Pickup 2WD L4-155 2555cc 2.6L SOHC VIN E 2-bbl (1988)
Deceleration Valve: Description and Operation
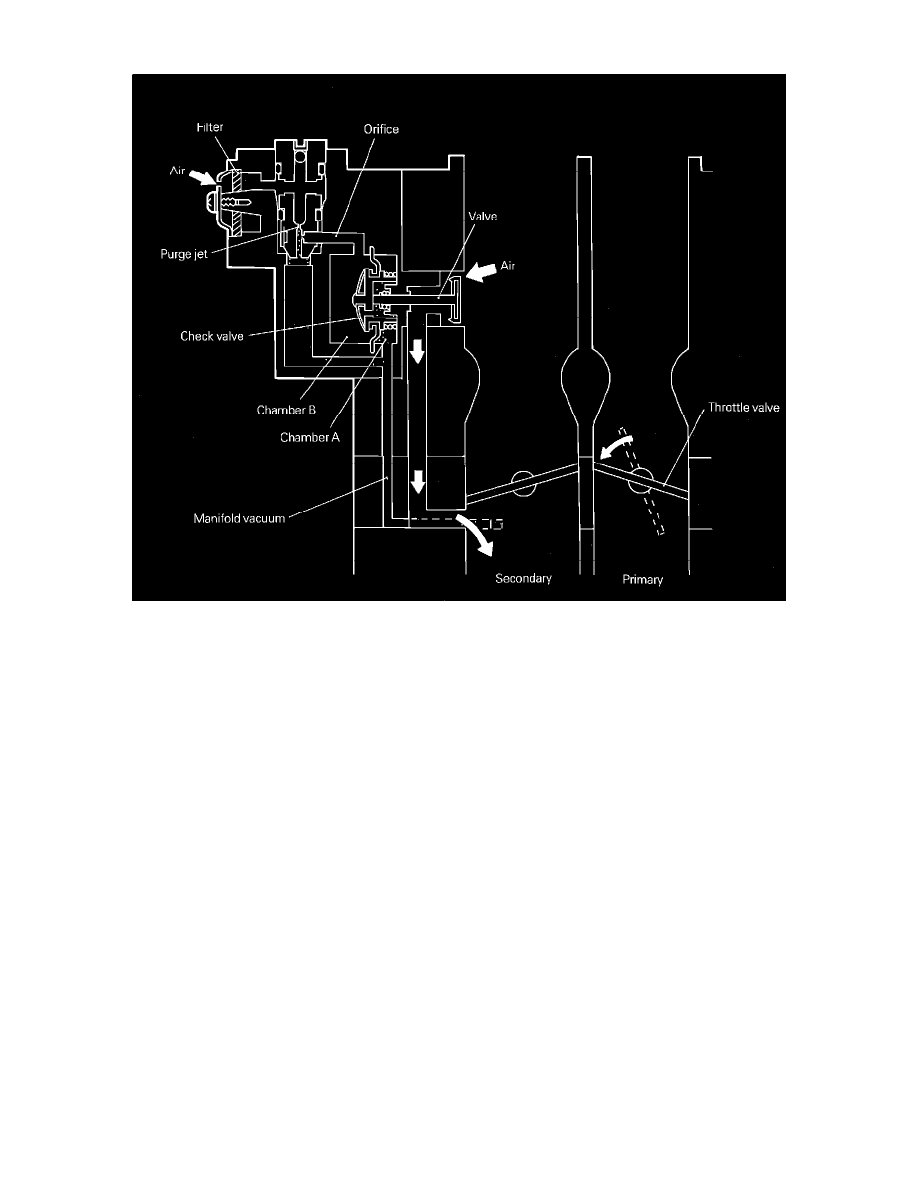
Fig. 106 Mixture control valve (MCV)
MIXTURE CONTROL VALVE
When the throttle is closed suddenly during deceleration or shifting, fuel residue remaining in the intake manifold causes an over-rich mixture
temporarily.
To prevent this momentary over-rich condition air is supplied temporarily from another passage by the mixture control valve, Fig. 106 to maintain
correct fuel/air ratio and reduce HC emissions.
OPERATION
When the throttle is closed suddenly manifold vacuum increases sharply. The increased manifold vacuum acts on the A chamber of the MCV to open the
valve supplying air to the intake manifold. Vacuum is also supplied to chamber B but with some delay due to the restriction caused by the orifice. When
the vacuum is supplied to both chambers A and B, pressure across the diaphragm is equal and spring force closes the valve halting the flow of air.
The check valve located at the diaphragm prevents high vacuum from remaining in chamber B when the engine is repeatedly accelerated and
decelerated.
