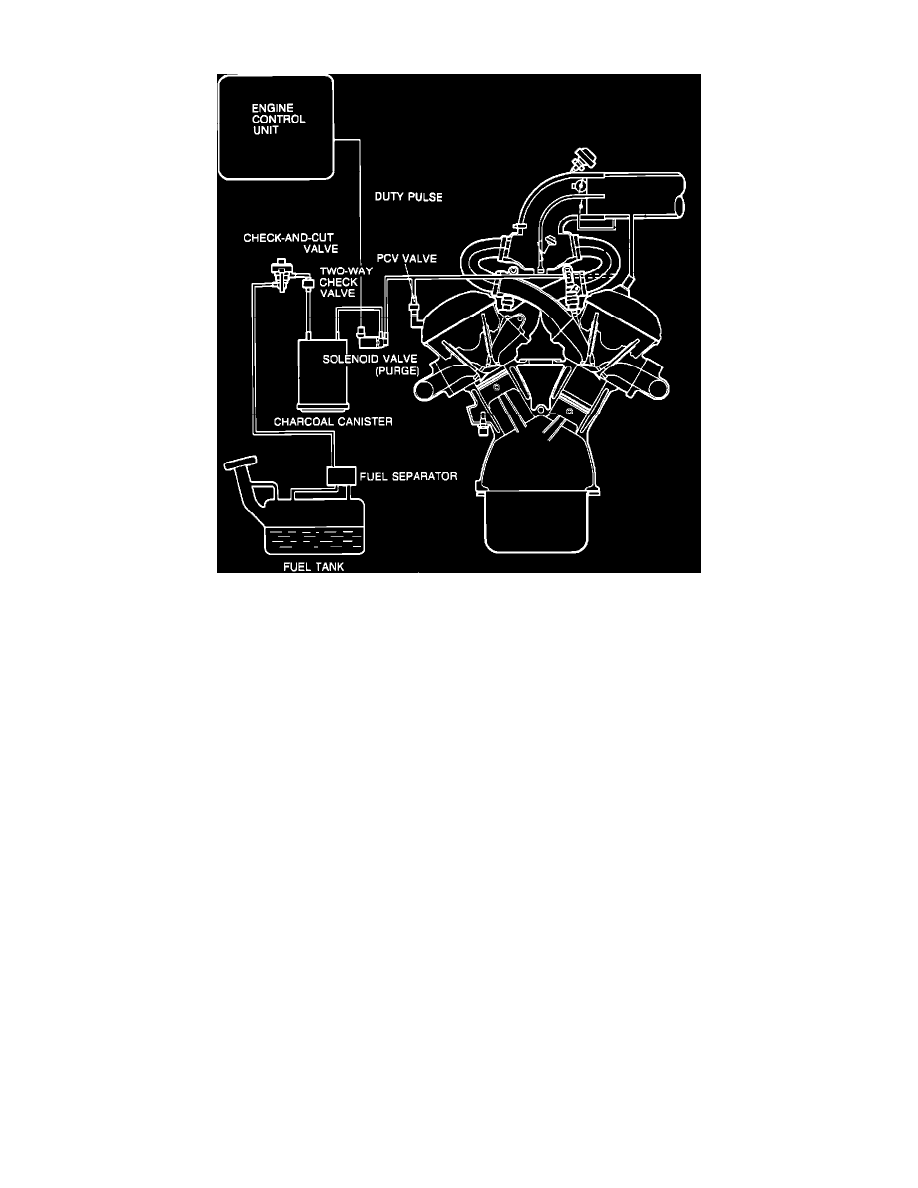
Evaporative Emission Control Canister: Description and Operation
Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP)
The evaporative emission control system stores fuel vapor generated in the fuel tank in the cannister when the engine is not running. The fuel vapor is
stored in the cannister until it is drawn into the dynamic chamber and burned when the engine is started.
The evaporative emission control system is used to collect and store the fumes generated by the fuel in the fuel tank. The fuel vapors are stored in the
charcoal cannister until it is purged by engine vacuum.
The evaporative emission control system consists of the charcoal cannister, fuel separator, solenoid purge valve, two way check valve, check and cut
valve, and PCV valve.
Fuel vapor is purged from the cannister under the following conditions:
When the vehicle is operating in the cruise mode (fuel feedback zone),
1.
Idle switch off
2.
Coolant temperature above 60°C (140°F)
3.
Transmission is in gear
Deceleration
4.
Idle switch on
5.
Coolant temperature above 60°C (140°F)
6.
Engine speed is above 3500 RPM
7.
Transmission is in gear
8.
Intake air temperature sensor is below 75°C (167°F)
CHARCOAL CANNISTER
The charcoal cannister stores gasoline vapors when the engine is not running.
FUEL/VAPOR SEPARATOR
The fuel/vapor separator is mounted outside the fuel tank and prevents liquid fuel from entering the charcoal cannister.
SOLENOID PURGE VALVE
The solenoid purge valve is connected in-line between the PCV valve and the charcoal cannister. The valve is used to vent the charcoal cannister
under certain conditions as controlled by the engine control unit.
