Prowler V6-3.5L VIN G (1999)
Spark Plug: Testing and Inspection
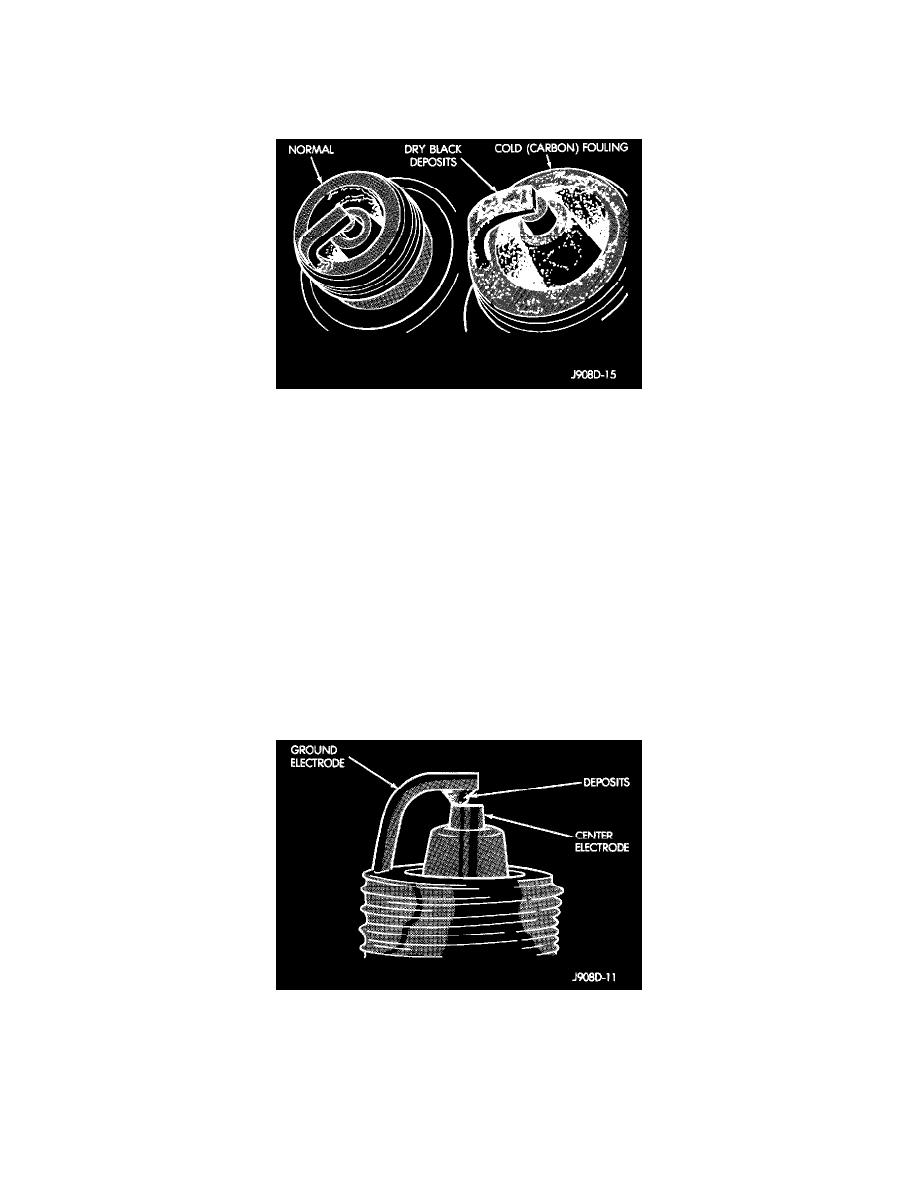
Cold or Carbon Fouling
COLD FOULING (CARBON FOULING)
Normal Operation And Cold(Carbon) Fouling
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon fouling because the deposits that cause cold fouling are basically carbon. A dry, black deposit on
one or two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves or misfire conditions. Cold (carbon) fouling of the entire set may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner or poor ignition output.
Cold fouling is normal after short operating periods. The spark plugs do not reach a high enough operating temperature during short operating
periods. Replace carbon fouled plugs with new spark plugs.
Combustion Deposits
COMBUSTION DEPOSITS
A shiny yellow glaze coating on the spark plug insulator is evidence of metallic by-products of fuel combustion, caused by chemical additives in
certain fuels. Avoid sudden acceleration with wide open throttle after long periods of low speed driving. Spark plugs with combustion deposits can
be cleaned and reused.
Electrode Gap Bridging
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Electrode Gap Bridging
Loose deposits in the combustion chamber can cause electrode gap bridging. The deposits accumulate on the spark plugs during continuous
stop-and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly subjected to a high torque load, the deposits partially liquefy and bridge the gap between the
electrodes. This short circuits the electrodes. Spark plugs with electrode gap bridging can be cleaned and reused.
Electrode Insulator
ELECTRODE INSULATOR
