RX7 2RTR- 1308cc 1.3L Turbo FI (1989)
Air Injection Pump: Description and Operation
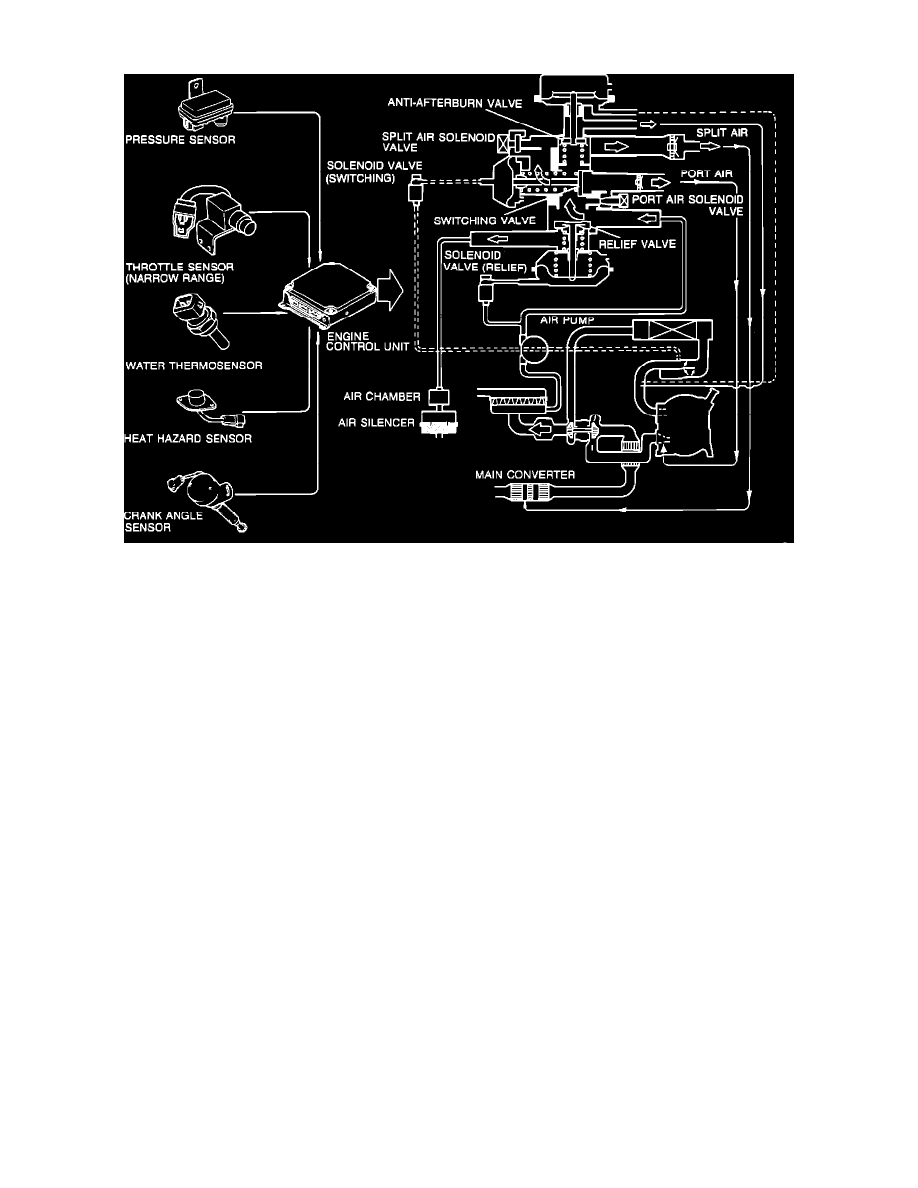
Air Injection System (AIS)
The air injection system supplies secondary air into the exhaust system to burn (oxidize) CO and HC in the exhaust gas and to control the oxygen
signal for the engine control unit. The main components of the air injection system are the air pump, the check valves, the air control valve, the
anti-afterburn valve, the solenoid switching valve, the solenoid relief valve, the heat hazard sensor, the split air solenoid valve, and the port air solenoid
valve.
AIR PUMP
The air pump is a belt driven pump that is used to supply air to the air injection system.
CHECK VALVE
There are two check valves located in the air injection system. One is located in the air line going to the exhaust ports and the other is located in the
air line going to the catalytic converter. The check valves allow air from the air pump to be delivered to their respective destinations while preventing
the exhaust gases from backfeeding and damaging the components of the air injection system.
AIR CONTROL VALVE
The air control valve directs air to either the exhaust port, main converter, or the relief air silencer.
ANTI-AFTERBURN VALVE
The anti-afterburn valve is a vacuum operated valve that supplies air to the intake manifold during deceleration to prevent afterburn.
SOLENOID SWITCHING VALVE
The solenoid switching valve controls the operation of the switching valve section of the air control valve.
SOLENOID RELIEF VALVE
The solenoid relief valve controls the operation of the relief valve section of the air control valve.
HEAT HAZARD SENSOR
