Fiero V6-173 2.8L (1986)
Fuel System Diagnosis
CHART A-7 - FUEL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (PART 1 OF 4)
Circuit Description:
When the ignition switch is turned "ON," the Electronic Control Module (ECM) will turn "ON" the in-tank fuel pump. It will remain "ON" as long as the
engine is cranking or running, and the ECM is receiving reference pulses. If there are no reference pulses, the ECM will shut "OFF" the fuel pump within
2 seconds after ignition "ON" or engine stops.
^
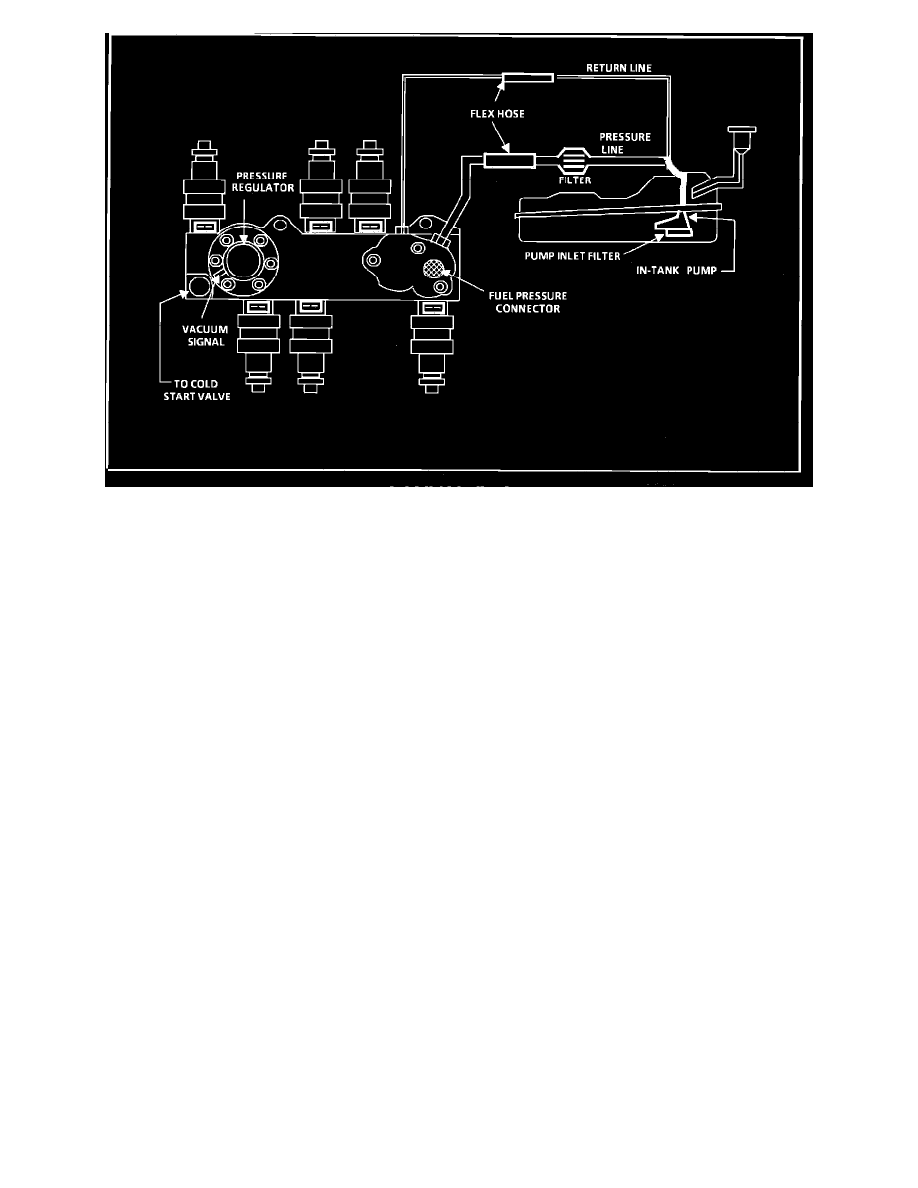
The pump will deliver fuel to the fuel rail and injectors, then to the pressure regulator, where the system pressure is controlled to about 234 to 325 kPa
(34 to 47 psi). Excess fuel is then returned to the fuel tank.
Test Description:
Numbers below refer to circled numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1.
Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure connector to absorb any small amount of fuel leakage that may occur when installing the gage. Ignition
"ON," pump pressure should be 280-325 kPa (40.5-47 psi). This pressure is controlled by spring pressure within the regulator assembly.
2.
When the engine is idling, the manifold pressure is low (high vacuum) and is applied to the fuel regulator diaphragm. This will offset the spring and
result in a lower fuel pressure. This idle pressure will vary somewhat depending on barometric pressure, however, the pressure idling should be less
indicating pressure regulator control.
3.
Pressure that continues to fall is caused by one of the following:
^
In-tank fuel pump check valve not holding
^
Pump coupling hose or pulsator leaking
^
Fuel pressure regulator valve leaking
^
Injector(s) sticking open
4.
An injector sticking open can best be determined by checking for a fouled or saturated spark plug(s). If a leaking injector can not be determined by
a fouled or saturated spark plug the following procedure should be used.
^
Remove Plenum, and fuel rail bolts, but leave fuel lines connected.
^
Lift fuel rail out just enough to leave injector nozzles in the ports.
