Grand AM V6-3100 3.1L MFI VIN M (1994)
Oxygen Sensor: Description and Operation
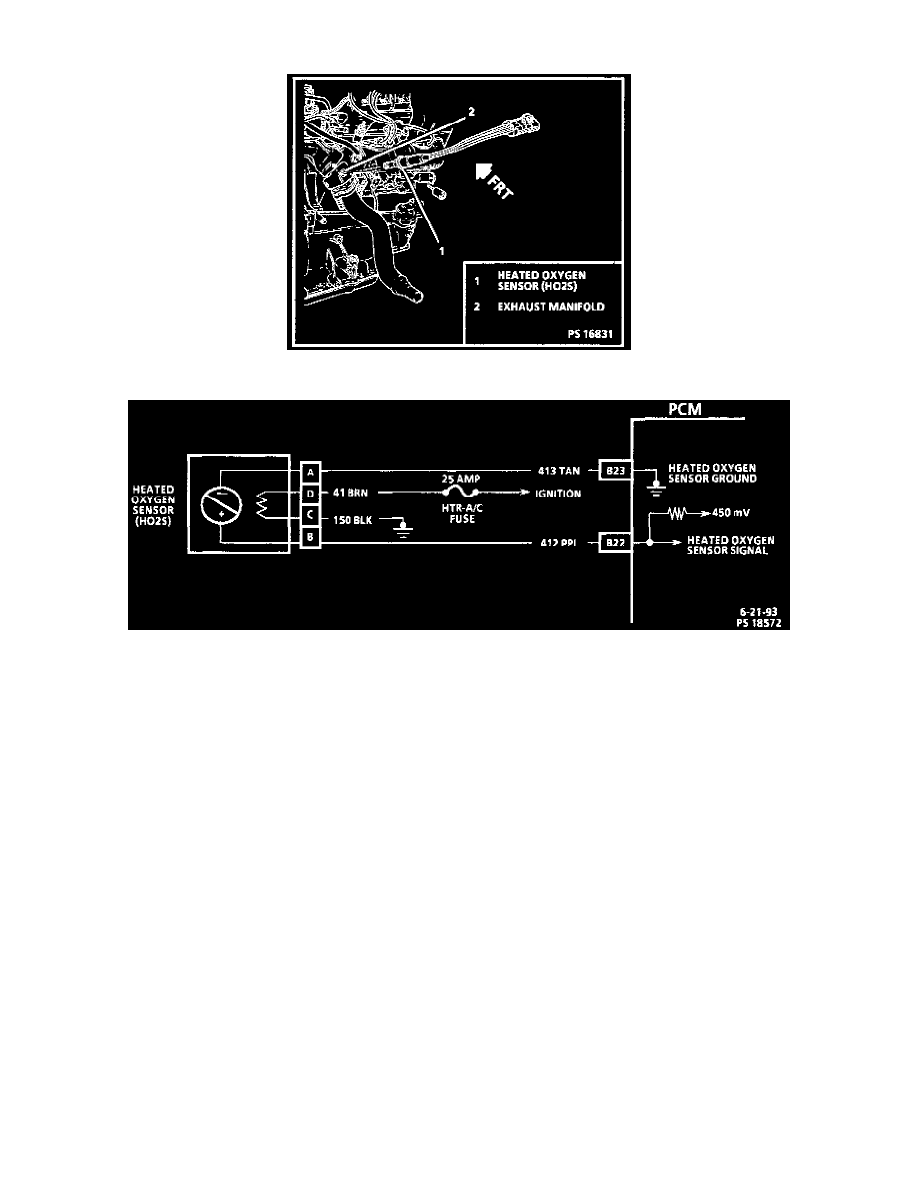
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Heated Oxygen Sensor Schematic
PURPOSE:
The Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) measures the oxygen content of the exhaust. The PCM monitors the sensor to maintain air/fuel mixture of
14.7 to 1.
OPERATION:
The HO2S monitors atmospheric air versus exhaust gas oxygen content to produce a voltage output. This voltage ranges from approximately 0.1
volt (high oxygen-lean mixture) to 0.9 volt (low oxygen-rich mixture). By monitoring the oxygen sensor output voltage, the computer can
determine the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas and adjust the air/fuel mixture accordingly, this is known as "CLOSED LOOP" operation.
When the sensor is cold it is like an open circuit and produces no voltage below 600°F (315°C). An open sensor circuit or cold sensor causes
"OPEN LOOP" operation.
Within the HO2S, B+ is supplied to a heating unit. This heater receives voltage from the generator charging circuit. The heater helps the PCM
control the fuel injection sooner for better fuel emissions.
An open Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) circuit should set a DTC 13. A constant low voltage in the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) circuit should
set a DTC 44.
CONSTRUCTION
The HO2S is constructed from a zirconia/platinum electrolytic element. Zirconia is an electrolyte that conducts electricity under certain chemical
conditions. The element is made of a ceramic material. The element is an insulator when cold. At operating temperature 315°C (600°F), the
element becomes a semiconductor.
A platinum coating on the outer surface of the element stimulates further combustion of the exhaust gases right at the surface and this helps
maintain a high operating temperature at the element.
