Grand Prix V6-204 3.4L DOHC VIN X SFI (1995)
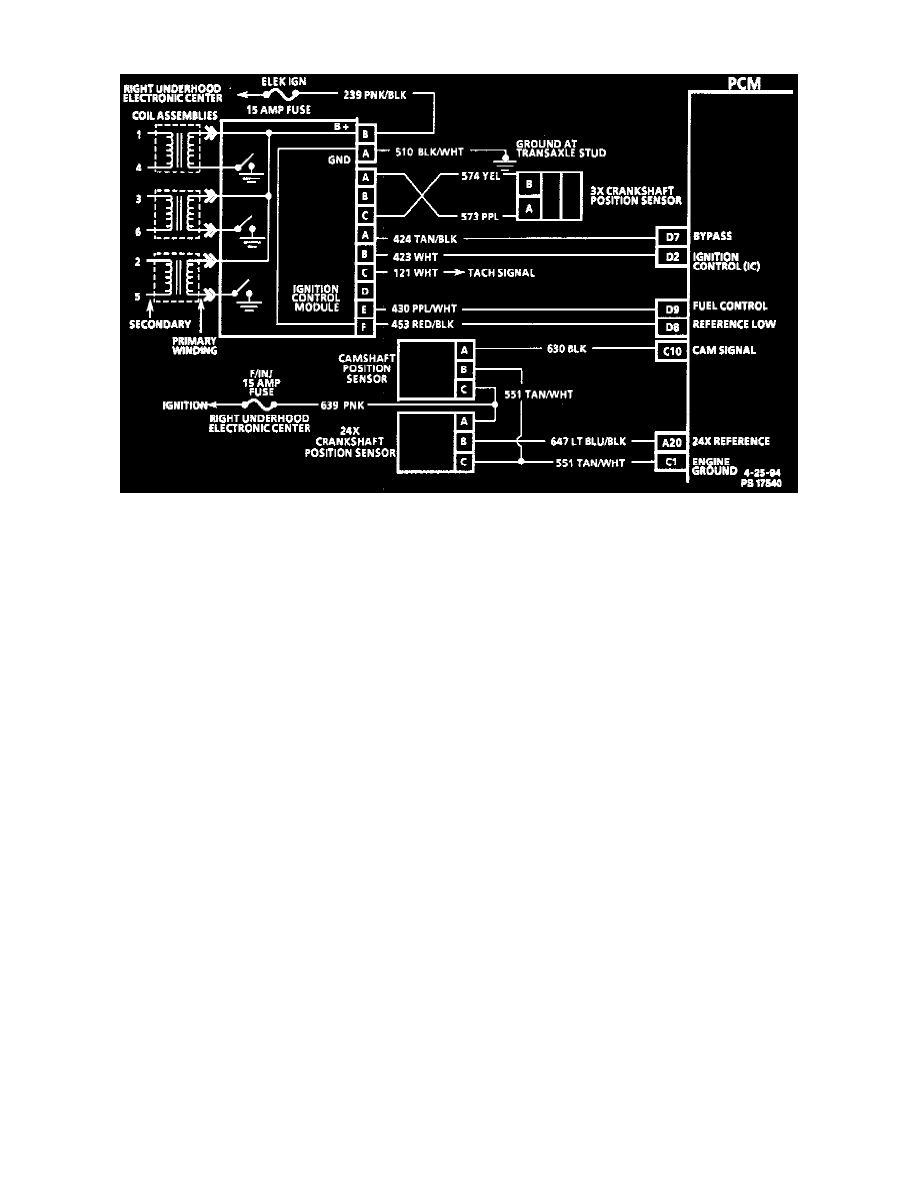
Ignition Control Module: Description and Operation
Ignition System
DESCRIPTION
The ignition control module performs several functions:
-
It determines the correct ignition coil wiring sequence, based on the sequence of 3X crankshaft position sensor pulses. This coil sequencing occurs
at start-up. After the engine is running, the module remembers the sequence, and continues triggering the ignition coils in proper sequence.
-
It determines whether or not the crankshaft is rotating in the proper direction, and cuts off fuel delivery and spark to prevent backfiring if reverse
rotation is detected.
-
It sends a "crankshaft reference" (fuel control) signal to the PCM. The PCM determines engine RPM from this signal. It is also used by the PCM
to determine crankshaft position for Ignition Control (IC) spark advance calculations. (The falling edge of each fuel control signal pulse occurs 70
before TDC of any cylinder:)
OPERATION
The fuel control signal sent to the PCM by the ignition module is an "ON-OFF" pulse occurring 3 times per crankshaft revolution (Figure C4-6).
This is not the 3X crank sensor pulse, but this is required before the ignition control module will generate the fuel control signal.
The ignition control module generates the fuel control signal based on the 3X crankshaft position sensor signal. If the crankshaft position sensor
signal is not present or the ignition control module cannot produce fuel control pulses for any reason, no fuel injector pulses will occur and the
engine will not start.
CRANKSHAFT REFERENCE GROUND (CKT 453)
This is a ground circuit for the digital RPM counter inside the PCM, but the wire is connected to engine ground ONLY through the ignition control
module. Although this circuit is electrically connected to the PCM, it is not connected to ground AT the PCM. The PCM compares voltage pulses
on the reference input CKT 430 to any on this circuit (453), ignoring pulses that appear on both. If the circuit is open, or connected to ground at
the PCM, it may cause poor engine performance and possibly a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) (Service Engine Soon) with no DTC.
FUEL CONTROL REFERENCE PCM INPUT (CKT 430)
From the ignition control module, the PCM uses this signal (CKT 430) to calculate engine RPM and crankshaft position. The PCM compares
pulses on this circuit to ground CKT 453. The PCM also uses the pulses on this circuit to initiate injector pulses. If the PCM receives no pulses on
this circuit, no fuel injection pulses will occur and the engine will not run.
