Mariner 4WD V6-3.0L (2010)
Yes
GO to Pinpoint Test H See: Headlamp/Testing and Inspection/Pinpoint Tests/Autolamps/Pinpoint Test H: The Autolamps Are On Continuously
No
For the high mounted stoplamp, GO to J2.
If only one side (the LH or RH rear stoplamp) is inoperative, GO to J6.
If both sides (LH and RH rear stoplamps) are inoperative, VERIFY the SJB fuse 6 (20A) is OK. If OK, GO to J4. If not OK, Refer to the Wiring
Diagrams to identify the possible causes of the circuit short. After the repair:
If no DTCs are present, TEST the system for normal operation. See: Diagrams/Electrical Diagrams/Diagrams By Number
If DTC B106E is present, CLEAR the DTCs and REPEAT the self-test (required to enable the stoplamp output driver if DTC B106E is present).
TEST the system for normal operation.
If DTC B106F is present, INSTALL a new SJB. REFER to Body Control Systems. TEST the system for normal operation.
-------------------------------------------------
J2 CHECK FOR VOLTAGE TO THE HIGH MOUNTED STOPLAMP
-
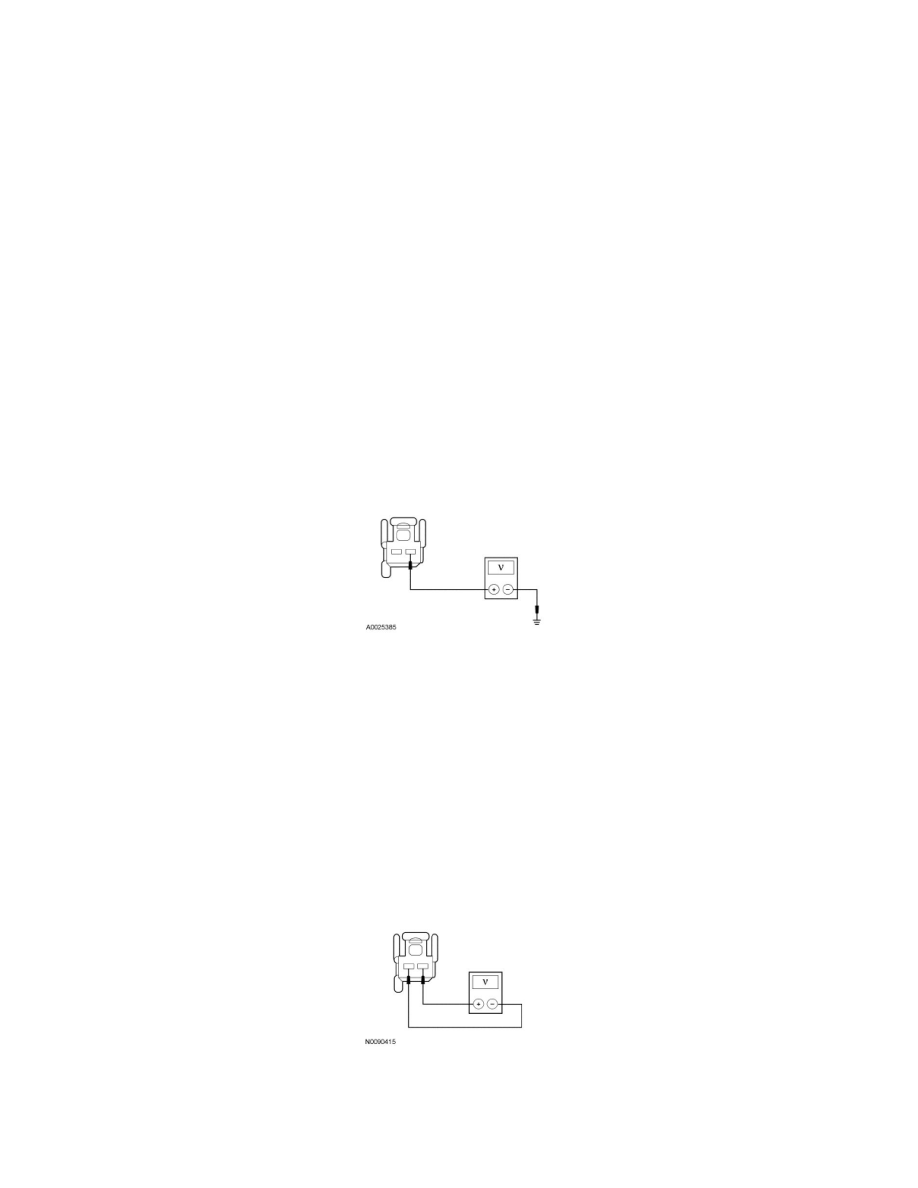
Disconnect: High Mounted Stoplamp C475.
-
While applying the brake pedal, measure the voltage between the high mounted stoplamp C475-1, circuit CCB08 (VT/GY), harness side and
ground.
-
Is the voltage greater than 10 volts?
Yes
GO to J3.
No
REPAIR CCB08 (VT/GY) for an open. TEST the system for normal operation.
-------------------------------------------------
J3 CHECK FOR VOLTAGE TO THE HIGH MOUNTED STOPLAMP USING THE CONNECTOR GROUND
-
While applying the brake pedal, measure the voltage between the high mounted stoplamp C475-1, circuit CCB08 (VT/GY), harness side and the
high mounted stoplamp C475-2, circuit GD149 (BK/GY), harness side.
-
Is the voltage greater than 10 volts?
Yes
INSTALL a new high mounted stoplamp. TEST the system for normal operation.
