900 S Sedan L4-2290cc 2.3L DOHC (1994)
Engine Control Module: Description and Operation
Functions
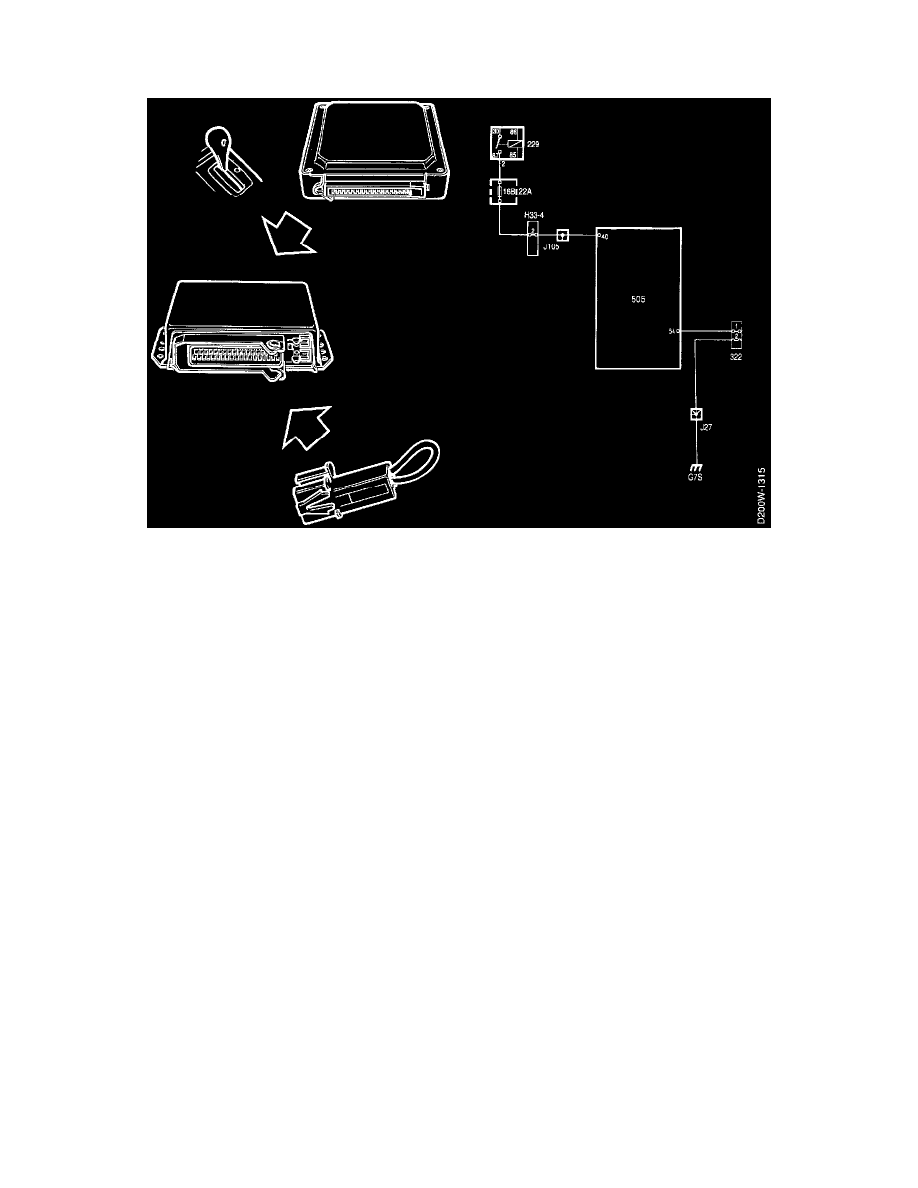
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION, CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
The control module for the MOTRONIC 2.10.2 has 55 connecting pins and incorporates ignition and fuel injection control functions.
By means of input signals from a large number of sensors, the control module receives continuous information on engine load, temperature, engine
rpm, exhaust gas composition, knocking (if occurring), etc.
The control module merges this information with the programmed maps in the permanent memory and utilizes the results to control both ignition
and fuel injection.
The control module is located behind the panel by the right-hand A pillar. The wiring is run through grommets in the bulkhead partition to the
engine bay. On removal of the power plant the control module connector and wiring is withdrawn through the bulkhead.
Manual/Automatic Programming
The MOTRONIC control module has the same part number for cars with a manual gearbox as for cars with automatic transmission.
By applying a voltage to pin 40, the control module is programmed for cars with automatic transmission.
On cars with a manual gearbox the circuit across pin 40 is open.
Coding the Control Module
By connecting different resistors across component 322 (Variant Coding) and pin 54, the control module is programmed to use different maps. On
M94 cars the circuit across pin 54 is open.
