Prowler V6-3.5L VIN G (1999)
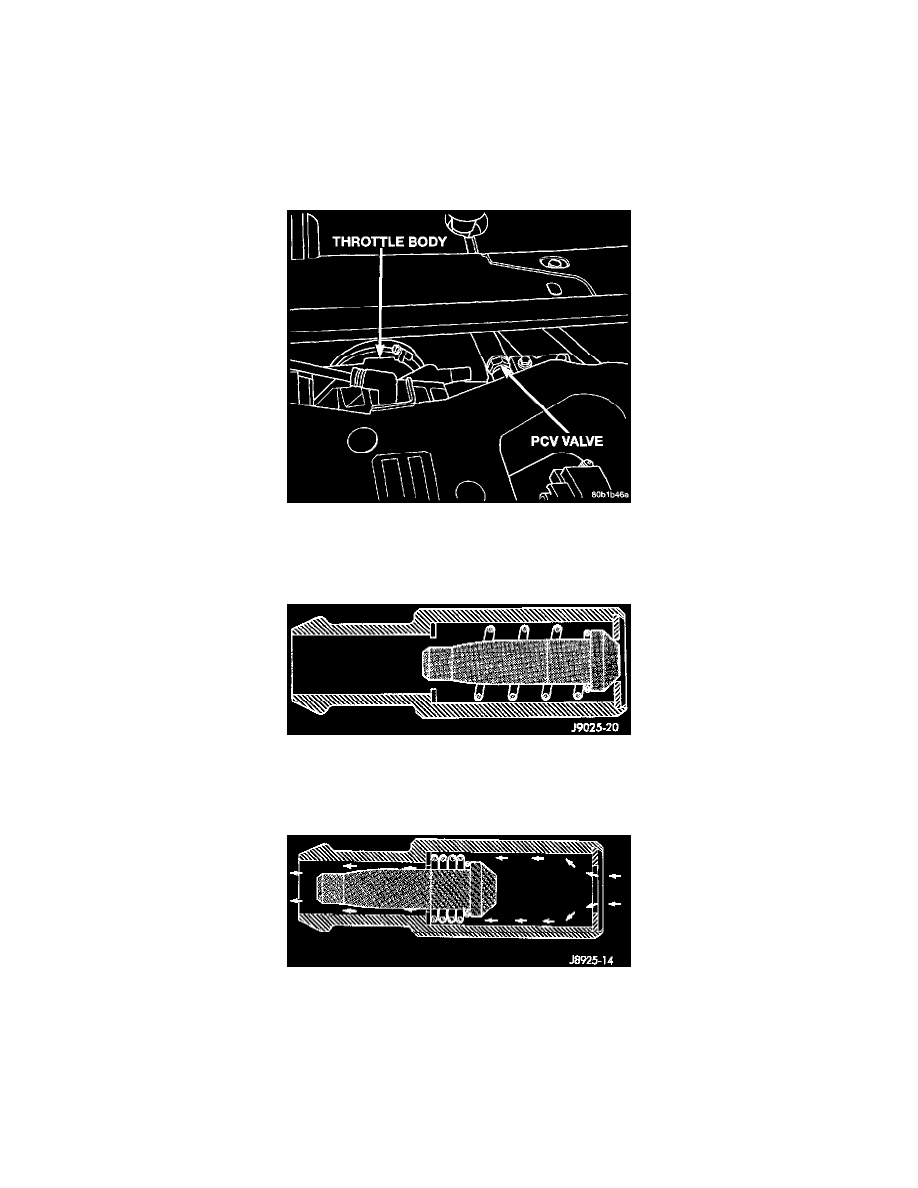
Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve: Description and Operation
PURPOSE
The purpose of the PCV system is to reduce Hydrocarbon (HC) and Carbon Monoxide (CO) emissions created by engine blow-by. Also the PCV
system is used to prevent sludge build up in crankcase
OPERATION
Intake manifold vacuum removes crankcase vapors and piston blow-by from the engine. Emissions pass through the PCV valve into the intake
manifold plenum. The vapors become part of the calibrated air-fuel mixture, are burned and expelled with the exhaust gases. The air cleaner
supplies make up air when the engine does not have enough vapor or blow-by gases.
1999 PCV Valve
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger. This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors routed into the combustion chamber based
on intake manifold vacuum.
Engine Off Or Engine Pop-Back - No Vapor Flow
When the engine is not operating or during an engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back against the seat. This will prevent vapors from
flowing through the valve.
High Intake Manifold Vacuum - Minimal Vapor Flow
During periods of high manifold vacuum, such as idle or cruising speeds, vacuum is sufficient to completely compress spring. It will then pull the
plunger to the top of the valve. In this position there is minimal vapor flow through the valve.
