Aurora V8-4.0L VIN C (1996)
Voltage Signal: Description and Operation
PCM Control Messages
LOW ENGINE COOLANT
General Description
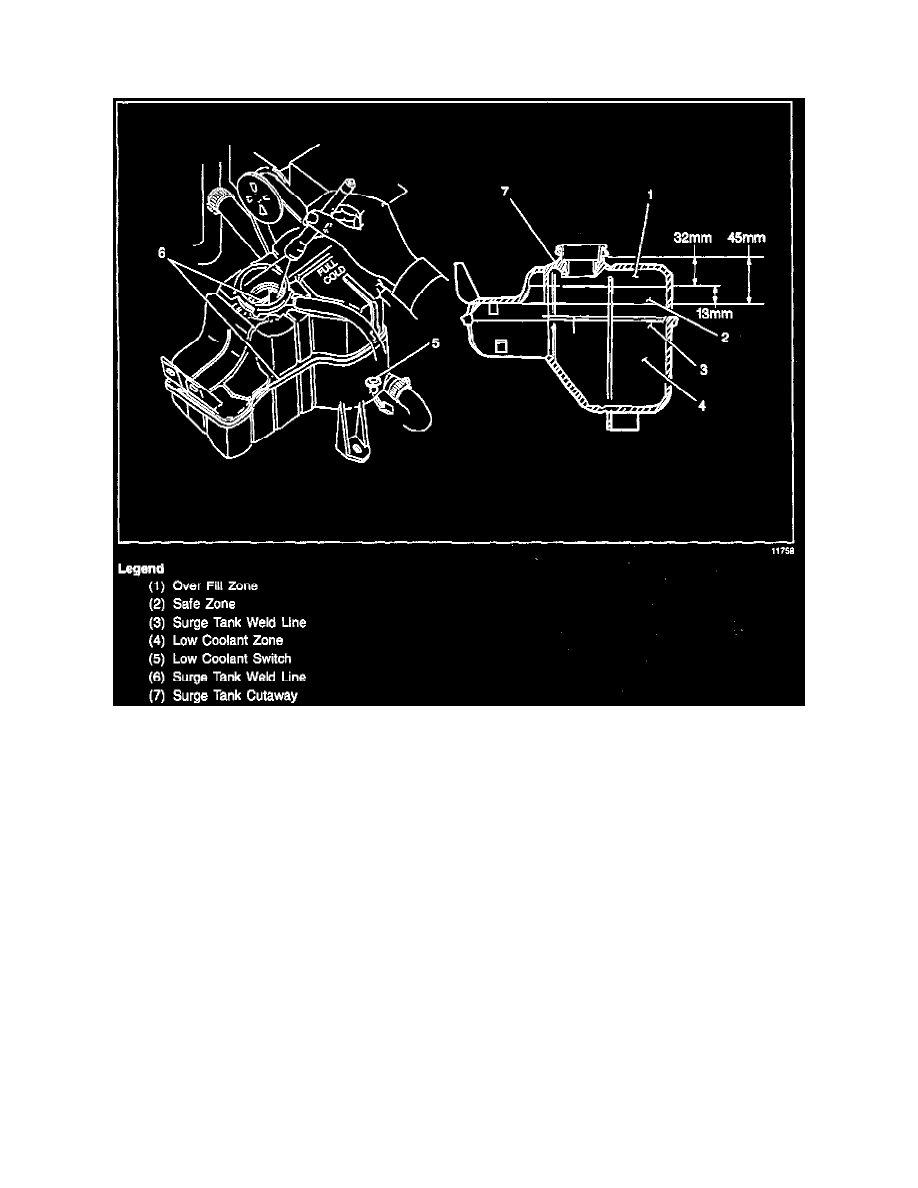
A plastic surge tank is connected to the cooling system with three hoses. As the car is driven, the coolant is heated and expands. Fluid displaced by
this expansion flows to the tank.
The tank is mounted at a point higher than all other coolant passages, thereby providing air bleed for the system. The coolant level in the radiator
surge tank should be maintained at or slightly above the weld line.
A coolant level float switch is located within the surge tank. When the coolant in the system falls below the recommended level (approximately 1
.5L), a message of low coolant level will be displayed on the IPC/DIC.
Operation
The coolant level switch senses the presence or absence of coolant in the pressurized coolant overflow bottle using a float. When the float is
suspended in coolant, the switch will be closed. When the float is not suspended in coolant, the switch will open, indicating low coolant level. The
PCM monitors the state of the coolant level switch through CKT 1478. When the coolant level switch is closed, CKT 1478 is at 0 volts, indicating
adequate coolant level. When the switch opens to indicate low coolant, CKT 1478 is open (12 volts).
OPTICAL OIL LEVEL
There are two messages associated with the Optical Engine Oil Level sensor. The Low Oil Level message is displayed when the system detects engine
oil level that is too low. The Oil Level Problem message indicates a circuit fault has been detected in the Optical Oil Level sensor system. The Optical
Oil Level sensor is located on the engine oil pan.
CHANGE ENGINE OIL MESSAGE
The CHANGE ENGINE OIL message is triggered by the Oil Life Left index. When the Oil Life Left index drops to 0%, the Change Engine Oil
