Vibe FWD L4-2.4L (2009)
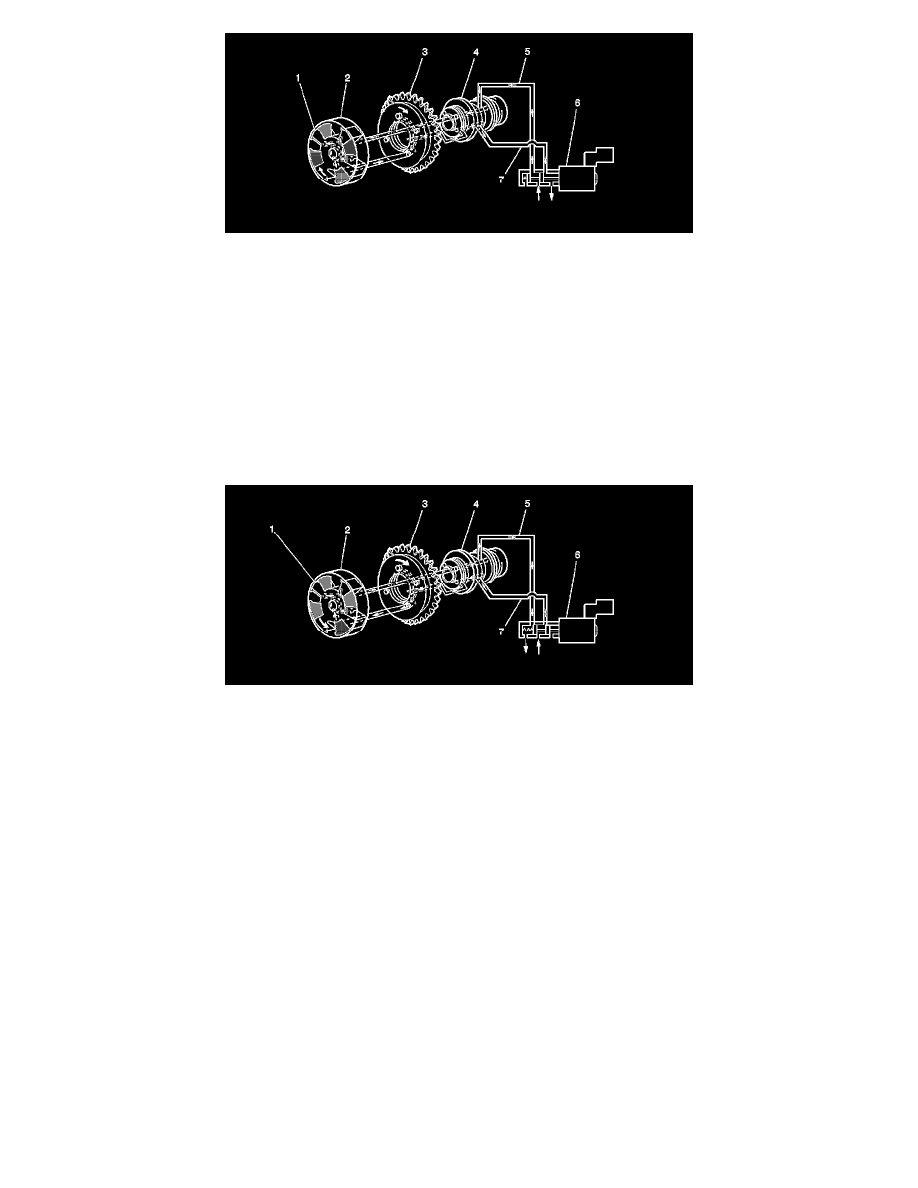
1 - Vane Wheel
2 - CMP Actuator Housing, part of CMP actuator assembly
3 - Intake Camshaft Gear, part of CMP actuator assembly
4 - Intake Camshaft
5 - Advance Side Oil Passage, applying pressure
6 - CMP Actuator Solenoid Valve
7 - Retard Side Oil Passage, relieving pressure
Oil flowing to the CMP actuator housing (2) from the CMP solenoid advance passage (5) applies pressure to the advance side of the vane wheel (1) in
the CMP actuator assembly. At the same time the CMP solenoid retard passage (7) is open, allowing oil pressure to decrease on the retard side of the
vane wheel. These two simultaneous actions cause the vane wheel (1) to rotate clockwise, advancing camshaft advance timing.
CMP Actuator System Retard
1 - Vane Wheel
2 - CMP Actuator Housing, part of CMP actuator assembly
3 - Intake Camshaft Gear, part of CMP actuator assembly
4 - Intake Camshaft
5 - Advance Side Oil Passage, relieving pressure
6 - CMP Actuator Solenoid Valve
7 - Retard Side Oil Passage, applying pressure
When the oil flowing to the CMP actuator housing (2) is from the CMP solenoid retard passage (7), oil pressure is applied to the retard side of the vane
wheel (1). Because the solenoid advance passage (5) is open, allowing oil pressure to decrease on the advance side of the vane wheel (1), the camshaft
position retards.
The PCM can also command the CMP actuator solenoid valve to stop oil flow from both passages in order to hold the current camshaft position. The
PCM is continuously comparing CMP sensor input with CKP sensor input in order to monitor camshaft position and detect any system malfunctions. The
following table provides camshaft phase commands for common driving conditions:
