PB 150 V8-318 5.2L VIN T 2-BBL (1983)
Oxygen Sensor: Description and Operation
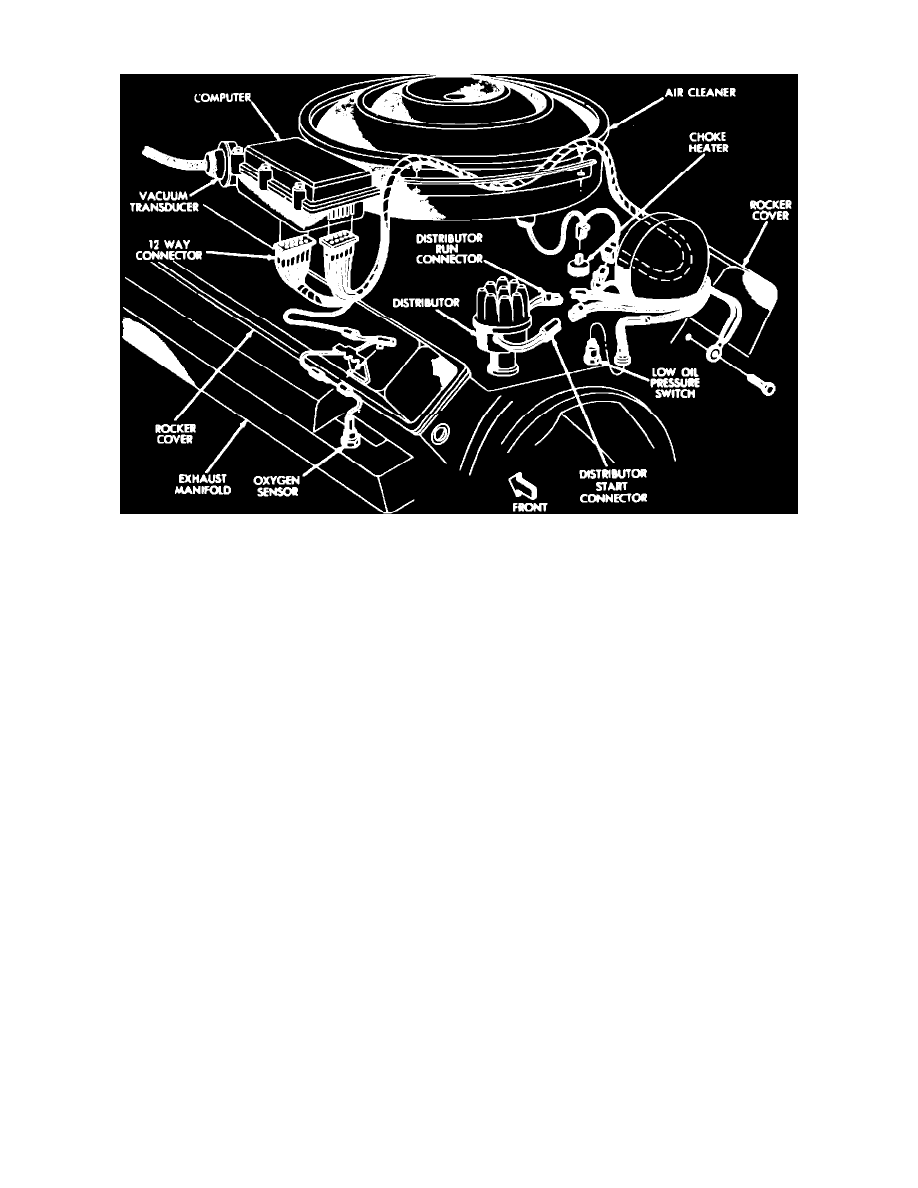
Fig. 7 Spark control computer & vacuum transducer location. V8 engine
To provide the EFC system with an indication of the exhaust gas composition, an oxygen sensor is threaded into the exhaust manifold and is exposed
directly to exhaust gas stream, Fig. 7.
The sensor is sensitive to the presence of or lack of oxygen. With an oxygen deficiency in the exhaust gas, outside oxygen diffuses through the sensor,
acting as an electrolyte and generating a voltage.
The oxygen sensor is basically a galvanic battery consisting of a cylindrical electrolyte element of zirconium dioxide which is coated inside and out
with platinum. The outer platinum electrode is exposed to atmosphere, while the inner is exposed to the hot exhaust gases. A porous ceramic (spinel)
coating protects the platinum against damage.
When heated to operating temperature by the hot exhaust gases, the sensor generates a voltage. If the oxygen is high, a low voltage (below .45 volts)
will be produced. When the oxygen content is low (rich mixture), a high voltage (.45 to 1 volt) will be produced. This relationship between available
oxygen and sensor output voltage causes the sensor to function as a rich-lean switch. The sensor output voltage is used by the Feedback Carburetor
Controller to calculate and adjust the air-fuel mixture as needed for optimum catalytic converter operation.
The sensor's internal impedance, output voltage and time response are all functions of temperature. This temperature dependency is important during
cold starts and other low temperature operating modes.
