Eclipse L4-1997cc 2.0L DOHC (1991)
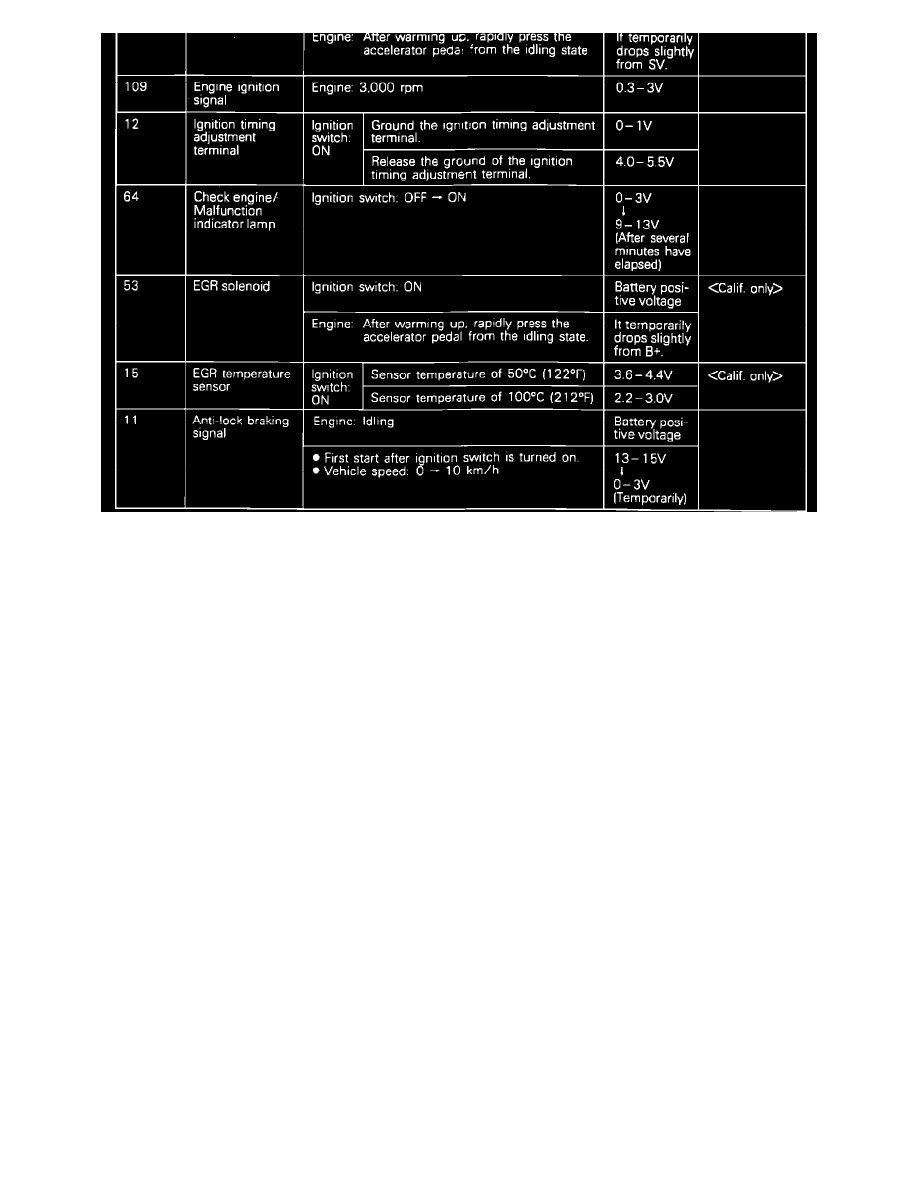
ECU Terminal Voltage Chart
NOTE: Before replacing a ECU that is found to be faulty, insure that no other condition exists that will damage the new unit. This can be best done
by testing the inputs and outputs to the ECU for over Voltage/inappropriate power readings or grounds. Use the image in the individual component
testing procedures to identify the correct readings for each pin.
Check all pins (at the harness with the ECU removed) that supply a signal to the ECU, for their correct readings and check all other pins to insure
that there are no uncalled for Voltage readings or grounds present.
3.
Compare all the remaining codes to the following list and perform the required inspections called for in each of the categories that are affected by a
code.
Check power supply for:
1. Faulty battery.
2. Faulty fusible link.
3. Faulty fuse.
4. Check for faulty body ground.
Check Fuel supply for:
1. Damaged fuel line.
2. Clogged or damaged fuel filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump.
Check ignition system for:
1. Faulty spark plugs.
2. Faulty ignition wiring.
3. Faulty distributor.
4. Faulty ignition coil.
Check emission control system for:
1. Faulty PCV system.
2. Faulty EGR system.
3. Vacuum leak.
4. Ignition timing and idle speed.
All categories:
ECU system faults are often caused by poor harness contact, therefore check that all of the connectors in all of the affected systems are secure and
have continuity.
4.
After completing all of the system inspections required in step 3, proceed to the ECU Codes and refer to "Check item (Remedy) column" of the
images supplied with "extracting fault codes".
