Montero 4WD L4-2555cc 2.6L SOHC (1984)
Exhaust Gas Recirculation: Testing and Inspection
1.
Check the vacuum hose routing and installation.
2.
Cold start and run the engine at idle speed.
3.
Check to ensure that increasing engine rpm (idle to 2,500 rpm) does not cause the secondary EGR valve to operate. If the secondary EGR valve
operates replace the thermo valve.
4.
Warm up the engine until the coolant temperature exceeds 55 degrees C or 131 degrees F.
5.
Check to ensure that when engine speed is increased as described in step 3 the secondary valve operates. If it does not operate inspect the EGR
control valve and the thermo valve.
6.
Disconnect the green striped hose from the thermo valve.
7.
Connect a vacuum pump to the thermo valve and apply vacuum. If it is impossible to achieve a vacuum the thermo valve is good.
8.
Disconnect the green striped hose from the nipple of the carburetor.
9.
Connect a vacuum pump to the green striped hose.
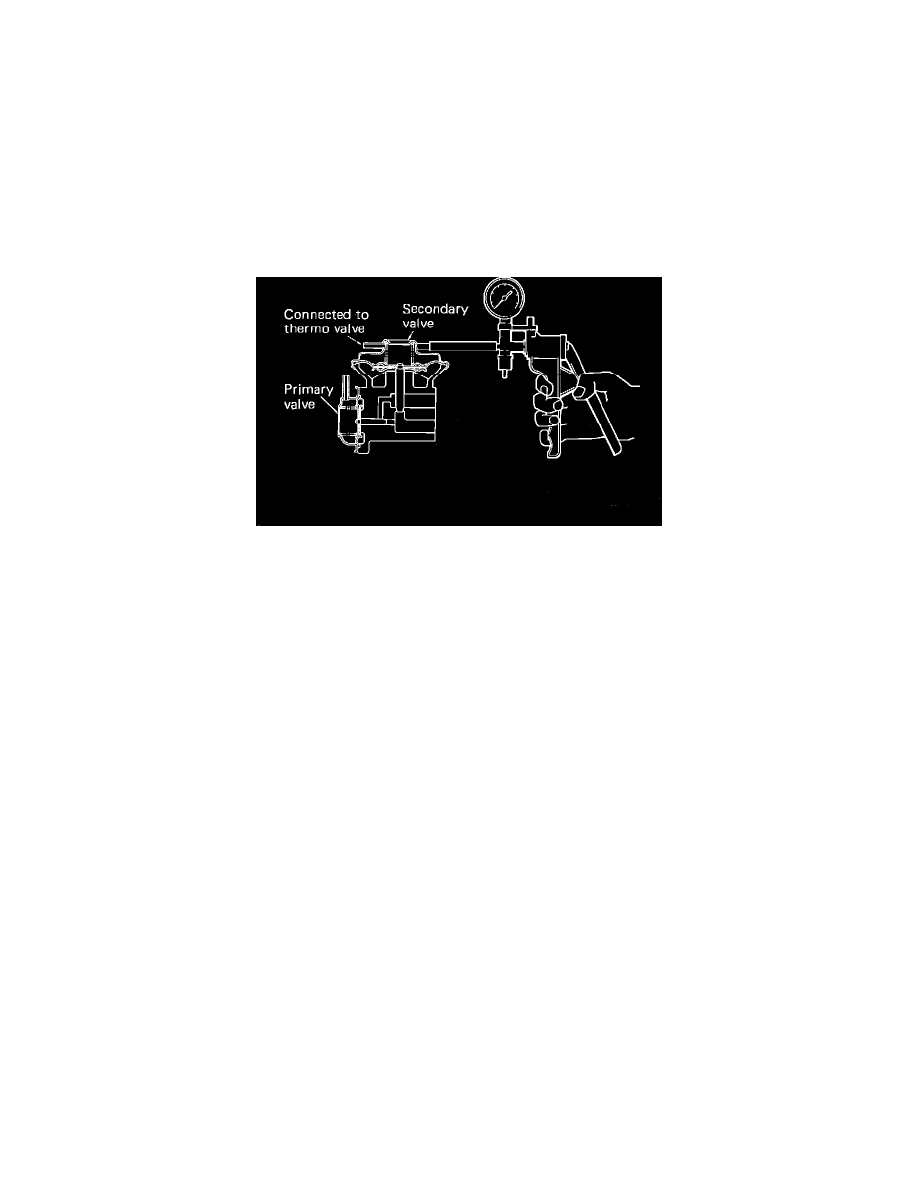
Fig. 25 Dual EGR valve
10. While opening the sub EGR valve by pulling it by hand and apply 20 kPa (5.9 in. Hg) vacuum with the vacuum pump, Fig. 25.
11. If the idling speed becomes unstable the secondary valve is operating properly. If the idling speed remains unchanged, the valve is not operating.
Replace the EGR valve.
SUB EGR VALVE
1.
Check to ensure that when the sub EGR valve is pulled by hand it moves smoothly. If the valve is hard to move, remove the sub EGR valve and
check it for carbon deposits and sticking. If necessary clean with a solvent and apply a slight amount of oil. If the valve is still hard to move,
replace it.
