Pickup 2WD L4-2350cc 2.4L SOHC 8 Valve (1996)
Suspension Strut / Shock Absorber: Technical Service Bulletins
Suspension - Shock Absorber Leakage Inspection
No: TSB-10-33-001
DATE: January, 2010
MODEL: All Models
SUBJECT:
INSPECTION CRITERIA FOR LEAKING SHOCK ABSORBERS
PURPOSE
This TSB provides instructions for shock absorber inspection, and criteria for determining oil leak severity to help dealers judge whether a shock
absorber requires replacement.
AFFECTED VEHICLES
All Models
DESCRIPTION
When inspecting shock absorbers, oil seen on the surface is not always an indication of a seal failure requiring shock replacement.
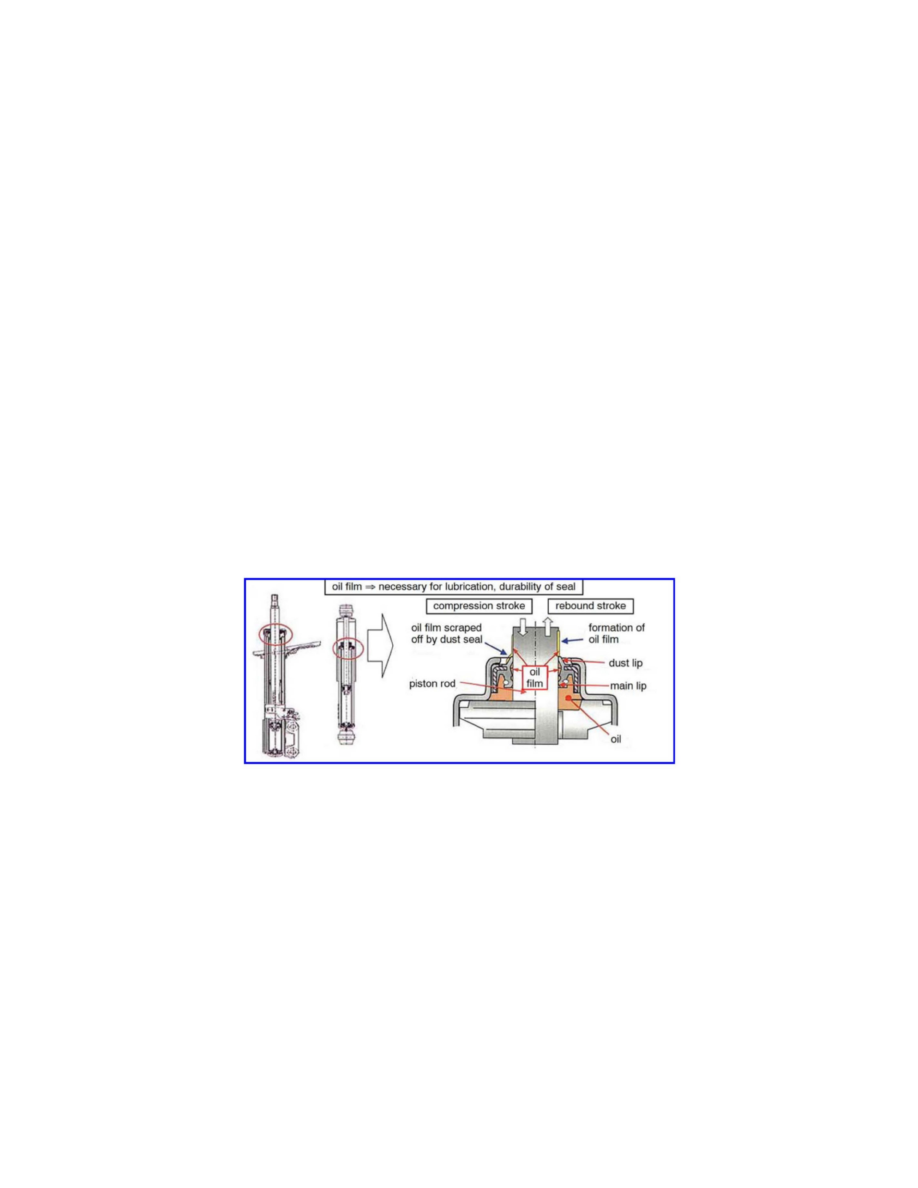
Shock absorber seals perform 3 functions:
1. seal the shock absorber oil inside the cylinder.
2. prevent dust entering the cylinder.
3. spread an even film of oil to lubricate the piston rod and seal.
Shock absorbers lose a small amount of oil during use and this is considered normal. As the piston rod travels through compression and rebound strokes
during shock absorber operation, a film of oil adheres to its surface, bypassing the seal. This helps lubricate and extend the life of the seal. During
compression of the shock, oil is scraped off the piston rod by the seal's dust lip and accumulates on the outer surface of the shock. This small amount of
oil does not always indicate a defective shock absorber.
PROCEDURE
SHOCK ABSORBER VISUAL INSPECTION FLOWCHART
Use the Shock Absorber Visual Inspection Flowchart when inspecting shock absorbers. If there is oil visible on the shock's surface, use the Oil Leak
Severity Guidelines to determine the extent of the leak, and proceed according to comments in the Remarks column.
SHOCK ABSORBER VISUAL INSPECTION FLOWCHART
