Tribute 2WD V6-3.0L (2008)
precious metals. As the exhaust gases come in contact with the catalyst, they are changed into mostly harmless products. The catalyst initiates and speeds
up heat producing chemical reactions of the exhaust gas components so they are used up as much as possible.
Light Off Catalyst
As the catalyst heats up, converter efficiency rises rapidly. The point at which conversion efficiency exceeds 50% is called catalyst light off. For most
catalysts this point occurs at 246°C to 302°C (475°F to 575°F). A fast light catalyst is a 3-way catalyst (TWC) that is located as close to the exhaust
manifold as possible. Because the light off catalyst is located close to the exhaust manifold it lights off faster and reduces emissions more quickly than
the catalyst located under the body. Once the catalyst lights off, the catalyst quickly reaches the maximum conversion efficiency for that catalyst.
Three-Way Catalyst (TWC) Conversion Efficiency
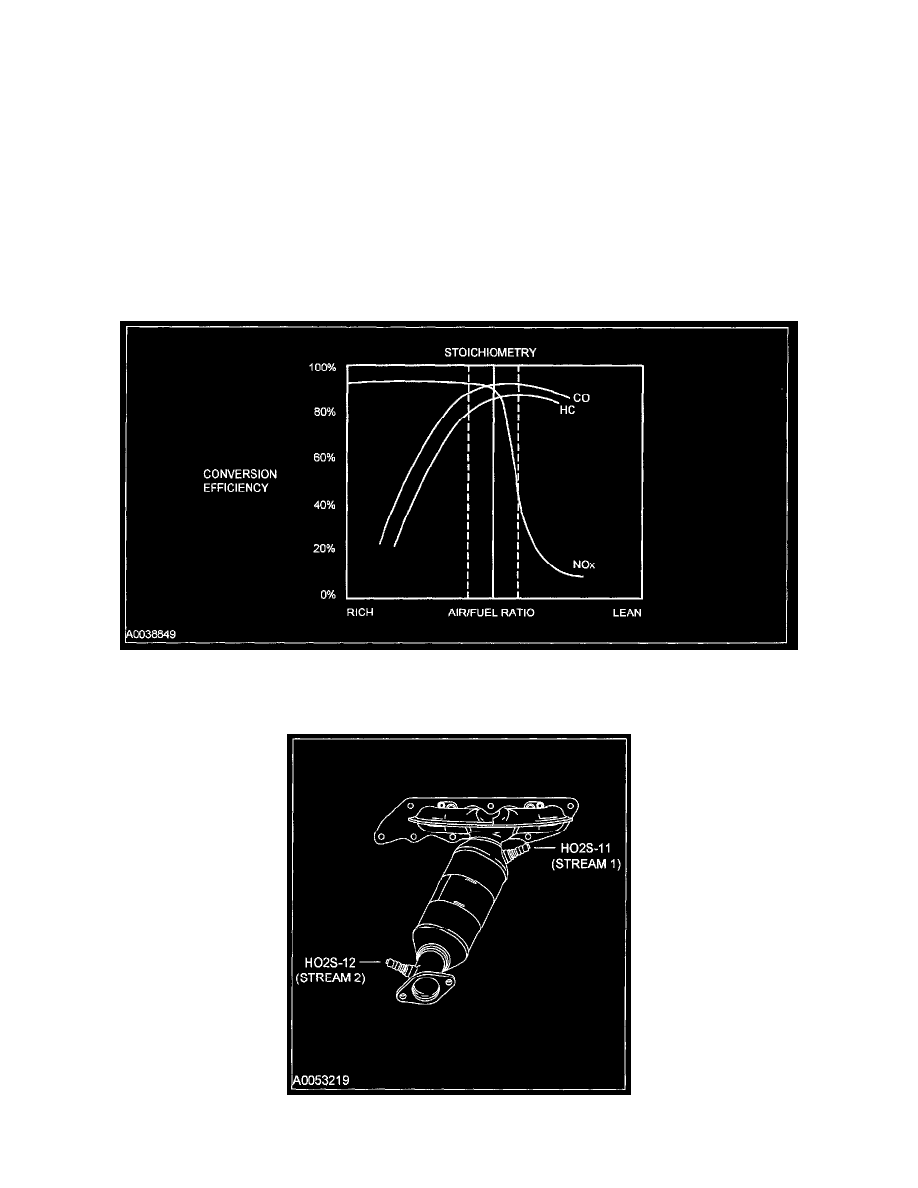
A TWC requires a stoichiometric fuel ratio, 14.7 pounds of air to 1 pound of fuel (14.7:1), for high conversion efficiency. In order to achieve these high
efficiencies, the air/fuel ratio must be tightly controlled with a narrow window of stoichiometry. Deviations outside of this window greatly decrease the
conversion efficiency. For example a rich mixture decreases the HC and CO conversion efficiency while a lean mixture decreases the NOx conversion
efficiency.
TWC Conversion Efficiency Chart
Exhaust System
Typical Bank 1 Catalyst 2 HO2S Configuration
