Sable V6-232 3.8L (1988)
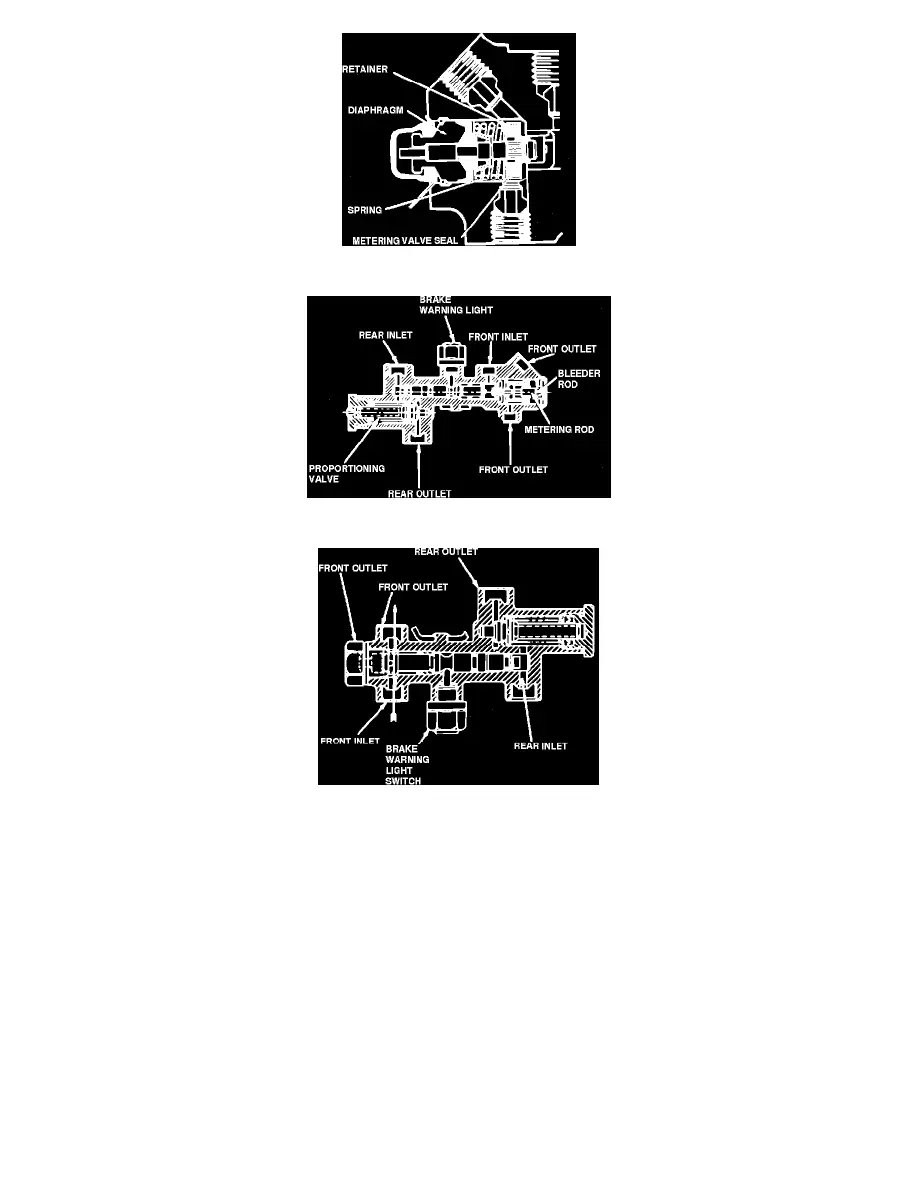
Fig. 10 Metering Valve, Initial Braking
Fig. 12 Three-way Combination Valve
Fig. 13 Two-way Combination Valve
Metering Valve
When the brakes are not applied, the metering valve permits the brake fluid to flow through the valve, thus allowing the fluid to expand and contract with
temperature changes.
When the brakes are initially applied, the metering valve stem moves to the left, preventing fluid to flow through the valve to the front disc brakes. This
is accomplished by the smooth end of the metering valve stem contacting the metering valve seal lip at 4 to 30 PSI, Fig. 10. The metering valve spring
holds the retainer against the seal until a predetermined pressure is produced at the valve inlet port which overcomes the spring pressure and permits
hydraulic pressure to actuate the front disc brakes, Fig. 11. The increased pressure into the valve is metered through the valve seal, to the front disc
brakes, producing an increased force on the diaphragm. The diaphragm then pulls the pin, in turn pulling the retainer and reduces the spring pressure on
the metering valve seal. Eventually, the pressure reaches a point at which the spring is pulled away by the diaphragm pin and retainer, leaving the
metering valve unrestricted, permitting full pressure to pass through the metering valve.
On some late model applications, either two-way or three-way combination valves are used. The three-way combination valve consists of a metering
valve, failure warning switch and a proportioner mounted in an aluminum body, Fig. 12. The two-way combination valve, Fig. 13, consists of a failure
warning switch and a proportioner. On models equipped with metering valves, the metering valve release rod must be pushed in during brake bleeding
operations on the front wheels.
