Lancer LS L4-2.0L SOHC (2002)
Electronic Brake Control Module: Description and Operation
Electronic Control Unit
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
-
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is integrated with the hydraulic unit. This makes it unnecessary to have drive signal harnesses for the solenoid
valves pump motor, thus providing improved reliability.
-
The ABS-ECU is equipped with a diagnostic function and a memory that a problem has occurred, it causes the fail-safe function to operate and the
ABS warning light to illuminate.
-
The ABS-ECU detects the vehicle speed by means of signals from the wheel speed sensors in order to determine the vehicle driving condition, and
also predicts if any of the wheels are about to slip based on a set logic. It then outputs signals to operate the solenoid valves inside the hydraulic
unit in order to help prevent any of the wheels from locking up.
-
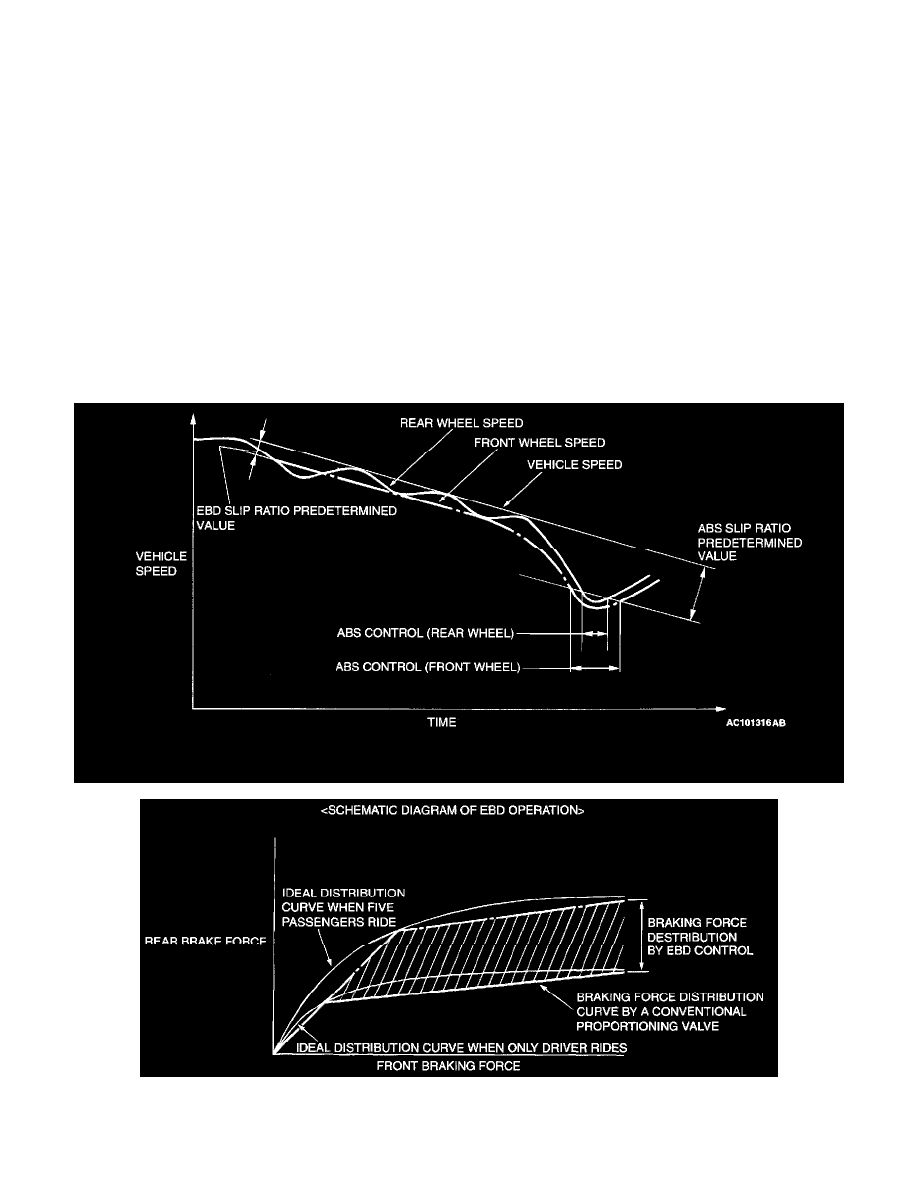
Electronic Brake-force Distribution system (EBD) control has been added to provide the ideal braking force for the rear wheels.
BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE CONTROL
ABS CONTROL CYCLE
This is basically the same as for the MIRAGE.
CONTROLLING VEHICLE SPEED
The ABS can operate when the vehicle speed is approximately 10 km/h (6 mph) or higher.
EBD HYDRAULIC PRESSURE CONTROL
The EBD control operates at the low slip region where the ABS does not operate.
The EBD control calculates the vehicle deceleration and the slip amount of front/rear wheels based on the wheel speed sensor signal. When the
difference between the rear wheel speed and the vehicle speed exceeds the set value, the solenoid valve for the rear wheel in the hydraulic unit is
