Pickup 2WD L4-2.3L DSL Turbo (1984)
through the valve is proportional to the valve opening which in turn is a function of the amount of vacuum applied to the EGR valve. The valve is open at
closed throttle and closed at wide open throttle.
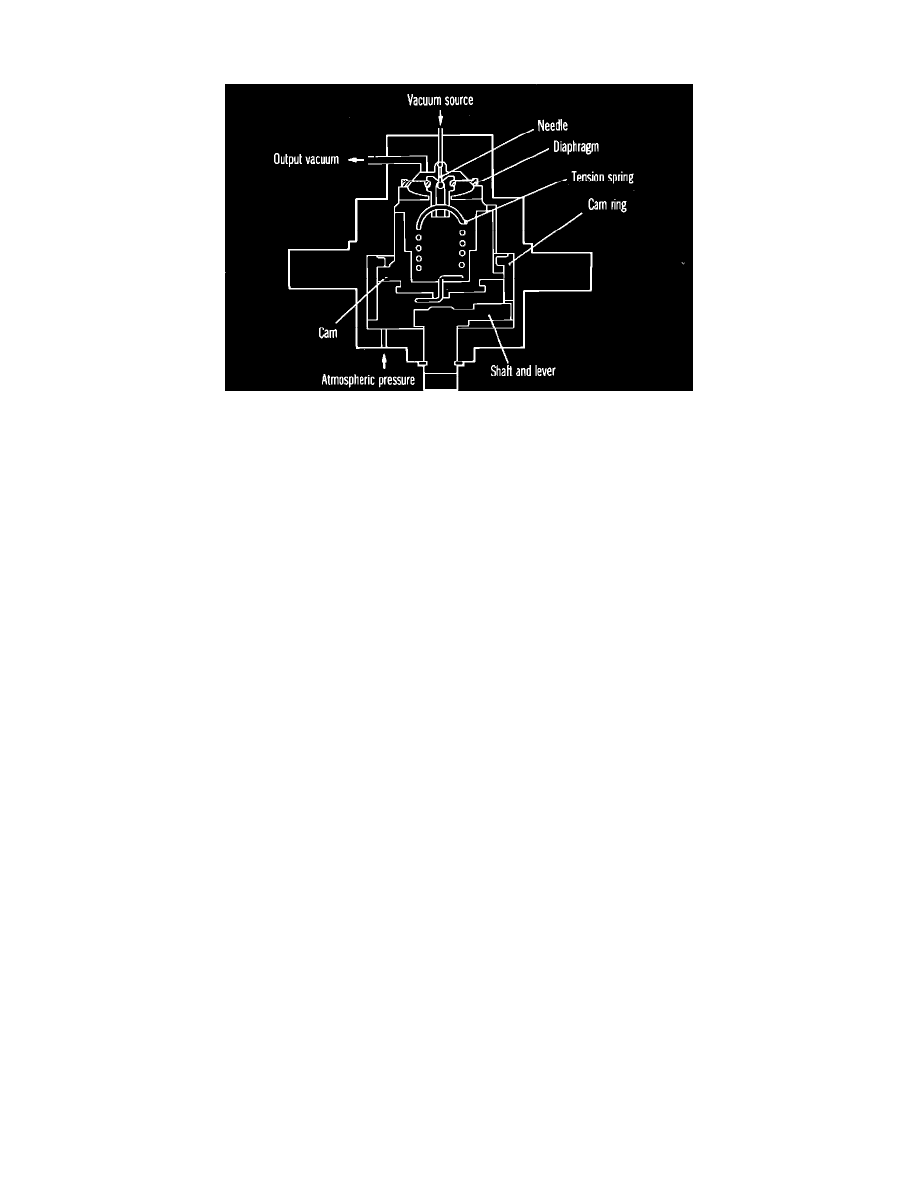
Fig. 42 Vacuum regulator valve
At intermediate throttle positions, EGR valve position is proportional to throttle position. Throttle position or movement is transferred to a vacuum
regulator valve, Fig. 42 mounted on the throttle shaft on the injection pump. The vacuum regulator valve then generates a vacuum signal proportional to
control lever travel.
The EGR system consists of an EGR control valve, EGR control solenoid valve, EGR vacuum reducer solenoid valve, vacuum regulator valve, EGR
control unit, coolant temperature sensor, accelerator switch, and engine speed sensor.
The EGR control unit monitors coolant temperature and engine speed to determine if the EGR control unit should generate an output signal to open the
EGR valve under the current engine operating conditions.
The EGR control unit de-energizes the EGR control solenoid during warm-up when less NOx is generated. When the solenoid valve closes the vacuum
signal to the EGR valve is removed allowing the valve to close. Less EGR during warm-up helps maintain acceptable driveability. The EGR control unit
also de-energizes the EGR solenoid valve during high and low engine speed operation to maintain acceptable driveability.
An accelerator switch energizes the EGR vacuum reducer solenoid valve when the throttle is open wider than a pre-set amount to improve driveablity or
when operating at high altitude to reduce smoking.
