MX-6 L4-2184cc 2.2L SOHC Turbo F2 (1989)
Fuel Injector: Description and Operation
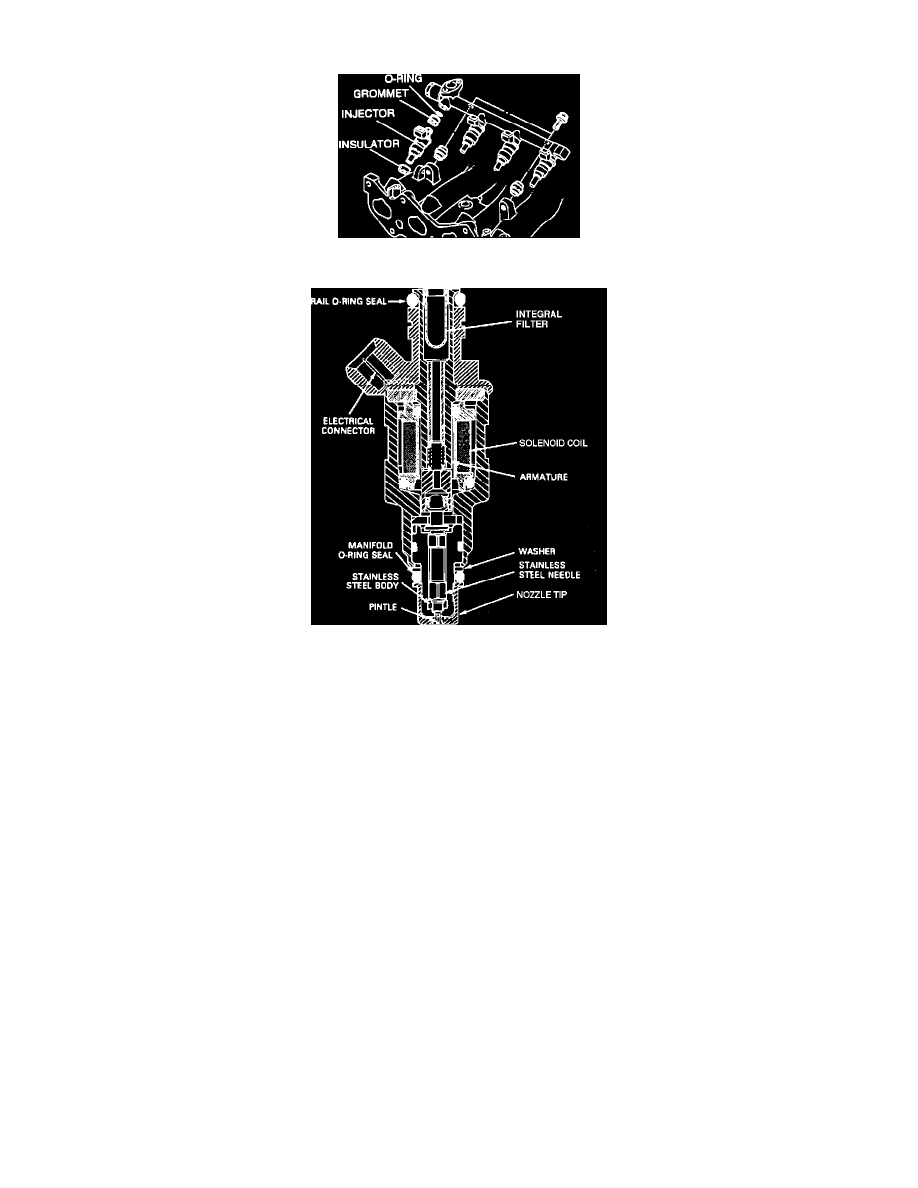
Fuel Rail (Delivery Pipe) And Injectors
Typical Fuel Injector
The fuel injectors, located on the intake manifold near the cylinder head, are electrically operated, high impedance solenoid valves that open when
energized. The injectors get battery power from the main relay when the ignition is in the either the "START" or "RUN" position, and are energized
when the ECU completes the circuit to ground. Injection timing and duration is determined by the engine control unit. Injectors are energized either all at
the same time once each crankshaft revolution (during cranking and cold engine operation), or in pairs (normal warm engine operation).
The injectors are constructed of stainless steel and high density plastic, to resist corrosion. They consist of a fuel inlet with filter screen, an electrical
solenoid and connector, and a pintle valve and nozzle. Injectors are held in place by the fuel rail and sealed by an O-ring and insulator.
To calculate fuel injection quantity and timing, the ECU utilizes information from various input sensors, making adjustments needed to maintain good
driveability, fuel economy and low emissions under the full range of operating conditions.
Input information is calculated from these devices:
Water thermosensor
Oxygen sensor
Airflow meter
Intake air thermosensor
Throttle sensor
Idle switch
Atmospheric pressure sensor
Distributor Ne and G signals
Stop light switch
Neutral and clutch switches
A/C switch
Inhibitor switch
Ignition switch ("START" position)
