9000 CSE L4-2290cc 2.3L DOHC Turbo EFI (1995)
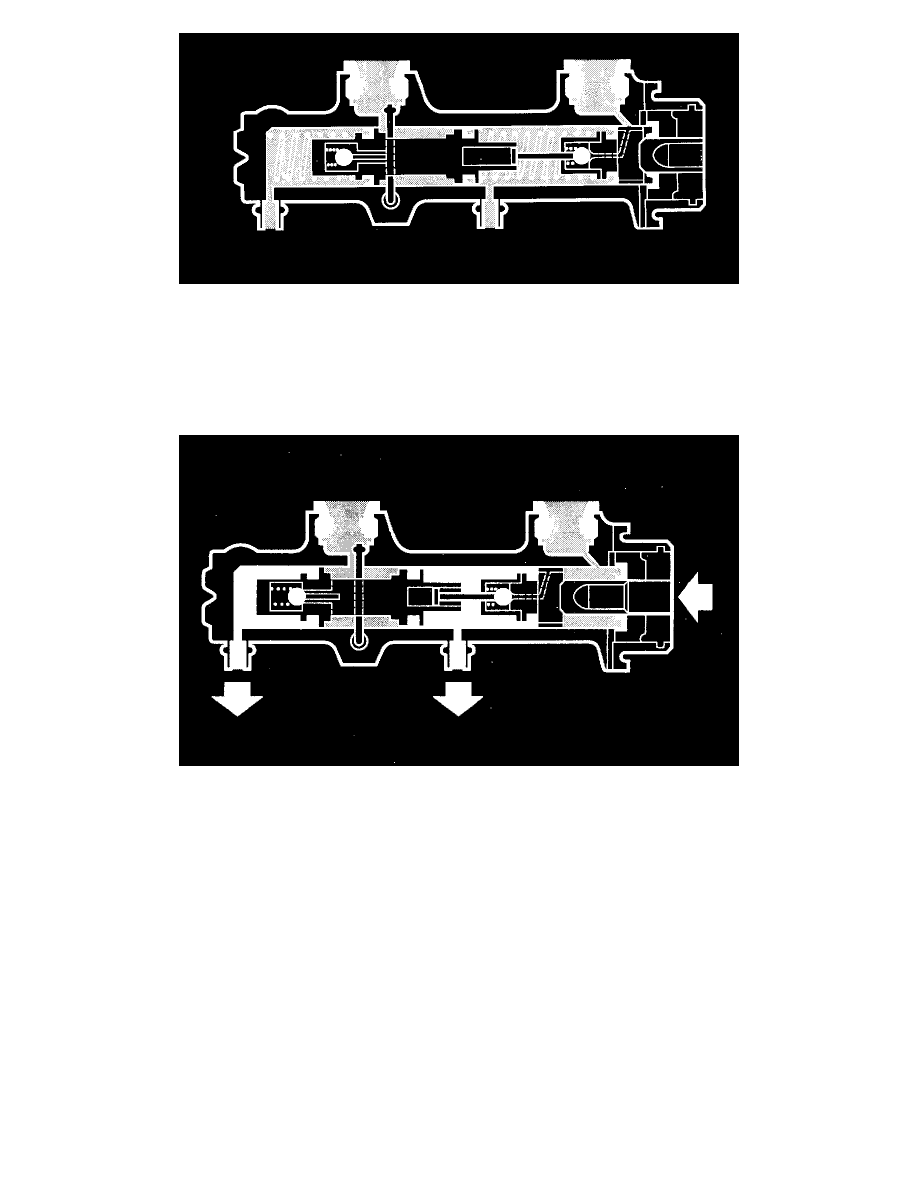
In the rest (brakes off) position the return springs press the pistons to the rear end. position. In this position, both return passages are open-and the
brake system is without pressure. Rearward movement of the pistons is prevented by a stop pin. The master cylinder and other hydraulic
components are filled with brake fluid under zero pressure.
In the valve block the inlet and outlet valves are in their rest (brakes off) positions and the central valves are also open.
Brakes Applied (Both Circuits Operative) Without ABS Control
The primary piston's central valve to the brake fluid reservoir closes the return flow and the pressure in front of the primary piston increases. The
pressure also acts on the secondary piston which is pushed forwards with the result that its central valve is also closed.
The hydraulic pressure in both circuits increases, and since the pistons have the same area the pressure through the valve block is equal in both
brake circuits.
The pressure is propagated in the brake system and acts on the brake piston in each hydraulic body. The brake pistons press the friction pads
against the brake discs. When the brake pedal is released the pistons in the master cylinder return to their rest (brakes off) position and the central
valves open. The pressure is relieved and the brake piston in each brake cylinder is returned to the rest (brake off) position by the piston sealing
ring.
Brakes Applied (One Circuit Inoperative)
