Vibe FWD L4-2.4L (2009)
The 2.4L engine is equipped with a flat design non-resonant type KS. The non-resonant KS enables the powertrain control module (PCM) to adjust the
ignition timing in order to adapt to any of the variables that affect the optimal ignition timing.
Operation
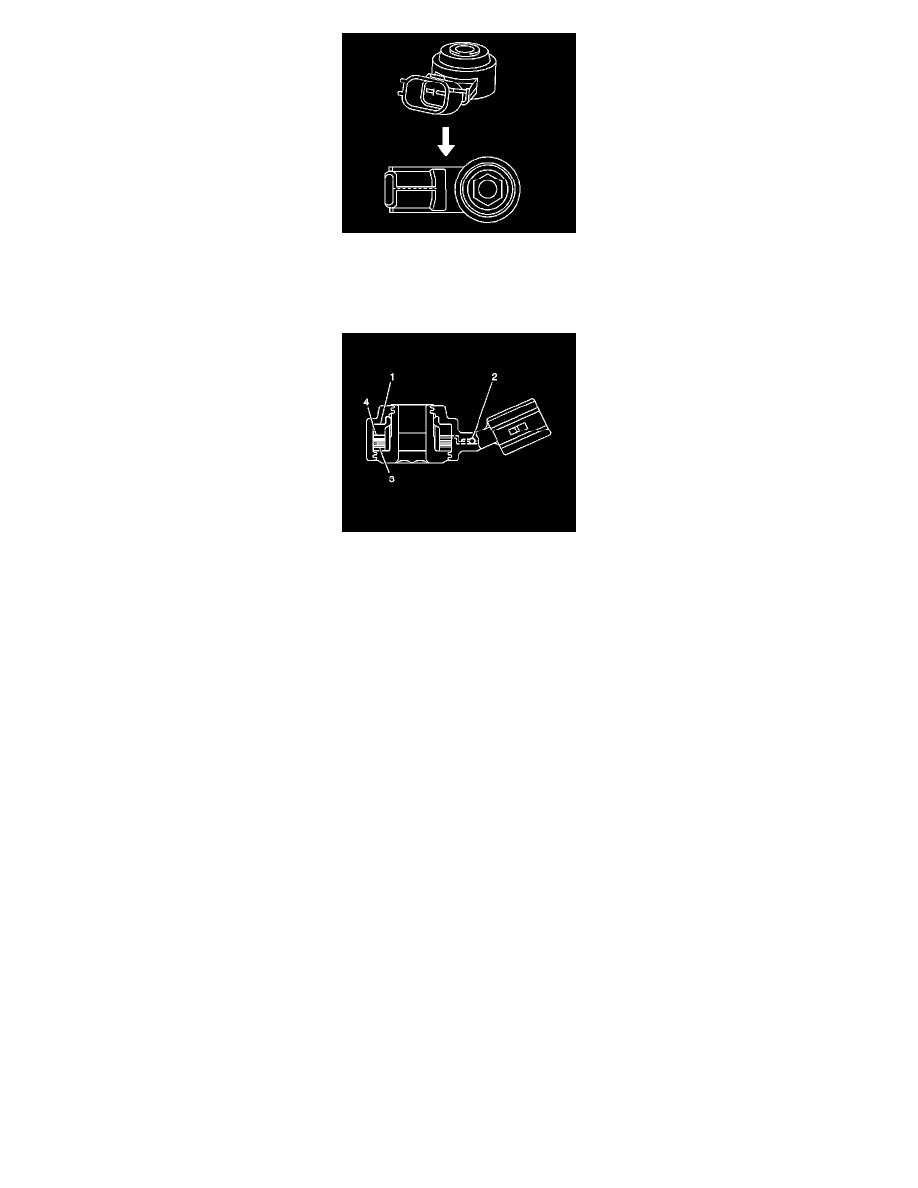
1 - Steel Weight
2 - Circuit Fault Detection Resistor
3 - Piezoelectric Element
4 - Insulator
The KS detects when the engine is experiencing detonation. The sensor then signals the PCM to reduce the spark advance until detonation is no longer
detected. A conventional resonant type KS uses a vibration plate that has the same resonance point as the expected knocking frequency of the engine.
The non-resonant type KS has a steel weight (1) with an insulator (4) separating the weight from a piezoelectric element (3). The vibration caused by
engine detonation is transferred to the weight, whose inertia applies pressure to the piezoelectric element. The weights action against the element,
generates an electromotive force that is modified and transmitted to the PCM. The non-resonant design sensor is able to detect detonation vibration over
a wide frequency band, from 6 kHz to 15kHz. In comparison, the resonant type KS detects only vibrations that are within a narrow frequency band.
In response to the KS signal the PCM retards the spark advance in order to reduce the detonation. The amount of timing retard that the PCM applies is
based on the engine speed and the length of time that the engine detonation is detected. Once the spark timing is retarded, the KS circuitry in the PCM
performs calculations in order to determine how much spark advance should be re-introduced. Normally the ignition timing advance is increased until
zero retard, or normal ignition timing, is re-established. If detonation occurs again, the whole cycle will repeat. The alteration of the ignition timing by
the KS often occurs continuously while the engine is running, even though no detonation is heard by the vehicle's operator.
Results of Faulty Knock Sensor Operation
Loss of the KS signal causes the PCM to operate in fail safe mode. In fail safe mode the PCM commands maximum spark retard. A KS that falsely
indicates detonation can cause the PCM to retard the ignition timing unnecessarily. Reduced spark advance can cause any of the following conditions:
*
Poor fuel economy
*
Sluggish engine performance
*
Higher exhaust emissions
A KS that fails to detect detonation can cause the PCM to control the ignition timing as if no detonation were occurring. Failure of the PCM to retard the
ignition timing when necessary could cause any of the following concerns:
*
An excessive engine detonation
*
Engine damage during heavy engine loads
*
Higher exhaust emissions
