Expo AWD L4-2350cc 2.4L SOHC 8 Valve (1992)
283.9-284.1 mm (11.177-11.185 in.) (4G63)
289.9-290.1 mm (11.413-11.421 in.) (4G64)
4. Check cylinder walls for scratches and seizure. If defects are evident, correct (rebore to an oversize) or replace.
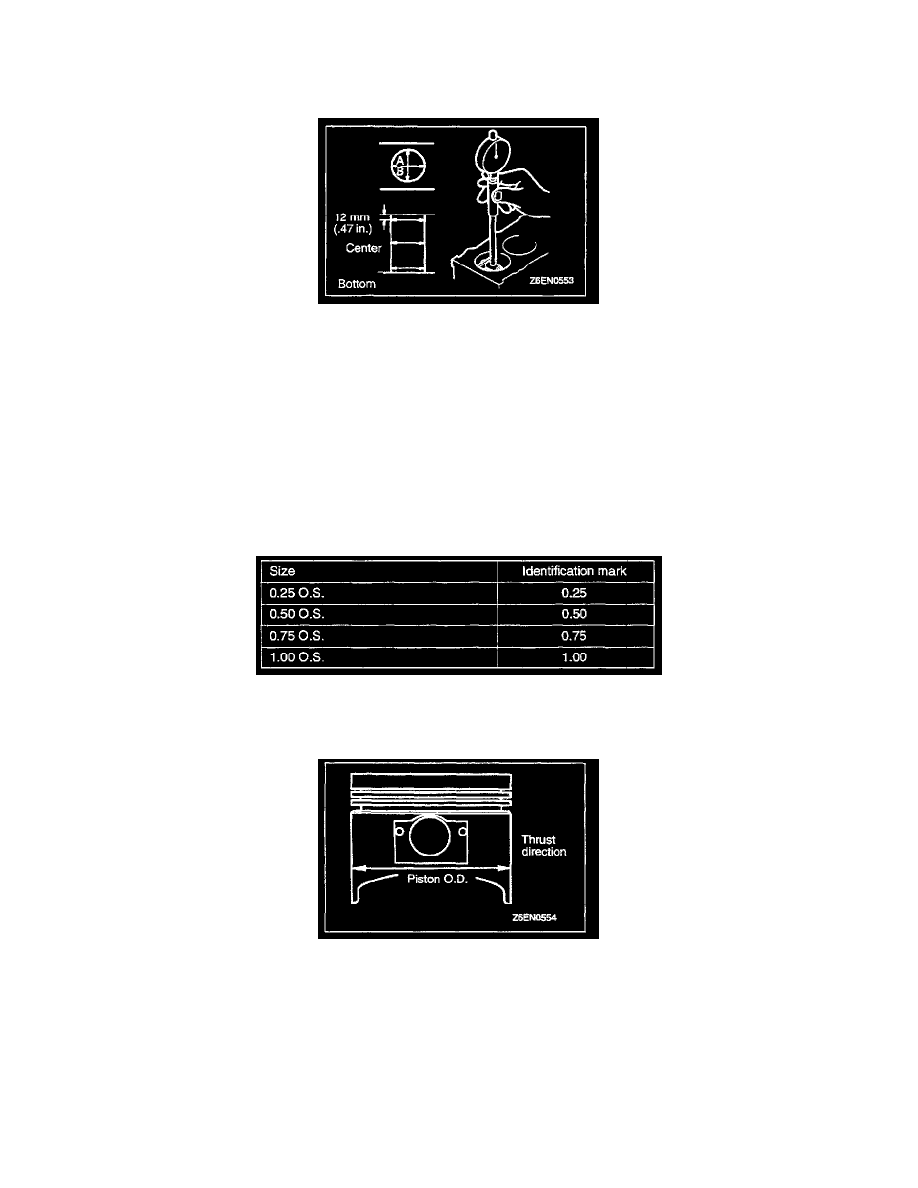
5. Using a cylinder gauge, measure the cylinder bore and cylindricity. If worn badly, correct the cylinder to an oversize and replace the piston and
piston rings. Measure at the points shown in illustration.
Standard value:
Cylinder l.D.
82.3 mm (3.24 in.) (4G61)
85.0 mm (3.35 in.) (4G63)
86.5 mm (3.41 in.) (4G64)
Cylindricity 0.01 mm (0.0004 in.)
BORING CYLINDER
1. Oversize pistons to be used should be determined on the basis of the largest bore cylinder.
Piston size identification
NOTE: Size mark is stamped on the piston top.
2. Measure outside diameter of piston to be used. Measure it in thrust direction as shown.
3. Based on the measured piston O.D. calculate the boring finish dimension.
Boring finish dimension = Piston O.D. + (clearance between piston O.D. and cylinder) - 0.02 mm (0.0008 in.) (honing margin)
4. Bore all cylinders to the calculated boring finish dimension.
CAUTION: To prevent distortion that may result from temperature rise during honing, bore cylinders, working from No. 2 to No.4
to No.1 to No.3.
5. Hone to final finish dimension (piston O.D. + clearance between piston O.D. and cylinder).
