MX-5 Miata LS L4-1.8L DOHC (2001)
Brake Rotor/Disc: Testing and Inspection
Front
FRONT BRAKE (DISC) INSPECTION
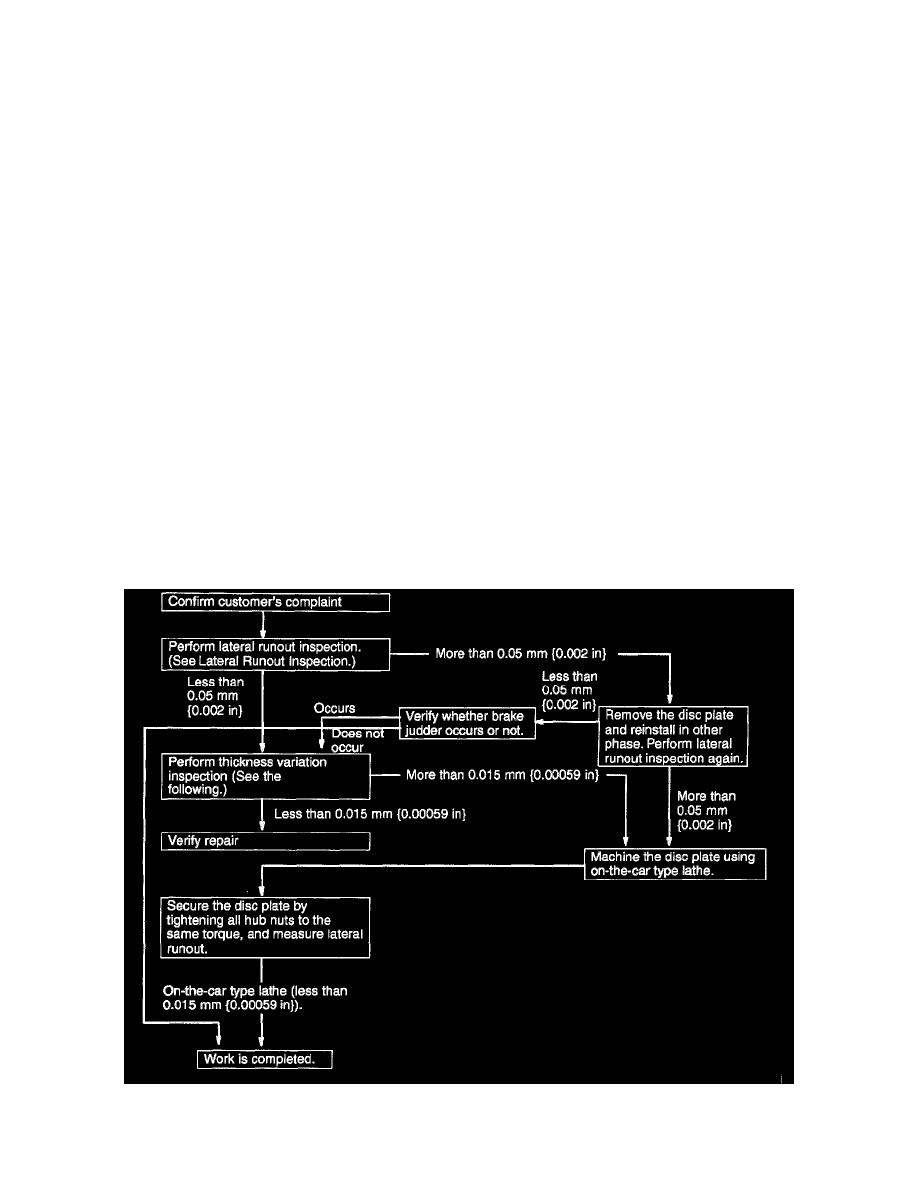
Brake Judder Repair Hint
Description
1. Brake judder concern has the following 3 characteristics:
Steering wheel vibration
1. Steering wheel vibrates in the direction of its rotation. This characteristic is most noticeable when applying brakes at a vehicle speed of 100 - 140
km/h (62.1 - 86.8 mph).
Floor vibration
1. When applying brakes, the vehicle body shakes back and forth. The seriousness of shake is not influenced by vehicle speed.
Brake pedal vibration
1. When applying brakes, a pulsating force tries to push the brake pad back occurs. The pulsation is transmitted to the brake pedal.
2. The following are the main possible causes of brake judder:
Due to an excessive runout (side-to-side wobble) of disc plate, the thickness of disc plate is uneven.
1. If the runout is more than 0.05 mm (0.002 inch) 10 mm (0.39 inch) from the disc plate edge, an uneven wear occurs on the disc plate because the
pad contacts the plate unevenly.
2. If the runout is less than 0.05 mm (0.002 inch), uneven wear does not occur.
The disc plate is deformed by heat.
1. Repeated panic braking may raise the temperature in some portions of disc plate by approximately 1,000°C (1,832°F). This results in deformed
disc plate.
Due to corrosion, the thickness and friction coefficient of disc plate change.
1. If a vehicle is parked under damp conditions for a long time, corrosion occurs on the friction surface of disc plate.
2. The thickness of corrosion is uneven and sometimes appears like a wave pattern, which changes the friction coefficient and causes a reaction force.
Inspection and repair procedure
Lateral runout inspection
